A Novel SERS Substrate to Detect Food Contamination

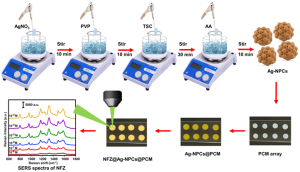
Dr Rajapandiyan P, Associate Professor, Department of Chemistry, and his PhD scholar, Ms Arunima Jinachandran, recently filed and published a patent, “A Substrate for Contaminant Detection and a Process for its Synthesis,” with Application Number: 202441043642 in the Patent Office Journal. The research duo has developed a novel SERS (Surface-Enhanced Raman Spectroscopy) substrate by synthesising silver nanopopcorn and depositing it on a polycarbonate membrane.
This novel substrate demonstrates excellent uniformity, reproducibility, and mechanical stability. It is used for the sensitive detection of toxic antibiotic nitrofurazone on fish surfaces and in honey. This breakthrough could significantly enhance food safety monitoring by providing a reliable and efficient method for detecting harmful substances.
Abstract
Detecting nitrofurazone (NFZ) in aquaculture and livestock is crucial due to its carcinogenic properties. This study presents a flexible polycarbonate membrane (PCM) with three-dimensional silver nanopopcorns (Ag NPCs) for NFZ detection on fish surfaces using surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy (SERS). The Ag-NPCs/PCM substrate demonstrates a significant Raman signal enhancement (EF = 2.36 × 106) due to hotspots from nanoscale protrusions and crevices. It achieves a low limit of detection (LOD) of 3.7 × 10−9 M, with uniform and reproducible signals (RSD < 8.34%) and retains 70% efficacy after 10 days. The practical detection LODs for NFZ in tap water, honey water, and on fish surfaces are 1.35 × 10−8 M, 5.76 × 10−7 M, and 3.61 × 10−8 M, respectively, demonstrating its effectiveness for various samples. This Ag-NPCs/PCM substrate offers a promising approach for sensitive SERS detection of toxic substances in real-world applications.
Practical Implementation/ Social Implications of the Research
The practical applicability of the proposed Ag-NPCs/PCM SERS substrate is validated by successfully detecting NFZ in various actual samples, such as tap water, honey water, and irregular fish surfaces.
Collaborations – Prof. Tzyy-Jiann Wang – National Taipei University of Technology, Taiwan
Dr Rajapandiyan and Ms Arunima will continue to work towards the development of novel flexible SERS substrates for detecting toxic pollutants in food.
- Published in Chemistry-news, Departmental News, News, Research News
“Nano Jatha”: A Pathway to Nanoscience and Technology
As part of the 13th edition of the Bengaluru India Nano 2024, heralded by Bharat Ratna recipient and renowned chemist Prof. C N R Rao, SRM University-AP hosted “Nano Jatha“, an intensive science outreach programme, catering to educate undergraduate graduates on the emerging trends of nanotechnology, on July 20, 2024. The Nano Jatha programme organised, aimed to raise awareness on nanoscience and technology through technical presentations by expert scientists and a distinctive live experiment demonstration of nano kits focused on showcasing nanoscience ideas.
The event featured two expert talks by eminent dignitaries. Prof. B L V Prasad, Director-Centre for Nano and Soft Matter Sciences (CeNS), Department of Science and Technology, Govt. of India, also serving as the Nodal Officer for organising Nano Jatha events, delivered a session on the introduction to nanoscience and technology. “Nanoscience and technology are often foretold as the technology of the future. This multidimensional technology will revolutionise our understanding of every natural phenomenon and every aspect of human life,” remarked Prof. Prasad in his session.

Prof. C P Rao, Senior Professor at the Department of Chemistry, presented the second expert talk on the applications of nanomaterials. The session delved into the properties of covalent molecules and its assemblage leading to cutting-edge technology. The programme also featured an exhibition were experiments on Gold nanoparticle; Galvanization reaction between metals; Piezoelectric pavement for futuristic applications; Humidity sensors for real-world applications and many more were displayed.
