All Management News
- SRM-AP organised a workshop on “Interactive Learning” July 28, 2022

SRM University-AP organised a workshop on “Interactive Learning” to acquaint faculty with the evolving dynamics of teaching and learning, and the state-of-the-art pedagogical approaches. The two-day workshop was held on July 21 & 27, 2022 under the auspices of Prof Ranjit Thapa, Associate Dean in charge (Sciences), School of Engineering and Sciences. Faculty members from different schools attended the sessions and exchanged views on alternative methodologies to unravel the different facets of learning.
Prof T Raghunathan, Associate Dean in charge (Engineering), School of Engineering and Sciences, addressed the gathering and expounded his ideas on teaching. “Teaching encompasses the features of arts and science necessitating a teacher to don the roles of an artist and scientist”, he stated. It is the ‘how’ and ‘why’ of learning that a teacher should shed light on, according to Prof Raghunathan, to awaken students to their passion and lead a life of purpose.
Prof B V Babu, Dean- School of Engineering and Sciences, interacted with the faculty and spoke on the responsibility of a teacher in a university. He specified the diverse opportunities the university provides to its student community, such as research, placements, and entrepreneurship, and how teachers can contribute to enhancing the performance of students in different arenas. Unlike the conventional understanding, today’s teachers are bound to perform multiple roles to fulfil their obligation.
The session was presided over by Dr Karthik Rajendran, Assistant Professor and Faculty Coordinator, Department of Environmental Science. He rendered an engaging talk on active learning, encouraging the teachers to take up an amicable approach in classrooms and skilfully guide students through the learning process. Flipped classes, project-based learning, and peer learning are some of the interesting techniques that teachers can put to practice.
Dr Satya Pramod Jammy, Assistant Professor, Department of Mechanical Engineering, presented a session on different types of assessments that can be carried out to test the understanding of the students. He further elucidated the goals of assessment and how it should be aligned with meeting the practical requirements of the course rather than making students reproduce the content. He listed out the various assessment patterns followed at SRM-AP to ensure the learning caters to the all-round development of the student.
In the latter half of the workshop, Dr V M Manikandan, Assistant Professor, Department of Computer Science and Engineering, delivered a talk on the learning management system used at the university, its features and clarified doubts on how the application can be availed to make teaching and learning a full-fledged activity. Dr Balaguruprasad Narayanan, Associate Professor from the Department of Teaching and Learning Centre wrapped up the workshop with an extended session on outcome-based learning.
Continue reading → - Gendered work and contemporary India July 28, 2022
 Economic institutions, technological developments, cultural norms, religious and intellectual currents, and popular beliefs have always played a huge role in asserting clear boundaries between men’s and women’s work. The recent research paper of Assistant Professor Dr Ipsita Pradhan, Department of Liberal Arts, focuses on the transformation of gendered work in contemporary India. The paper is titled Women and the Changing Nature of Work in Hyderabad’s Hitec City and was published in the journal Sociological Bulletin.
Economic institutions, technological developments, cultural norms, religious and intellectual currents, and popular beliefs have always played a huge role in asserting clear boundaries between men’s and women’s work. The recent research paper of Assistant Professor Dr Ipsita Pradhan, Department of Liberal Arts, focuses on the transformation of gendered work in contemporary India. The paper is titled Women and the Changing Nature of Work in Hyderabad’s Hitec City and was published in the journal Sociological Bulletin.Abstract
This article looks at the ways in which gendered work is being transformed in contemporary India by focussing on Hyderabad, the capital of Telangana. Since the mid-1990s, after India opened its doors to multinational agencies, new forms of gendered labour have manifested. One of the ramifications of this gendered process is the feminisation of labour that enabled the participation of more women in the workforce, engaging in activities that were low-paid. The basis of feminisation is that certain jobs require fewer skills or particular kinds of skills, for which women are thought to be suitable. This also has implications for the low bargaining power of women workers. The feminisation of the labour force in HITEC city, Hyderabad is a consequence of the changing labour markets with globalisation, offshore factories, migration, and other changes in the workplace.
