Recent News
- DST-INSPIRE Subject Expert Committee Meeting July 18, 2022
 A two-day DST-INSPIRE Subject Expert Committee meeting was held on July 14 & 15 at SRM University-AP campus. Experts in the area of Physical Sciences from across the country gathered at the university to evaluate this year’s INSPIRE Fellowship applications in Physical Sciences.
A two-day DST-INSPIRE Subject Expert Committee meeting was held on July 14 & 15 at SRM University-AP campus. Experts in the area of Physical Sciences from across the country gathered at the university to evaluate this year’s INSPIRE Fellowship applications in Physical Sciences.INSPIRE Fellowship component offers 1000 Fellowships every year for carrying out doctoral degrees in both basic and applied sciences, including engineering and medicine, in the age group of 22-27 years.
The Chairperson of the Expert Committee in the area of Physical Sciences was Dr Dinakar Kanjilal, Professor, Inter-University Accelerator Centre (IUAC), New Delhi. “The fellowship ensures geographical distribution of excellence, and we look forward to more applicants from SRM AP”, Prof. Kanjilal said. Since its inception, SRM University-AP has INSPIRE Fellows as faculty members in the various departments of Sciences.
University Pro-Vice-Chancellor Prof D Narayana Rao, who also is the co-chair of the expert committee, said that it is gratifying to know that the PhD students have chosen to enrol in reputed universities and institutes. The applicants have chosen extremely accomplished scientists and faculty members as their research supervisors. “We are glad that 61 are girl students out of the 116 applications we received”, highlighted Prof D Narayana Rao. He expressed his happiness about the increasing number of women representation in Indian academia.
The other eminent scientists in the INSPIRE Fellowship selection committee included Member Secretary Dr Umesh K Sharma, Prof. Shikha Verma, Dr G. Vijaya Prakash, Dr AnandamayeeTej, Dr Rajendra Prasad Pant and Dr Arjit Chowdhuri.
Innovation in Science Pursuit for Inspired Research (INSPIRE)” is a flagship scheme of the Department of Science and Technology (DST), Government of India, which aims to attract meritorious youth to study basic and natural sciences at the college and university level and to pursue research careers in both basic and applied science areas including engineering, medicine, agriculture, and veterinary sciences.