Prof. C V Tomy, Dean-School of Engineering & Sciences and Dr Pardha Saradhi Maram, Head-Department of Chemistry, emphasised that the Nano Jatha exemplified the university’s commitment to hands-on learning in science, specifically nanotechnology.They commented that the Department of Chemistry is dedicated to fostering scientific knowledge and igniting passion for chemistry among students and educators alike and will continue to organise events like Nano Jatha, conferences, workshops, and Faculty Development Programmes to achieve the same.
Over 300 students from 7 regional colleges in Andhra Pradesh participated in the programme, displaying their zeal in the discussions and nano kit demonstrations. The event was well executed benefitting the student community significantly in understanding various emerging fields in science and technology.
- Published in Chemistry-news, Departmental News, News
Dr Chinmoy Das’s Groundbreaking Research Unveils Promising Discoveries

Dr Chinmoy Das, Assistant Professor at the Department of Chemistry at SRM University-AP, has made an impactful contribution with the publication of his research paper, “Insights into the Mechanochemical Glass Formation of Zeolitic Imidazolate Frameworks” in the prestigious Angewandte Chemie International Edition with an impact factor of 16.6. His paper unveils a rapid, eco-friendly, and efficient mechanochemical approach to transform glasses from their crystalline zeolitic imidazolate frameworks. This pioneering work opens new doors for sustainable and effective glass formation, showcasing the power of innovation in the field of chemistry.
Abstract:
We describe a rapid, ecofriendly, and efficient mechanochemical approach to transform glasses from their crystalline zeolitic imidazolate frameworks (ZIFs). We exposition mechanochemical technique through which the traditional melt-quench preparation of glassy phases can be replaced. In this study, we explore that Zn(II), Co(II), and Cu(II)- based crystalline ZIFs transformed into the glassy phases within five minutes through the mechanical ball milling technique. The appearance of glass transition temperature(T g ) upon mechanical milling of crystalline states demonstrated by different characterization techniques, such as X-ray powder diffraction (XRPD), differential scanning calorimetry (DSC), simultaneous thermogravimetric and differential thermal analyses (TG/DTA), scanning electron microscopy (SEM), X-ray total scattering and its deduced pair distribution functions (PDFs). We characterized the porosity and density of the glassy phases through CO 2 gas sorption techniques which aligned with the observation of thermal, structural, and textural features of the ZIFs after varying ball milling times beyond five minutes.
Practical implementation
We can prepare bulk ZIF glasses within five minutes of the mechanochemical approach that will guide the greater feasibility to produce the glass materials for industrial implications. In addition, the greater the accessibility of glassy materials, the greater the fabrication of glassy materials-based device fabrication.
Collaborations
This article has been published with the collaboration of Prof. Sebastian Henke (Henke Group), Department of Chemistry and Chemical Biology, TU Dortmund University, Dortmund, Germany.
Future Research Plans
Recently, we established our research group in SRM University-AP, and our group has started to explore an emergent research area of crystal-glass composite materials towards the applications of atmospheric water harvesting, solid-state electrolytes (Alkali and Alkaline metal ions-based), photovoltaics, and conversion of gaseous Carbon-dioxide molecules to industrially relevant liquids, such as methanol or ethanol.
