The Department of Economics is delighted to announce that Dr Ghanshyam Kumar Pandey and his research group; Sheeba Moghal, Rakshit Barodia, and William Carey have published an article titled “COVID-19 and its effects on the mental health of people living in urban slums in India” in the ‘Journal of Information and Knowledge Management’, having an Impact Factor of 1.3.
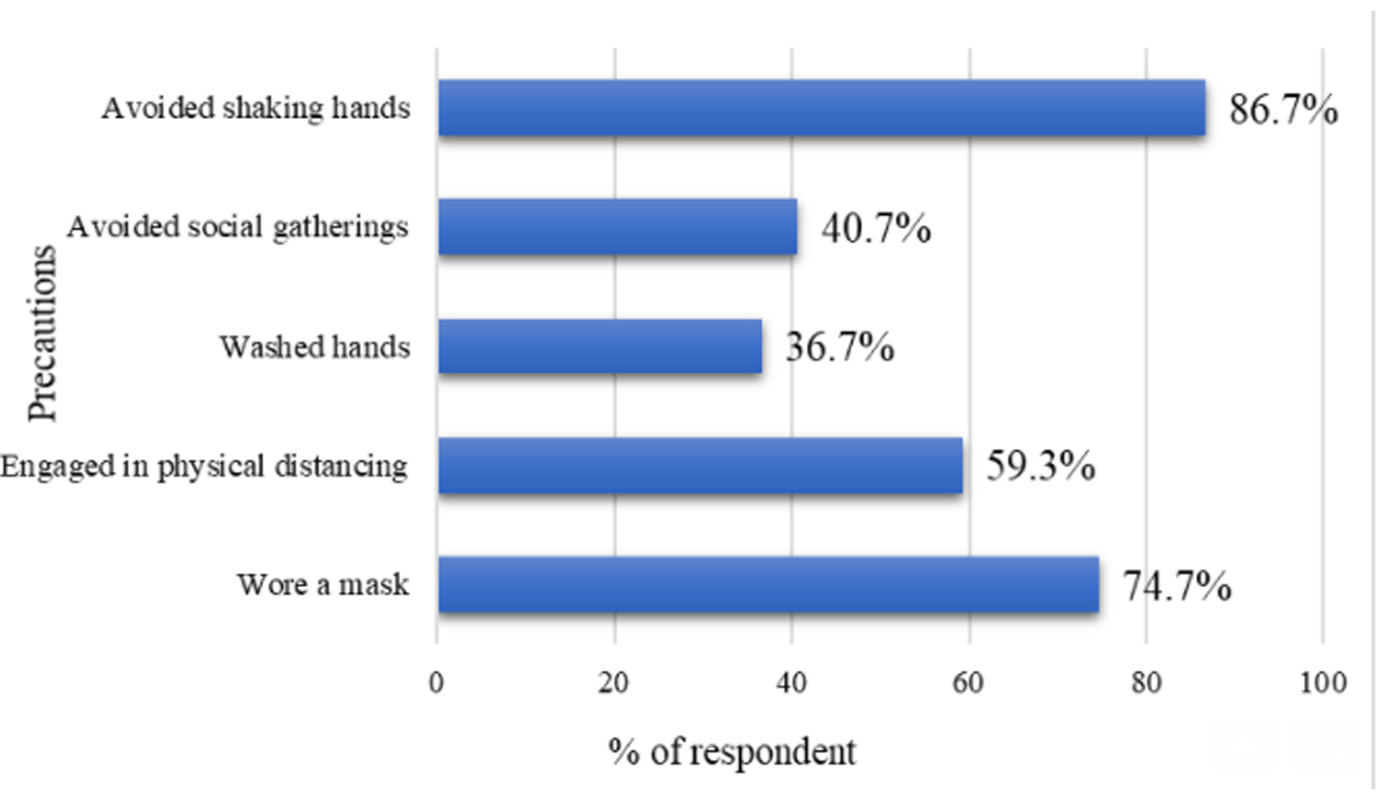
The study confirms that more than three-fourth of the population suffer from mental stress due to the spread of COVID-19 and the lockdown imposed by the government. Eighty per cent of those surveyed stated that the stress had affected their decision-making. The study also confirms that the number of dependents, monthly income, number of living rooms, maintenance of physical distancing norms, avoidance of social gatherings, government support, health insurance, and living in a rented house are significantly related to the mental stress of people living in slums in Andhra Pradesh in India.
Abstract of the Research
The COVID-19 pandemic has had a devastating effect on the mental health of people from different backgrounds; these effects have been particularly acute among lower-income households and in slums. There has been a steep rise in mental illness and behaviours associated with it since 2020, especially in slums characterized by poverty, poor housing, high density, and unhealthy environments. This paper aims to examine the effect of COVID-19 on the mental health of people living in the slums of Vijayawada and Visakhapatnam in the state of Andhra Pradesh in India.