Continue reading → - Highly stable ruthenium catalyst for hydrogen evolution reaction July 12, 2022
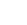
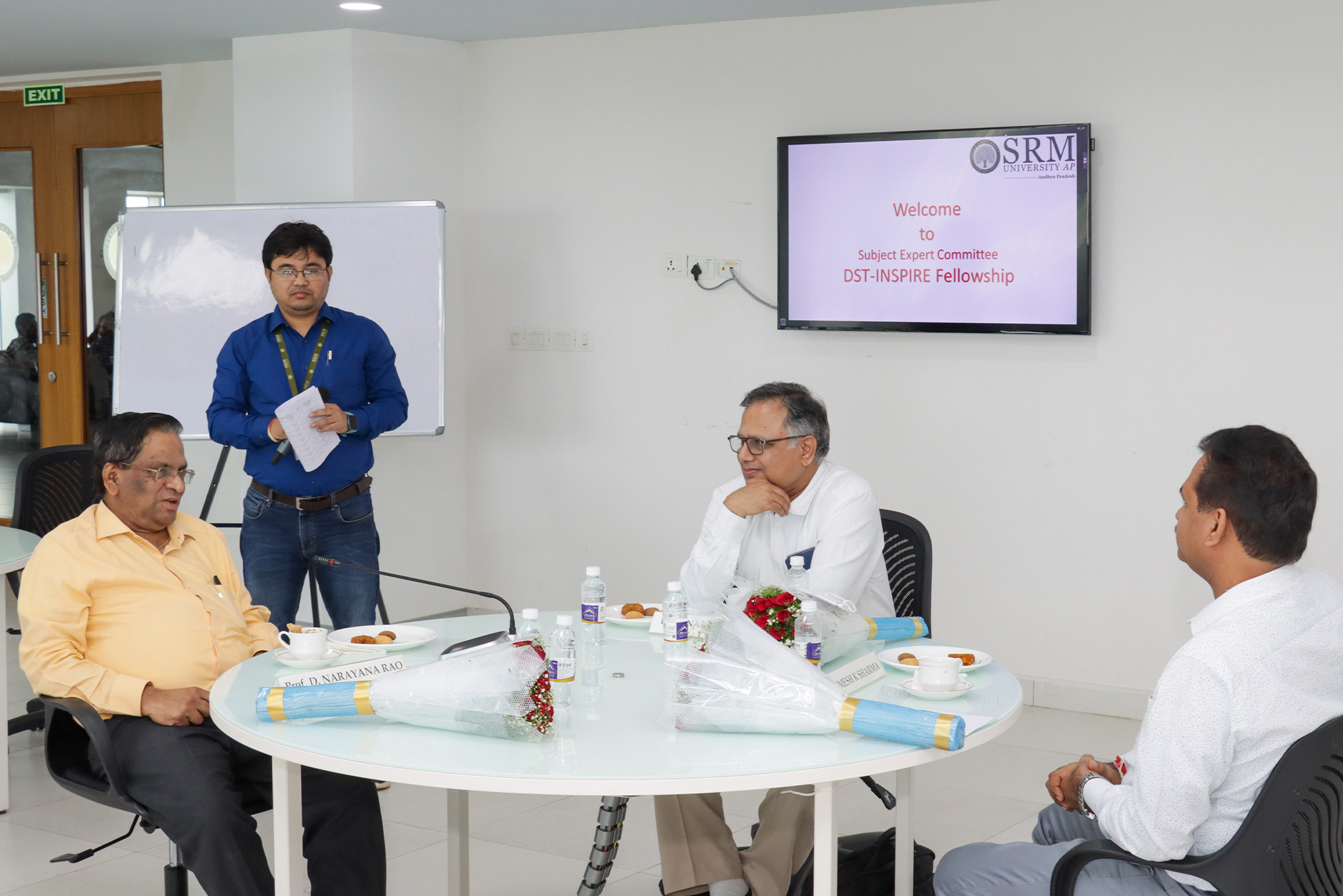
The Department of Physics is glad to announce that Prof Ranjit Thapa and his PhD scholar, Mr Samadhan Kapse, have published a patent titled “Highly Stable Ruthenium Single-Atom Catalysts on Fe3O4/MWCNTs for Hydrogen Evolution Reaction” (Application no. 202241006087). The research was done in collaboration with Ms Shwetha K R, Mr Shivanna M and Dr Nagaraju D H, from the Department of Chemistry, School of Applied Sciences, REVA University, Bangalore.
A Brief Description of the Research
In the current work, Fe3O4 nanoparticles were prepared by a simple chemical co-precipitation method under an inert atmosphere, and it was utilised for HER studies. Ru nanoparticles were profitably deposited over Fe3O4/MWCNTs modified glassy carbon electrode by the electrochemical deposition technique. The superior HER activity was achieved on Fe3O4/MWCNTs/Ru in 0.1M H2SO4 aqueous media. We demonstrated that synthesised electrocatalyst offers low over potential 101 mV to reach a current density of 10 mA cm-2 towards hydrogen evolution reaction. It displays exceptional stability and finds to be of no change in the HER activity despite 1000 cycles. It is emphasised that a small weight percentage of ruthenium in the prepared catalyst can replace high-cost platinum in renewable energy technologies.
Social Implications of the Research
Production of renewable energy has greater significance in the present situation owing to the impact of the depletion of non-renewable energy resources such as fossil fuels and the release of greenhouse gases into the atmosphere. Hydrogen has gained considerable interest as an energy storage and energy carrier due to its high energy density (146kJ/g), and its utilisation also eliminates pollution and toxicity. Several methods have been explored to produce molecular hydrogen. Among them, the electrolysis of water is the best way to produce high purity hydrogen from water. An excellent electrocatalyst is obligatory to liberate hydrogen gas effectively from water. It is known that Superior HER activity has been achieved using platinum (Pt) and Pt-based catalysts. Due to its high cost and low surplus, its expansion has been limited to the industrial scale. The research proposes that Ru-based catalysts can overcome these challenges.