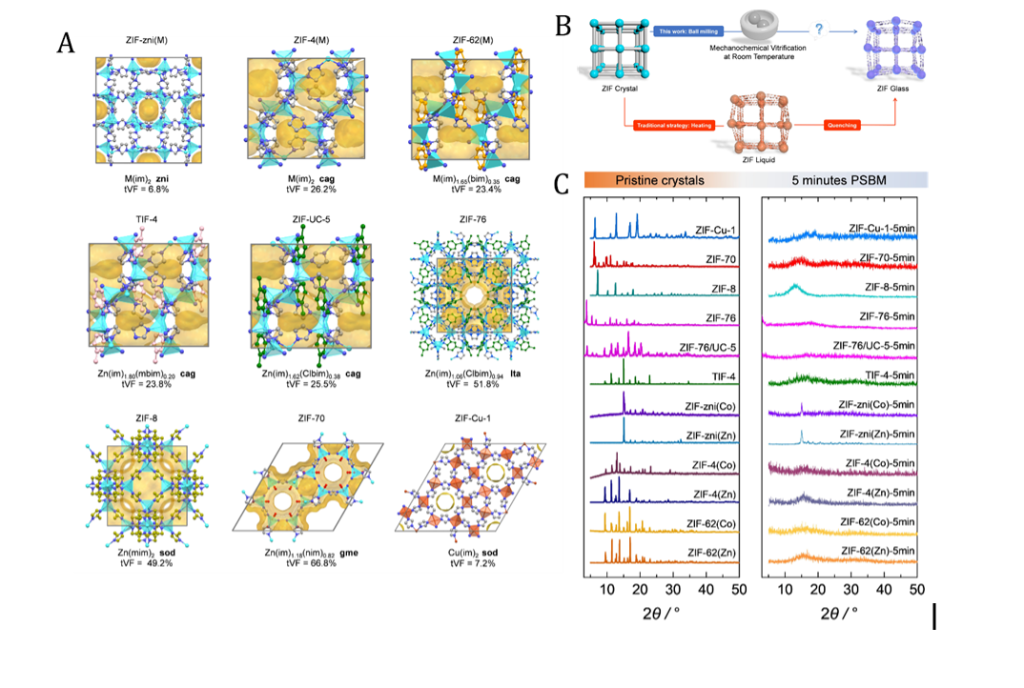
- Figure 1. (A) Single crystal structures of various ZIFs indicated in the figure. (B) Schematic representation of the traditional route to ZIF glass formation (red line) and the mechanochemical vitrification approach followed in this work (blue line). (C) PXRD patterns of the pristine ZIF polycrystalline materials and after five minutes of mechanical ball milling.
- Published in Chemistry-news, Departmental News, News, Research News
Significant Advancement in Analytical Detection of NFZ by the Department of Chemistry and RARE Lab

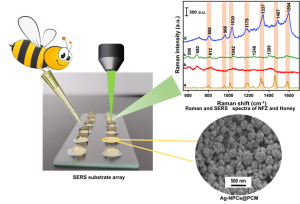
The Department of Chemistry and RARE Lab are excited to announce a groundbreaking advancement in the field of analytical detection. Researchers Dr Rajapandiyan Panneerselvan, Asst. Professor and Ph.D scholars, Ms Arunima Jinachandran and Ms Jayasree Kumar have developed a novel method for detecting nitrofurazone (NFZ) using three-dimensional silver nanopopcorns (Ag NPCs) on a flexible polycarbonate membrane (PCM) in their paper “Silver nanopopcorns decorated on flexible membrane for SERS detection of nitrofurazone” published in Microchimica Acta. This innovative technique leverages the power of surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy (SERS) to provide a highly sensitive and practical solution for detecting NFZ on various surfaces, including fish.
Nitrofurazone (NFZ) is an antibiotic commonly used in veterinary medicine that poses significant health risks if residues enter the food chain. Despite regulatory bans, its illegal use continues, necessitating highly sensitive detection methods. While effective, traditional methods such as high-performance liquid chromatography and mass spectrometry are often costly and labor-intensive. The new SERS-based method offers a more efficient and straightforward alternative.