Continue reading → - Dual-Band 2×2 Elements MIMO Antenna-Diplexer July 27, 2022
Dr Divya Chaturvedi, Assistant Professor, from the Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering has been keenly pursuing research on wearable antennas that are used within the context of Wireless Body Area Networks. These antennas are commonly used in wearable wireless communication and bio-medical RF systems. Her latest publication “Design and Investigation of Dual-Band 2×2 Elements MIMO Antenna-Diplexer Based on Half-mode SIW” was featured in the Q1 journal, IEEE Access, having an Impact Factor of 3.37. The research was done in collaboration with Assistant Professor Dr Goutam Rana and Research Scholar Ms Buela Pramodini from the Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering.
This antenna is designed to enhance data rate twice as much as a single antenna. The antenna can be used to operate in two frequency bands simultaneously, without causing any interference. One frequency band can be used for the transmission of data while the other frequency band can be utilised for the reception of data. The radiating elements are configured in such a way that it occupies a compact size. Thus, the designed antenna can be easily mounted or integrated into a portable wireless electronic device. The field from one radiating element is not coupled to the other element due to their adequate isolation that mitigates the interference problem.
The dual-band self-diplexing 4-port MIMO antenna operates in the lower frequency band around 3.4 GHz (3.35-3.55 GHz, 160 MHz) for the TD-LTE system and in the higher frequency band around 4.2 GHz (4.14-4.34 GHz, 200 MHz) for FCC ID WLAN in 5G LTE communication. The electronic devices which operate in these frequency bands can enhance the data transmission and reception speed twice as much as a single element. In other words, the proposed design prototype also improves the reliability of communication by employing the spatial multiplexing technique. In future, they plan to work on the design and investigation of MIMO-based self-diplexing antenna using the polarization diversity technique.
Abstract of the Research
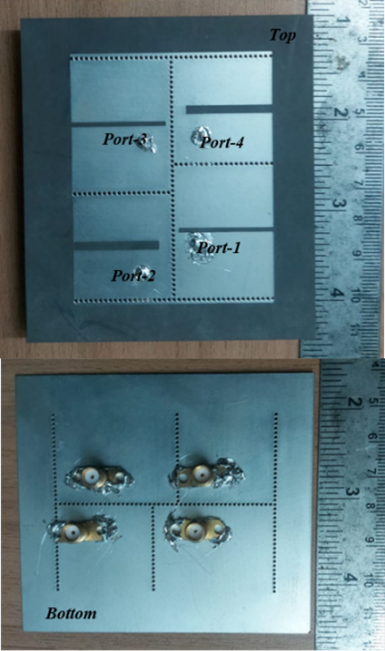
In this article, a compact dual-band, 2-elements antenna-diplexer is investigated and extended to a 2×2 multi-input and multi-output (MIMO) antenna. The proposed design employs half-mode Substrate Integrated Waveguide (HMSIW) technology, which reduces the antenna footprint by 50%. To enhance the bandwidth, a rectangular slot is engraved at the center of each HMSIW cavity. The slot splits the dominant mode of the HM cavity into two odd- and even-half TE110 modes in proximity, which leads to enhancement in the bandwidth by 50%. The antenna resonates around 3.4 GHz with a fractional bandwidth of 5% and around 4.3 GHz with a bandwidth of 4.7%, when corresponding ports are excited, respectively. Both the lower and upper frequency bands can be tuned individually, by simply altering the dimensions of each HMSIW cavity. This can be achieved in a common antenna, without employing filters, which satisfies the antenna-diplexer function. The isolation levels between any two radiating elements are obtained below -23 dB for the proposed MIMO antenna, and it occupies an overall size of 1.0λg × 0.8λg. The peak gain of the antenna is obtained at 5.35 dBi in the lower frequency band and at 6.75 dBi in the upper frequency band while radiation efficiency is better than 80% in both frequency bands.