DFT study is more effective to find the origin of catalytic activity in materials for designing highly promising catalysts for various catalytic reactions. The researchers expressed their gratitude to SRM University-AP for providing the required computational facility and support.
Continue reading → - 100% Erasmus Mundus Scholarship and MS opportunities in Europe July 5, 2022
 SRM University-AP has numerous success stories and student accomplishments to share with the world. What makes the story of Bennet Benny different is the magnitude of his winning and the miles he has crossed after setting foot to achieve his dreams. He has secured the much-coveted Erasmus Mundus Joint Masters Scholarship with a whopping sum of € 33,600 for two years. With the 100% EMJM scholarship, he can now pursue QuanTEEM Master’s across four different universities, each semester in one of these universities:
SRM University-AP has numerous success stories and student accomplishments to share with the world. What makes the story of Bennet Benny different is the magnitude of his winning and the miles he has crossed after setting foot to achieve his dreams. He has secured the much-coveted Erasmus Mundus Joint Masters Scholarship with a whopping sum of € 33,600 for two years. With the 100% EMJM scholarship, he can now pursue QuanTEEM Master’s across four different universities, each semester in one of these universities:University Bourgogne Franche-Comté (France)
Technische Universität Kaiserslautern (Germany)
Aarhus University (Denmark)
Moskovskiy Fiziko-Tekhnicheskiy Institut (Russia)Internship at JAIST, Japan -2019
Like every other student, Bennet joined the Bachelor’s degree programme at the Department of Physics in 2018 with an irrepressible desire to dive into the depths of Physics. His undying passion for grasping the subject’s nuances is an influential lesson for all students to emulate. When he was in the second year of his graduate studies, Bennet won the Sakura Science Internship under the supervision of Prof. Ryo Maezono at JAIST, Japan. The internship was funded by the Japan Science and Technology Agency (JST), a government funding agency. For him, this was an excellent opportunity to learn more deeply about quantum mechanics. It also helped him raise his awareness of computational physics, its advantages, uses and the latest research around it.
“I was able to interact with many international scholars and researchers at the Japan Advanced Institute of Science and Technology. It helped me learn about the various ways through which I could fund my higher education. Therefore, after returning to SRM University-AP, I could work in the necessary direction to build my profile accordingly.” Bennet remarked. The enormous lessons he learned there helped him publish a research paper under the guidance of Prof Ranjit Thapa and his PhD students in the Computational Physics laboratory. “The Department of Physics has always motivated me to reach greater heights”, he added.
NTU-India Connect Research Programme 2022
Bennet has also proved his mettle by securing yet another internship opportunity as part of the NTU-India Connect Research Programme 2022. He was selected to spend a semester (Spring term) at NTU, Singapore with a full fellowship during the final year of graduation. As a young researcher, he has gained immense exposure and experience in such a short period giving him a competitive edge to move further in the direction of his dreams. “It has always been my dream to pursue a research career in Physics”, he asserted.
Looking Forward to QuanTEEM Master’s
The QuanTEEM Master’s programme is based on Quantum technologies and provides an excellent opportunity to build a research network in multiple countries in the European Union. He aspires to gain a deeper understanding of quantum mechanics and wishes to use the knowledge to improve our civilisation. In the words of Bennet, “We should never let the fear of failure deter us from trying. I feel that to reach our best potential; we need to face the challenges in life rather than be disheartened by them. Hence, I would encourage my fellow students never to hesitate to seek new opportunities.”