Abstract
The synthesis of three-dimensional silver nanopopcorns (Ag NPCs) onto a flexible polycarbonate membrane (PCM) for the detection of nitrofurazone (NFZ) on fish surfaces by surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy (SERS) is presented. The proposed flexible Ag-NPCs/PCM SERS substrate exhibits significant Raman signal intensity enhancement with a measured enhancement factor of 2.36 × 10^6. This enhancement is primarily attributed to the hotspots created on Ag NPCs, which include numerous nanoscale protrusions and internal crevices distributed across the surface. The detection of NFZ using this flexible SERS substrate demonstrates a low limit of detection (LOD) of 3.7 × 10^−9 M and uniform, reproducible Raman signal intensities with a relative standard deviation below 8.34%. The substrate also exhibits excellent stability, retaining 70% of its efficacy even after 10 days of storage. Notably, the practical detection of NFZ in tap water, honey water, and fish surfaces achieves LOD values of 1.35 × 10^−8 M, 5.76 × 10^−7 M, and 3.61 × 10^−8 M, respectively, highlighting its effectiveness across different sample types. The developed Ag-NPCs/PCM SERS substrate presents promising potential for the sensitive SERS detection of toxic substances in real-world samples.
Methodology
The synthesis involves creating silver nanopopcorns on a flexible polycarbonate membrane using a simple chemical method. The resulting Ag NPCs exhibit high surface roughness with numerous nanoscale features that enhance the Raman signal. This flexible substrate can easily collect samples from irregular surfaces without requiring extensive preparation.
This SERS substrate can detect NFZ in various real-world samples, including:
- Tap water
- Honey water
- Fish surfaces
The method’s sensitivity and ease of use make it a promising tool for ensuring food safety and monitoring environmental contaminants.
The Department believes this development will significantly impact public health by providing a reliable and accessible method for detecting harmful substances in the food chain.
- Published in Chemistry-news, Departmental News, News, Research News
Dr Chimoy Das’ Research Makes Latest Breakthrough in Material Science

The Department of Chemistry is thrilled to announce the paper “Mechanochemically-induced glass formation from two-dimensional hybrid organic-inorganic perovskites”, published by Dr Chinmoy Das, Assistant Professor in the reputed Q1 Journal Chemical Science with an 8.4 Impact Factor. This groundbreaking research introduces a novel method for transforming crystalline phases into glasses through mechanochemical processes. This environmentally friendly and efficient method opens new doors for manufacturing glasses, revolutionising traditional processes. This remarkable research celebrates this extraordinary blend of chemistry, physics, and innovation!
Abstract
The first mechanochemically-induced hybrid organic-inorganic perovskites (HOIPs) crystal-to-glass transformation was reported as a quick, environmentally friendly, and productive method of making glasses. Within ten minutes of mechanical ball milling, the crystalline phase transformed into the amorphous phase, demonstrating glass transition behaviour as shown by thermal analysis methods. The microstructural evolution of amorphization was studied using time-resolved in situ ball-milling with synchrotron powder diffraction. The results indicated that energy may accumulate as crystal defects because the crystallite size reaches a comminution limit before the amorphization process is finished. The limited short-range order of amorphous HOIPs was discovered through total scattering experiments, and photoluminescence (PL) and ultraviolet-visible (UV-vis) spectroscopy were used to examine their optical characteristics.
Explanation of the research in layperson’s terms
Crystalline inorganic perovskites (general chemical formula is ABX3, where A and B are cations, and X is anion) are generally known for their unique optoelectronic applications, such as solar cells, photodetectors, and LEDs (light emitting diodes). In this research, Dr Das revealed hybrid materials comprised of organic linkers and inorganic nodes, which constitute hybrid organic-inorganic perovskites (HOIPs). The research demonstrated a rapid and environment-friendly (mechanochemically ball milling assisted) synthetic approach to transform the crystalline phase to its non-crystalline/amorphous phase. Interestingly, the amorphous phase of HOIPs showed temperature-dependent glass transition temperature (Tg) at very low temperatures, ~50 C. The structure of the HOIP glasses has been characterised through total-X-ray diffraction studies and pair-distribution functions. The crystalline and glassy HOIPs showed optical properties, which were studied by photoluminescence (PL) and ultraviolet-visible (UV-vis) spectroscopy.