- Dr Ipsita Pradhan selected for a seminar on Urban Ethnography and Theory in Italy July 27, 2022
 Recently, Assistant Professor Dr Ipsita Pradhan from the Department of Liberal Arts has been selected for the IUS Field Training School and Research Seminar on Urban Ethnography and Theory in Tuscany, Italy. The seminar was held from July 18 to 26, 2022.
Recently, Assistant Professor Dr Ipsita Pradhan from the Department of Liberal Arts has been selected for the IUS Field Training School and Research Seminar on Urban Ethnography and Theory in Tuscany, Italy. The seminar was held from July 18 to 26, 2022.This eight-day Field Training School and Research Seminar is addressed to researchers, who are interested in ethnographic research and empirically grounded analysis. It is organised and hosted by the International Urban Symposium-IUS in collaboration with an international group of senior scholars from European, Indian, Middle Eastern, and US Universities. The school offers an interactive learning environment and opportunities to discuss the rationale and practices of research methods and mainstream debates. Participants will have the opportunity to present their own research and receive feedback from leading scholars. The Teaching Seminars will focus on methodological and theoretical debates, benefiting from senior scholars’ wide range of ethnographic, methodological, and theoretical expertise.
Continue reading → - Dr Manjesh Kumar July 27, 2022
- Item feature refinement for improved content-based recommendation July 26, 2022
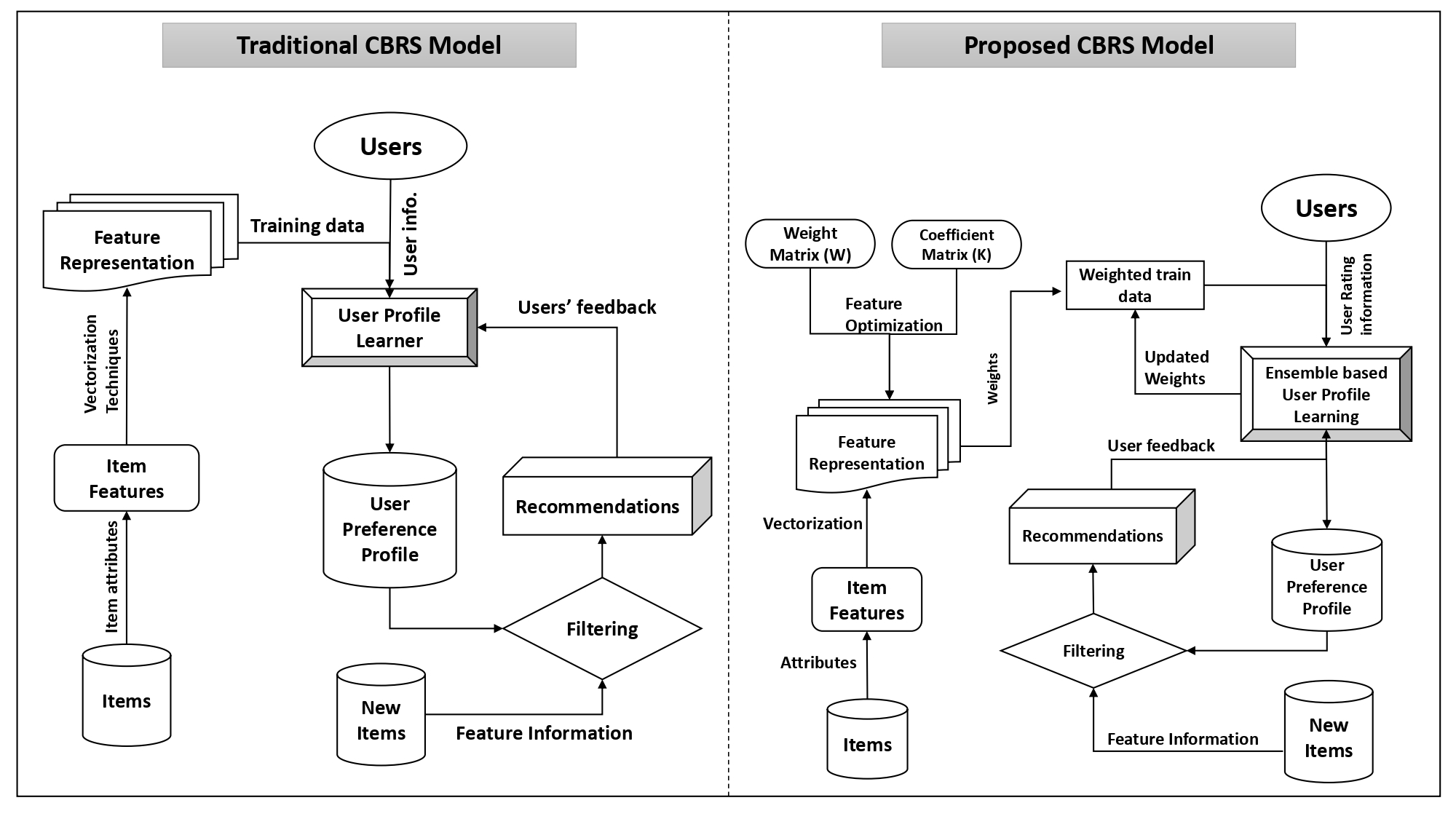
The Department of Computer Science and Engineering is delighted to announce that Dr Abinash Pujahari, Assistant Professor, has published his research article “Item Feature Refinement using Matrix Factorization and Boosted Learning based User Profile Generation for Content-Based Recommender Systems” in the journal Expert Systems with Applications having an Impact Factor of 8.665. The research was done in collaboration with Dr Dilip Singh Sisodia, Assistant Professor, National Institute of Technology Raipur.
