Current Happenings ENVS News
- Predicting Biogas Production Using Time Series Algorithms January 23, 2024
With the advent of the climate crisis, the use of the latest scientific technologies to develop methods for sustainable energy usage is pivotal. Dr Karthik Rajendran, Associate Professor, Department of Environmental Science and Engineering, his PhD scholar Mr Prabakaran G & UG Student Mr Nalluri Rishi Chaitanya Sri Prasad have filed and published a patent titled “A System and a Method for Building a Forecasting Model for Biogas Production” with Application No.: 202341074196, on their radical invention of predicting future biogas production using advanced Machine Learning techniques.
Abstract
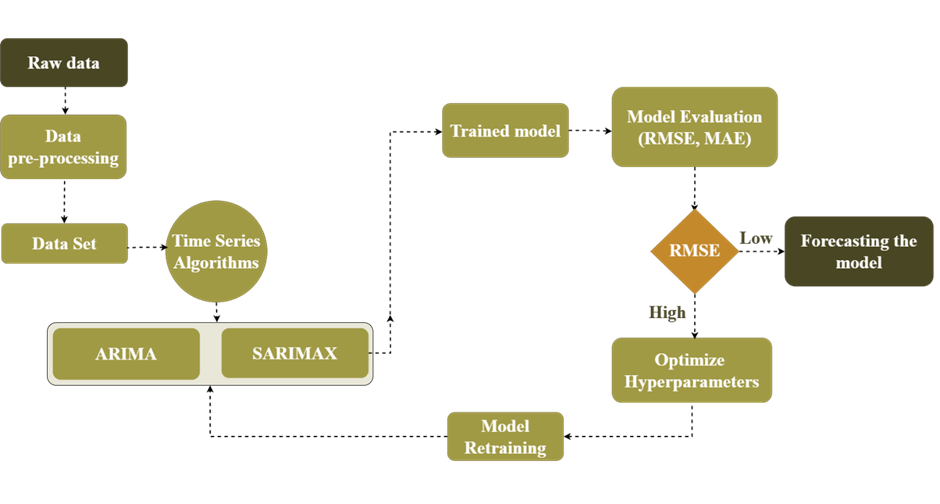
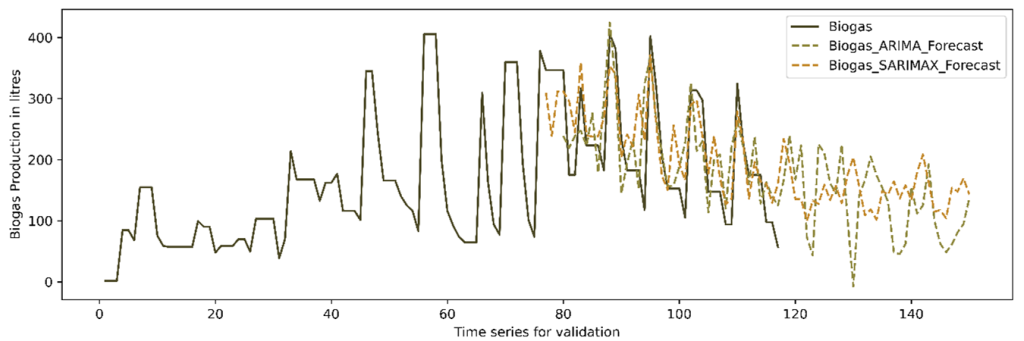
The anaerobic digestion (AD) process poses challenges in maintaining process stability and time series-based prediction and forecasting due to the intricate nature of the system. Process instability is a consequence of the unpredictability in the raw material received at the facility, as well as temperature fluctuations and pH changes resulting from microbiological processes. Consequently, it is necessary to implement constant monitoring and control measures for higher biogas production. The challenges associated with anaerobic digestion (AD) systems can be effectively addressed through the integration of advanced machine learning (ML) algorithms and industry 4.0 systems within biogas facilities. This integration holds the potential to enhance system efficiency and enable on-site control capabilities. Machine learning (ML) based solutions have the potential to enhance process performance in AD facilities, leading to improved system operation and maintenance. The present study focuses on advanced ML techniques, specifically time series algorithms (ARIMA and SARIMAX), which have been employed to forecast daily biogas production. These algorithms are trained to discern critical process parameters and forecast daily biogas production rates, measured in Liters. For forecasting, 117 days of experimental data were used and ARIMA was identified as the best algorithm to forecast the daily production. This algorithm excelled not only in predicting biogas production but also in forecasting yield, resulting in a Root Mean Square Error (RMSE) of 3.26. Furthermore, a comparison between the forecasted values of both ARIMA and SARIMAX was conducted. The predictive ARIMA model underwent statistical validation with unknown data, resulting in a P-value is >0.05.
Explanation of the Research in Layperson’s Terms
This paper focuses on predicting future biogas production using advanced mathematical methods. The researchers used data collected over 117 days of biogas experiments, divided into three periods. They kept track of important factors like methane production, consumed volatile solids, methane percentage in biogas, and initial and final pH levels. To make the predictions more accurate, the researchers addressed missing data and fine-tuned certain parameters using a process called hyperparameter tuning. They wanted to find the best settings for the mathematical models they used, which are called ARIMA and SARIMAX. These models consider patterns and relationships in the data to make predictions. The researchers checked their models’ using measures like AIC and BIC values and examined certain plots to ensure they were getting good results. After applying the models to the data, they were able to predict future biogas production. The accuracy of their predictions was assessed using a metric called RMSE, and they found values of 3.26 for ARIMA and 24.02 for SARIMAX. In simpler terms, these values help us understand how close their predictions were to the actual values. The researchers also did some statistical analysis, and the results showed that both methods (ARIMA and SARIMAX) were equally good at predicting biogas production. Therefore, they concluded that these mathematical models are reliable tools for forecasting biogas production in the future.
Practical Implementation/ Social Implications of the Research
The integration of advanced machine learning (ML) algorithms and Industry 4.0 systems within anaerobic digestion (AD) facilities holds significant promise in addressing the challenges associated with process instability and unpredictability in biogas production. The utilization of ML techniques, particularly time series algorithms like ARIMA (AutoRegressive Integrated Moving Average) and SARIMAX (Seasonal AutoRegressive Integrated Moving Average with eXogenous factors), to forecast daily biogas production presents a practical solution to enhance system efficiency and control.
- Real-time Decision Making
- Reduced Operational Costs
- AESEE 2024 Receives Grants from the Ministry of Jal Shakti January 22, 2024

The Department of Environmental Science and Engineering is thrilled to share the exciting news regarding its upcoming 1st International Conference on Advances in Environmental Sustainability, Energy, and Earth Science (AESEE 2024). The Department of Water Resources, River Development, & Ganga Rejuvenation (DoWR, RD & GR), the Ministry of Jal Shakti, have generously sanctioned Rs. 5 lakhs to support this groundbreaking event.
The International Conference scheduled to take place from March 14 – 16, 2024 aims to explore innovative advancements in science and technology while promoting inclusive growth across various sectors. This collaborative approach between environmentalists and the academic community will ensure a sustainable future.
The financial grant sanctioned in this regard underscores the importance of AESEE 2024 and highlights the commitment of the Department to advancing knowledge in the field. AESEE 2024 promises to facilitate meaningful discussions, bringing together diverse stakeholders to contribute to a more sustainable and interconnected future.
Continue reading →