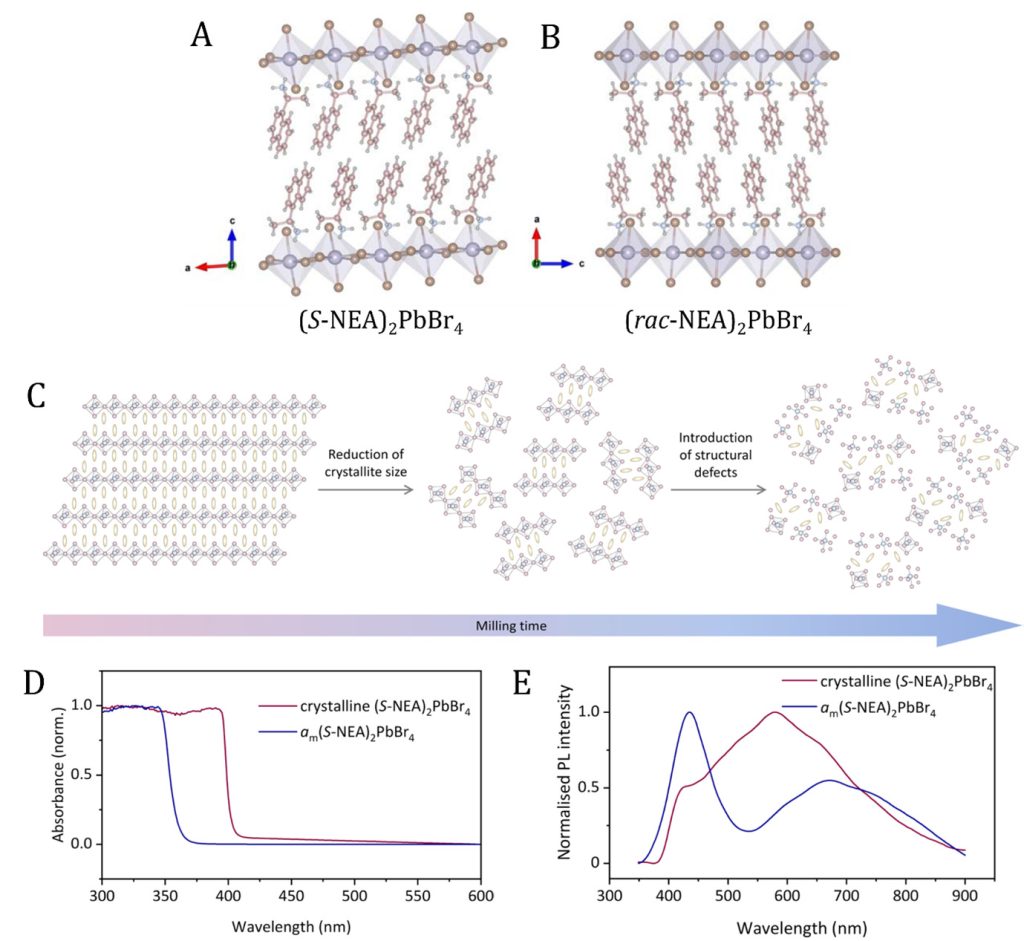
Figure 1. Single crystal structures of (A) (S-NEA)2PbBr4 and (B) (rac-NEA)2PbBr4. Pb, Br, C, N and H atoms are represented by purple, brown, pink, blue, and grey colours, respectively. (C) Schematic illustration of the microstructural evolution on 2D HOIPs upon ball-milling. (D) UV-Vis and (E) photoluminescent properties of crystalline (S-NEA)2PbBr4 (purple) and glassy (S-NEA)2PbBr4 (blue) HOIPs.
Practical implementation/ social implications of your research
Through the mechanochemical approach, we prepared novel hybrid organic-inorganic perovskite (HOIP) glasses within ten minutes, showing the greater feasibility of processing the glass material for industrial implication. On the other hand, we also demonstrated that the HOIP glasses showed photoluminescence properties, which would enable us to fabricate the device for solar cells, photodetectors, LEDs and many more.
Collaborations
- Department of Materials Science and Metallurgy, University of Cambridge, United Kingdom.