This research focuses on improving the quality of information available about the features of various items so that it can be used for content-based recommendations. Content-based recommender systems are used in many e-commerce platforms (e.g., NetFlix, Amazon Prime, etc.). Here, the item (i.e., movies, TV shows) feature information is compared with the users’ past behaviour to recommend similar things. This research enables such systems to study the feature information for more accurate recommendations.
Most of the items’ feature information is sparse, redundant, and inconsistent. Matrix Factorization is used to avoid such inconsistencies. Further, iterative learning of user profiles is used using boosted learning approach for model building. The proposed research is compared with state-of-the-art related works using benchmark datasets and can be implemented in most e-commerce platforms and online streaming service providers. Dr Pujahari looks forwards to employing the same in group recommender systems where individuals have their preferences, in his future research endeavours.
Continue reading → - Colonial Impact on Pastoral Nomads and Caravan Traders in India July 26, 2022
 Cultural and Post-colonial studies enclose various historical approaches. It ranges from cultural studies and comparative social history to analysis of the means of domination and resistance. Nevertheless, there are communities that didn’t get the space they deserve in the studies of settled communities. Assistant Professor Dr Bikku R from the Department of Liberal Arts published a paper titled Colonial Impact on Pastoral Nomads and Caravan Traders in India: The Raika and the Banjara to analyse the aftereffects of colonialism in the most unexplored communities. The article was published in the book Tribe, Space, and Mobilisation.