Continue reading → - A new aqueous electrolyte to enhance the yield of Ammonia June 25, 2022
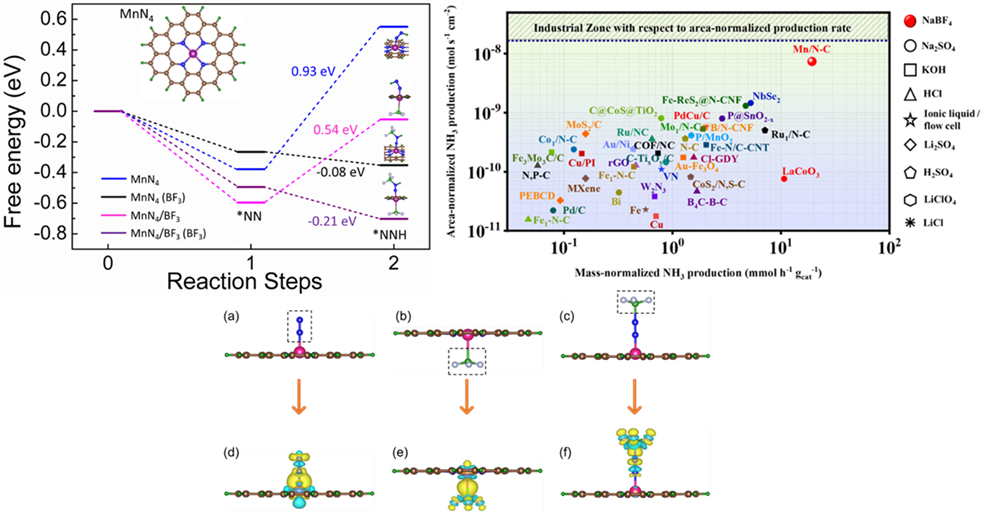
The Department of Physics is proud to announce that Prof Ranjit Thapa and his PhD scholar Mr Samadhan Kapse have published an article titled “Lewis acid-dominated aqueous electrolyte acting as co-catalyst and overcoming N2 activation issues on catalyst surface” in the most prestigious and highly cited multidisciplinary research journal, ‘Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences’ (PNAS), having an Impact Factor of 11.2. The research was done in collaboration with Ms Ashmita Biswas, Mr Bikram Ghosh, and Dr. Ramendra Sundar Dey from the Institute of Nano Science and Technology (INST), Punjab.
Abstract of the Research
The growing demands for ammonia in agriculture and transportation fuel stimulate researchers to develop sustainable electrochemical methods to synthesize ammonia ambiently, to get past the energy-intensive Haber Bosch process. But the conventionally used aqueous electrolytes limit N2 solubility leading to insufficient reactant molecules in the vicinity of the catalyst during electrochemical nitrogen reduction reaction (NRR). This hampers the yield and production rate of ammonia, irrespective of how efficient the catalyst is. Herein we introduce a new aqueous electrolyte (NaBF4), which not only acts as an N2-carrier in the medium but also works as a full-fledged “co-catalyst” along with our active material MnN4 to deliver high yield of NH3 (328.59 μg h-1 mgcat-1) at 0.0 V vs RHE. BF3-induced charge polarization shifts the metal d-band center of MnN4 unit close to the Fermi level, inviting N2 adsorption facilely. The Lewis acidity of the free BF3 molecules further propagates their importance in polarizing the N≡N bond of the adsorbed N2 and its first protonation. This push-pull electronic interaction has been confirmed from the change in d-band center values of MnN4 site as well as charge density distribution over our active model units, which turned out to be effective enough to lower the energy barrier of the potential determining steps of NRR. Resultantly, a high production rate of NH3 (7.37 × 10-9 mol s-1 cm-2) was achieved, approaching the industrial scale where the source of NH3 was thoroughly studied and confirmed to be chiefly from the electrochemical reduction of the purged N2 gas.