The Department of Chemistry has established a research group at SRM University-AP, and the group has started to explore an emergent research area of crystal-glass composite materials towards the applications of atmospheric water harvesting, solid-state electrolytes, photovoltaics, and conversion of gaseous Carbon-dioxide molecules to industrially relevant liquids, such as methanol or ethanol.
Any interested candidate can reach out to Dr Chinmoy for exciting projects.
- Published in Chemistry-news, Departmental News, News, Research News
Inauguration of NMR Spectrometer Marks a Milestone in SRM University-AP’s Research Capabilities
 In a significant leap forward for scientific research, SRM University-AP proudly inaugurated the 400 MHz NMR (Nuclear Magnetic Resonance) Spectrometer, procured through the DST-FIST program. This acquisition is a vital component of the broader DST FIST project, which has been awarded to the Department of Chemistry at SRM University- AP with a budget of 2.20 crores.
In a significant leap forward for scientific research, SRM University-AP proudly inaugurated the 400 MHz NMR (Nuclear Magnetic Resonance) Spectrometer, procured through the DST-FIST program. This acquisition is a vital component of the broader DST FIST project, which has been awarded to the Department of Chemistry at SRM University- AP with a budget of 2.20 crores.
As part of the project, the Department of Chemistry was recommended a 400 MHz NMR spectrometer by DST, which will play a crucial role in enhancing our expertise and aiding in achieving the proposed objectives. This state-of-the-art equipment is capable of characterising organic, inorganic, and biomolecules, enabling us to conduct comprehensive analyses and advance our understanding of complex chemical systems.
The ceremony, graced by esteemed guests, university dignitaries, faculties, and students, heralded a new era of scientific exploration and innovation. Prof. Lakshmi Kantam Mannepalli, Dr B P Godrej Distinguished Professor, ICT Mumbai, Chief Guest at the event, expressed, ” The inauguration of the 400 MHz NMR Spectrometer heralds a new era of precision and insight in scientific exploration. This instrument will unravel the mysteries of molecular structures and catalyse groundbreaking discoveries in the realm of chemistry and beyond.”
Dr S Mannathan, Associate Professor, Department of Chemistry, extended a warm welcome to the esteemed gathering and offered an insightful demonstration of the equipment’s operation, highlighting its advanced features and functionalities.
Prof. Manoj K Arora, Vice Chancellor, conveyed heartfelt congratulations to the team for this remarkable accomplishment, emphasising the transformative impact the new NMR Spectrometer will have on research and academic pursuits within the Department of Chemistry and beyond.”
Prof D Narayana Rao, Executive Director – Research, SRM Group of Institutions, emphasised, “The addition of this advanced equipment will significantly enhance the research capabilities, opening new avenues for exploration and discovery.”
V S Rao, Advisor, lauded the team for their achievement, stating, “This state-of-the-art equipment embodies our commitment to providing cutting-edge resources for our researchers and fostering a culture of innovation and discovery.”
Dr Pardha Saradhi Maram, Head of the Department of Chemistry, expressed his gratitude to all present and extended heartfelt thanks for their support and encouragement.
The acquisition of the 400 MHz NMR Spectrometer represents a significant advancement in scientific instrumentation, enabling researchers to delve deeper into molecular structures, chemical compositions, and dynamic processes. The Equipment will not only benefit the Department of Chemistry and Physics but also serve as a valuable resource for faculties and students across various disciplines.
The university has already trained 70 to 80 individuals in the operation of this equipment and is planning to organise a workshop for students and faculties from different universities, offering them the opportunity to leverage this advanced technology for their research and academic pursuits.
- Published in Chemistry-news, Departmental News, News, Research News
ETSST 2024: Exploring the Next Frontier in Supra Molecular Technology

The Department of Chemistry at SRM University-AP has taken a significant initiative by organising an International Conference on “Emerging Trends in Supramolecular Science and Technology” (ETSST-2024) on March 07 and 08, 2024. This two-day conference brought together some of the most renowned and accomplished national and international intellectuals in the field of chemistry, who will share their insights and expertise on the latest advancements, emerging trends, and future prospects in the domain of supramolecular science and technology. The conference promises to be a great platform for researchers, scientists, academicians, and students to exchange ideas, network, and collaborate towards making breakthrough contributions in the field.