Cultural and Post-colonial studies enclose various historical approaches. It ranges from cultural studies and comparative social history to analysis of the means of domination and resistance. Nevertheless, there are communities that didn’t get the space they deserve in the studies of settled communities. Assistant Professor Dr Bikku R from the Department of Liberal Arts published a paper titled Colonial Impact on Pastoral Nomads and Caravan Traders in India: The Raika and the Banjara to analyse the aftereffects of colonialism in the most unexplored communities. The article was published in the book Tribe, Space, and Mobilisation.Abstract
The Raika of Rajasthan and the Banjara or Lambadi tribe of the Deccan region had been self-sustained as nomadic pastoralists and caravan traders, respectively, in pre-British India. Colonial policies imposed several restrictions on nomadic communities and their economic activities by branding them as ‘criminals’ under the Criminal Tribes Act of 1871. As a result, many of the nomadic communities lost their cultural economy and struggled to survive. Colonial and post-colonial studies have primarily focused on settled communities. However, little attention is paid to pastoral nomads and itinerary communities. The present paper focuses on the transformation of traditional nomadic livelihoods, culture, and economy of the two communities; the Raika pastoralist and the Banjara traditional caravan traders and livestock breeders’ as a consequence of colonial policies. It also emphasises current livelihood strategies. Empirical data resulting from ethnographic fieldwork and colonial and post-colonial literature have been examined. An ethnographic study among the Banjaras from the Deccan region during the year 2009- 2010 and the Raika of Rajasthan between 2013- 2015 and 2019 helped to understand their past and present situations. Colonial and post-colonial policies, governance, and their impact on pastoralists and other nomadic communities have been critically examined.
Continue reading → - Find your way to a sense of purpose July 26, 2022
 Ever wanted to live resolutely? Felt the need to be aware of where and why are you going and what are your intentions?
Ever wanted to live resolutely? Felt the need to be aware of where and why are you going and what are your intentions?Dreams that foster a sense of purpose can potentially change the trajectory of an individual’s life. Finding meaning in life is one of the fundamental human needs. But for most people, finding a purpose is not apparent. The modern world tends to distract people from their actual goals and let them be pretentious about something which is not.
Our deepest fear is not that we are inadequate but powerful beyond measure. We are unaware of how to hold and direct our own light that it tends to frighten us more than our darkness. The secret to the meaning of life lies in recognising the true goals and aligning everything in life around that.
The Department of Entrepreneurship and Innovation is conducting a 45-minute workshop on How to fix progressive goals in life to give a glimpse of how powerful a simple act of discovering your purpose of life could be. This will be a demo session and is open to all. Post that, only 10 students will be taken for a coaching of 30 days impact programme, where mentors will be closely working with the ten individuals to create the change and become instrumental in the expected transformation. Students will be filtered for the 30 days impact programme through interviews and one-to-one interaction.
Date: July 27, 2022
Time: 7 pm to 8 pm IST
Join the session to pave your way to a sense of purpose.
Continue reading → - Sustainable IoT system for freshwater pearl farming July 26, 2022
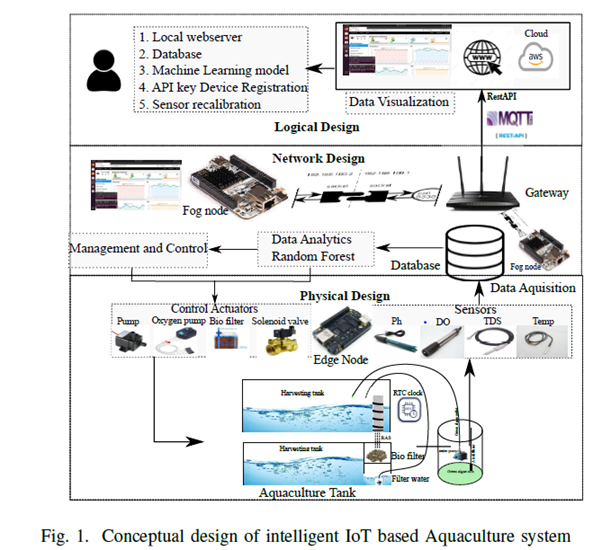
The Department of Computer Science Engineering is glad to announce that Dr Kshira Sagar Sahoo, Assistant Professor, has published an article titled ‘Sustainable IoT Solution for Freshwater Aquaculture Management’ in the Q1 journal, IEEE Sensors, having an Impact Factor of 4.325. The research was published in collaboration with Munesh Singh, from the Department of Computer Science and Engineering, PDPM IIITDM Jabalpur Campus, Madhya Pradesh, and Anand Nayyar, Graduate School, Faculty of Information Technology, Duy Tan University, Vietnam.
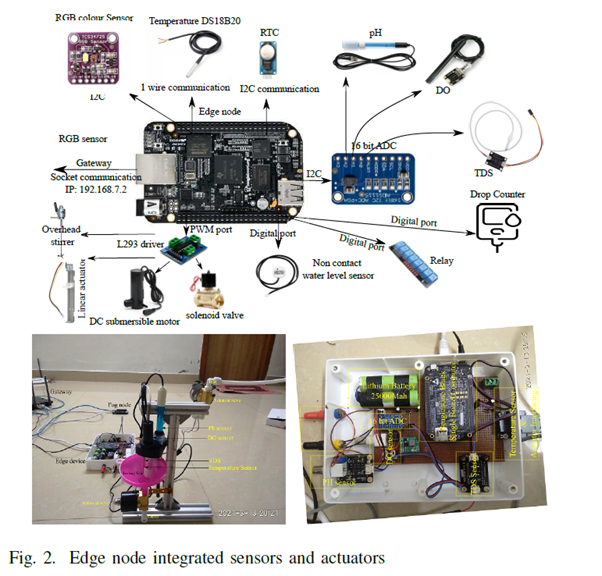 Freshwater pearl farming has the potential to generate an alternative source of income for small farmers. Indian freshwater river bodies have 51 types of species that can produce pearls. Still, India imports 2.4 billion dollars’ worth of pearls from China and Japan. To reduce the import burden on the Indian economy, the government encouraged the farmers to do integrated freshwater pearl farming. Aquaculture-based farming needs a small investment for the initial setup. Although the Indian government promotes aquaculture-based farming through subsidies and free training programs, farmers find it difficult to get success in aquaculture-based farming.
Freshwater pearl farming has the potential to generate an alternative source of income for small farmers. Indian freshwater river bodies have 51 types of species that can produce pearls. Still, India imports 2.4 billion dollars’ worth of pearls from China and Japan. To reduce the import burden on the Indian economy, the government encouraged the farmers to do integrated freshwater pearl farming. Aquaculture-based farming needs a small investment for the initial setup. Although the Indian government promotes aquaculture-based farming through subsidies and free training programs, farmers find it difficult to get success in aquaculture-based farming.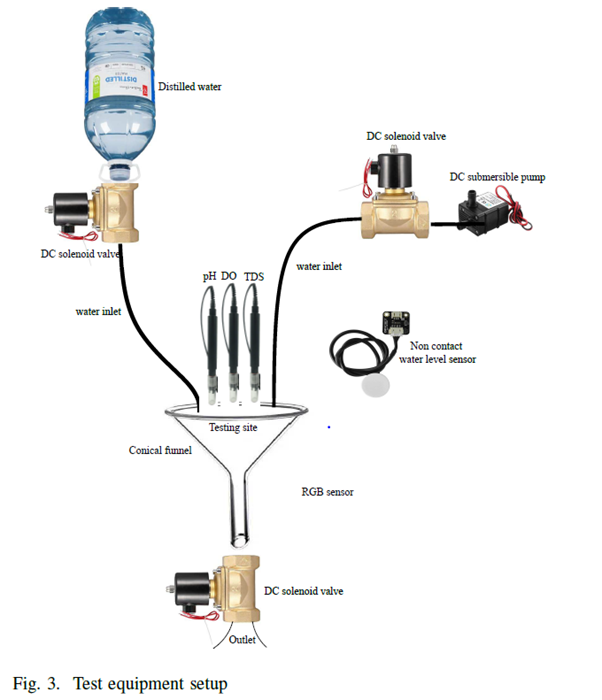 The paper proposes a comprehensive IoT system for freshwater pearl farming which has an intelligent control system for maintaining the aquaculture environment. The proposed system monitors and supports the habitable underwater environments for aquaculture. To train the farmers and educate them in pearl farming business is a time taking and skill-oriented job. The comprehensive IoT system will encourage farmers for freshwater pearl farming and proper utilisation of the government subsidy granted for aqua farming. In future, the researchers will consider more relative water parameters for robust forecast and analyse the best model for predictive analysis.