The conference marked the presence of academic stalwarts from institutes of national and international repute who expounded on the relevance of the conference and discoursed upon the various topics.
The event also featured the unveiling of the abstract book compiled by the department. Vice Chancellor, Prof. Manoj K Arora; Registrar, Dr R Premkumar; the Associate Dean- Science, Prof. Jayaseelan Murugaiyan; Chairman and Convenor ETSST-2024, Prof. C Pulla Rao; HoD- Chemistry, Dr Pardha Saradhi Maram; Dr Seema Rani and Dr Balaji Babu, Assistant Professors, Department of Chemistry, SRM AP bore witness to this momentous occasion.
At its core, the essence of this conference lay in its audacious objective – to unravel the enigmatic world of supramolecular science, where chemistry transcends the boundaries of individual molecules. It is a domain where complexity breeds innovation, and practical applications pave the way for unprecedented advancements in engineering and technology.
As the curtains drew to a close on this grand spectacle, the echoes of inspiration and collaboration continued to reverberate within the hearts and minds of all who were part of this transformative experience. The bonds forged and the knowledge shared during ETSST-2024 will forever shape the trajectory of supramolecular science and technology.




- Published in Chemistry-news, Departmental News, News
Revolutionising Sustainable Living: A Discourse on Green Chemistry

In a world of fast-escalating environmental challenges, the idea of sustainability comes as a ray of hope for a safe and sound future. The present scenario calls for the kind of development that meets the needs of the present without compromising the future. In this regard, the Department of Chemistry at SRM University-AP organised a colloquium, that aimed to provide students with a comprehensive understanding of the concepts of Green Chemistry.
Dr Ram Mohan, an expert in the field of Green Chemistry and a renowned academician at the Department of Chemistry, Illinois Wesleyan University, delivered a lecture on the topic “Better Living Through Green Chemistry: An Introduction to Toxic Molecules”. Dr Mohan spoke elaborately on the grave dangers of toxic molecules and their adverse effects on the environment and human health. He raised awareness about the critical role of green chemistry in reducing the usage of such harmful molecules and replacing them with environmentally safe alternatives.
Dr Mohan also conducted workshops on “Better Living Through Green Chemistry”, as a continuation of his lecture. During the workshop, he quoted several case studies that showcased the benefits of using environmentally safe processes and chemicals in industry. These case studies demonstrated how the practice of green chemistry can lead to the development of numerous Eco-friendly processes and chemicals that have greatly improved human life and reduced environmental impact.
- Published in Chemistry-news, Departmental News, News
ChemZeal 2: An Outreach Initiative by the Dept. of Chemistry

The Department of Chemistry at SRM University-AP organised an academic colloquium called ChemZeal 2 on December 02, 2023. The event aimed to promote the Department and its research among undergraduate and graduate students from various colleges. It also provided a platform for students to interact with chemistry enthusiasts and learn about the latest advancements and research in the field.
ChemZeal 2 featured a lecture by academic stalwart, Prof. U V Varadaraju on Solid-State Materials in Chemistry from the Department of Chemistry, IIT Madras. Prof. Varadaraju also spoke about various aspects of the field, including research, career paths, higher studies, and job opportunities in the industry.
The welcome note was given by the Department Head, Dr Pardha Saradhi Maram, while Vice-Chancellor Prof. Manoj K Arora and Prof. Jayaseelan Murugaiyan, Associate Dean in-charge (Science), also addressed the gathering with their valuable inputs. The event also included an interactive session with the guest speaker, where faculty and students could interact and get expert insights.
ChemZeal 2 also featured a talent test for over 320+ students from different colleges, with prizes awarded to the top three winners. The event was designed to attract students to pursue higher education and research in the field of Chemistry and provided a platform for BSc/MSc/PhD students to showcase their research and interact with potential candidates.