The paper proposes a comprehensive IoT system for freshwater pearl farming which has an intelligent control system for maintaining the aquaculture environment. The proposed system monitors and supports the habitable underwater environments for aquaculture. To train the farmers and educate them in pearl farming business is a time taking and skill-oriented job. The comprehensive IoT system will encourage farmers for freshwater pearl farming and proper utilisation of the government subsidy granted for aqua farming. In future, the researchers will consider more relative water parameters for robust forecast and analyse the best model for predictive analysis.Abstract of the Research
In recent years, we have seen the impact of global warming on changing weather patterns. The changing weather patterns have shown a significant effect on the annual rainfall. Due to the lack of annual rainfall, developing countries like India have seen a substantial loss in annual crop production. Indian economy largely depends on agro products. To compensate for the economic loss, the Indian government encouraged the farmers to do integrated aquaculture-based farming. Despite government subsidies and training programs, most farmers find it difficult to succeed in aquaculture-based farming. Aquaculture farming needs skills to maintain and monitor underwater environments. The lack of skills for monitoring and maintenance makes the aquaculture business more difficult for farmers. To simplify the pearl farming aquaculture, we have proposed an Internet of Things (IoT)-based intelligent monitoring and maintenance system. The proposed system monitors the water quality and maintains an adequate underwater environment for better production. To maintain an aquaculture environment, we have forecasted the change in water parameters using an ensemble learning method based on random forests (RF). The performance of the RF model was compared with the linear regression (LR), support vector regression (SVR), and gradient boosting machine (GBM). The obtained results show that the RF model outperformed the forecast of the DO with 1.428 mean absolute error (MAE) and pH with 0.141 MAE.
- Pre-existing health conditions and the risk of Covid-19 July 26, 2022
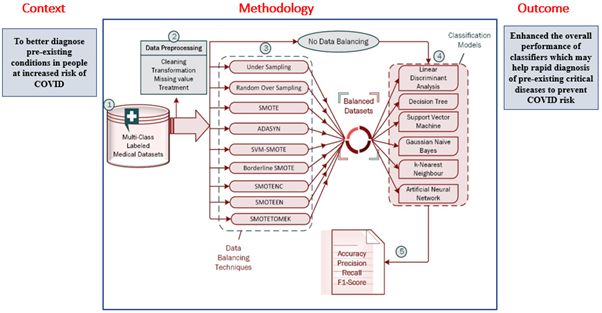 Individuals with pre-existing medical conditions are more vulnerable to Covid-19 and its variants. Patients in countries like India require early testing to diagnose crucial disorders to reduce the risk. Research at the Department of Computer Science and Engineering has come up with a system that automatically identifies and categorises diseases based on the patient’s medical test results. Assistant Professor Dr Ravi Kant Kumar published a paper Improving Performance of Classifiers for Diagnosis of Critical Diseases to Prevent COVID Risk as a co-author in the Q1 journal Computers and Electrical Engineering and has an impact factor of 4.152. With an accurate diagnosis, the required actions can be planned and executed to stop the patients from serious health issues as well as covid risk.
Individuals with pre-existing medical conditions are more vulnerable to Covid-19 and its variants. Patients in countries like India require early testing to diagnose crucial disorders to reduce the risk. Research at the Department of Computer Science and Engineering has come up with a system that automatically identifies and categorises diseases based on the patient’s medical test results. Assistant Professor Dr Ravi Kant Kumar published a paper Improving Performance of Classifiers for Diagnosis of Critical Diseases to Prevent COVID Risk as a co-author in the Q1 journal Computers and Electrical Engineering and has an impact factor of 4.152. With an accurate diagnosis, the required actions can be planned and executed to stop the patients from serious health issues as well as covid risk.Abstract
The risk of developing COVID-19 and its variants may be higher in those with pre-existing health conditions such as thyroid disease, hepatitis C virus (HCV), breast tissue disease, chronic dermatitis, and other severe infections. As a result, early and precise identification of these disorders is critical. A huge number of patients in nations like India require early and rapid testing as a preventative measure. Machine learning methods for automatically identifying and classifying diseases have been created, and they function effectively when the dataset is well specified and balanced at every class level, including “no disease”. The problem of imbalance arises from the skewed nature of data, in which a large number of cases belonging to one class (known as the majority class) are classified correct, while the other class (known as the minority class) has lesser instances; is unfortunately misclassified by many classifiers. When it comes to human life, this kind of misclassification is unacceptable. To solve the misclassification issue and improve accuracy in such datasets, we applied a variety of data balancing techniques to several machine learning algorithms. The outcomes are encouraging, with a considerable increase in accuracy. As an outcome of these proper diagnoses, we can make plans and take the required actions to stop patients from acquiring serious health issues or viral infections.
Explanation of the research
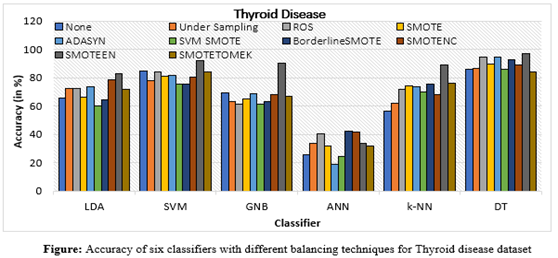 Lethal COVID-19 and its mutant forms may be more likely to arise in patients with pre-existing medical conditions such as thyroid illness, hepatitis C virus (HCV), breast tissue disease, chronic dermatitis, compromised immune systems, obesity, diabetes, heart disease, cancer, etc. For patients, an early and accurate diagnosis of these illnesses is crucial. Based on patient data, machine learning algorithms can assist in the early and quick detection of numerous diseases in a huge population like India. On the other side, machine learning algorithms perform poorly when a dataset has a class unbalanced problem. As a result, we used a variety of smote and its variants in this study to address the problems about the imbalanced class size. The experimental work showed that all six classifiers (DT, SVM, LDA, k-NN, GNB, and ANN) performed better overall on clinical datasets when class balancing strategies and classification techniques were combined. It recommends the use of the recommended classifications and class balancing technique with regard to specific data to identify the disease accurately and automatically
Lethal COVID-19 and its mutant forms may be more likely to arise in patients with pre-existing medical conditions such as thyroid illness, hepatitis C virus (HCV), breast tissue disease, chronic dermatitis, compromised immune systems, obesity, diabetes, heart disease, cancer, etc. For patients, an early and accurate diagnosis of these illnesses is crucial. Based on patient data, machine learning algorithms can assist in the early and quick detection of numerous diseases in a huge population like India. On the other side, machine learning algorithms perform poorly when a dataset has a class unbalanced problem. As a result, we used a variety of smote and its variants in this study to address the problems about the imbalanced class size. The experimental work showed that all six classifiers (DT, SVM, LDA, k-NN, GNB, and ANN) performed better overall on clinical datasets when class balancing strategies and classification techniques were combined. It recommends the use of the recommended classifications and class balancing technique with regard to specific data to identify the disease accurately and automaticallyFor this work, Dr Ravi Kant Kumar has collaborated with Mr Vinod Kumar, Koneru Lakshmaiah Education Foundation, Vaddeswaram,India, and Mr Gotam Singh Lalotra, University of Jammu, India. Their future research will investigate and design the most effective multi-class balancing method to address the multi-class imbalance problem in medical data.
Continue reading →