The event organisers – Dr Sabyasachi Chakrabortty (Convenor) & Dr J P Raja Pandiyan (Co-convenor) helped culminate the outreach activity with a campus tour, where attendees could witness state-of-the-art facilities, high-end research labs, and futuristic technology.
- Published in Chemistry-news, Departmental News, News
Dr Nimai Mishra’s research group develops a new synthetic strategy to make ultra-stable CsPbBr3 perovskite nanocrystals for light-emitting application
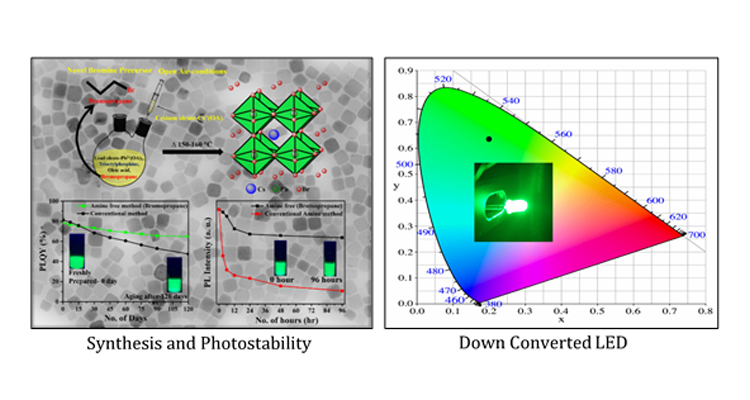 Dr Nimai Mishra, Assistant Professor in the Department of Chemistry, SRM University-AP, Andhra Pradesh, along with his research group comprising of students pursuing PhD under his supervision, Mr Syed Akhil and Ms V.G.Vasavi Dutt have published a research article titled “Bromopropane as a Novel Bromine Precursor for the Completely Amine Free Colloidal Synthesis of Ultra-Stable and Highly Luminescent Green-Emitting Cesium Lead Bromide (CsPbBr3) Perovskite Nanocrystals” in the Journal “Nanoscale” (The Royal Society of Chemistry, Impact Factor-7.8).
Dr Nimai Mishra, Assistant Professor in the Department of Chemistry, SRM University-AP, Andhra Pradesh, along with his research group comprising of students pursuing PhD under his supervision, Mr Syed Akhil and Ms V.G.Vasavi Dutt have published a research article titled “Bromopropane as a Novel Bromine Precursor for the Completely Amine Free Colloidal Synthesis of Ultra-Stable and Highly Luminescent Green-Emitting Cesium Lead Bromide (CsPbBr3) Perovskite Nanocrystals” in the Journal “Nanoscale” (The Royal Society of Chemistry, Impact Factor-7.8).
Recently, lead halide perovskite nanocrystals (PNCs) have attracted intense interest as promising active materials for optoelectronic devices. However, their extensive applications are still hampered by poor stability in ambient conditions. In this work, Dr Mishra’s research group report an open-atmospheric, facile, efficient, completely amine-free synthesis of caesium lead bromide perovskite nanocrystals using a novel bromine precursor, bromopropane, which is inexpensive, and available at hand. Their finding concludes that the PLQY can maintain 83% of their initial one even after 120 days. Furthermore, after 96 h of continuous irradiation by UV light with 365 nm (8 W/cm2) in the open ambient condition the photoluminescence (PL) intensity showed retention of 68% of its original value with no significant change in full width at half-maximum, whereas amine-based sample retains only 5% of its original PL intensity. Furthermore, Dr Mishra’s group has fabricated stable down-converted LED devices with these perovskite nanocrystals.
“More importantly, the present work demonstrates the synthesis of ultra-stable CsPbBr3 NCs which can be an ideal candidate for display applications”, says Dr Nimai Mishra.
Read the full paper: https://pubs.rsc.org/en/Content/ArticleLanding/2021/NR/D1NR03560F#!divAbstract
- Published in Chemistry-news, Departmental News, News, Research News