A Brief Summary of the Research
The widely highlighted problem of NRR is that the competitive HER is most likely worked upon with several catalyst development and electrolyte modifications, while the N2 solubility and activation issues in the aqueous medium are generally neglected. This work justifies our aim to contribute towards this troublemaker by using NaBF4 as a working electrolyte, which served as a “full-packaged co-catalyst” along with MnN4, reinforcing the NRR kinetics at the cost of low overpotential. The Lewis-acidic nature of BF3 induced adduct formation with the N2 molecules acted as a carrier of N2 gas into the medium in vicinity of the electrocatalyst. Simultaneously, the charge polarization over MnN4 active site due to BF3 delocalized the metal d-band centre, which triggered N2 adsorption on the catalyst site. Under this condition, free BF3 form the medium interacted with the adsorbed N2 and brought about the facile polarization of the N≡N bond and its first protonation at a much lower energy barrier. This push-pull charge transfer effect enormously helped to overcome the potential determining steps and this BF3 mediated NRR resulted in a huge production rate of NH3, which could be compared to that of industrial scale, which was not achieved so far with any aqueous or ionic liquid electrolytes. In short, this kind of user-friendly aqueous electrolyte is being investigated for the first time for NRR. Since BF3 displayed tremendous potential in triggering the kinetics of NRR, this new finding may encourage researchers to work more on aqueous electrolyte designing towards an even improved NRR performance of the electrocatalysts. Not only that, electrocatalysts could also be functionalized with BF3 derivatives, which could be one entirely new route of study in the field of NRR.
Social Implications
Ammonia is considered as the most abundant and widely used synthetic fertilizer in the world. The sole mean of large-scale ammonia production relies on the century-old Haber-Bosch process, which takes in more energy than it can produce, while the electrochemical nitrogen reduction reaction (NRR) offers a carbon-free and sustainable way of ammonia synthesis. However, electrochemical NH3 synthesis is often arrested by a few factors such as NH3 detection, contaminations from source gases, nitrogen-containing chemicals and the presence of labile nitrogen in the catalysts. In the recent past, several protocols have been proposed to correct the fallacious results. Recently, Choi et el. have concluded that it is difficult to believe from the too-low yield rate of NH3 that the reduction of N2 has actually occurred in the aqueous medium. It is noteworthy that the electrolyte plays a crucial role and offers a suitable environment for any electrochemical reactions to occur. However, the issue with the solubility of N2 in conventional aqueous electrolytes is a real troublemaker to achieve a high yield and production rate of NH3 during electrochemical synthesis. Therefore, it is necessary to solve the most important issue i.e., to solvate a promising concentration of N2 molecules into the electrolyte such that it becomes accessible to the catalyst surface for its subsequent reduction.
- A unique bridging facets assembly of gold nanorods June 15, 2022
 The paper “A unique bridging facets assembly of gold nanorods for the detection of thiram through SERS” has been published by Prof Ranjit Thapa, Professor of Physics and his PhD student, Ms Anjana Tripathi, in ACS Sustainable Chemistry & Engineering having an Impact Factor of 8.198.
The paper “A unique bridging facets assembly of gold nanorods for the detection of thiram through SERS” has been published by Prof Ranjit Thapa, Professor of Physics and his PhD student, Ms Anjana Tripathi, in ACS Sustainable Chemistry & Engineering having an Impact Factor of 8.198.Abstract
The addition of Au NRs (Gold Nanorods) to TRM (Thiram) of higher and lower concentrations, yields side-by-side assembly (SSA) and bridging facets assembly (BFA), respectively, and exhibited excellent hotspots for the ultra-low detection of TRM. Bridging facets of Au NRs, such as (5 12 0) and (5 0 12) planes are mainly responsible for the BFA. This kind of interaction is observed for the first time and not reported elsewhere. The detailed facets of Au NRs, namely side facets, bridging facets, and pyramid facets, were discussed with the 3D model of Au NRs. The computational studies confirm the SSA and BFA for Au NRs with varying concentrations of TRM are well in agreement with the experimental results.
Research in brief
Au NRs were synthesized successfully using the seed-mediated method and characterized by UV-Vis analysis, SEM, TEM, FT-IR, Raman, and XPS analysis. Synthesized Au NRs were employed for the detection of TRM. Upon adding Au NRs to TRM of higher and lower concentrations yields side by side (SSA) and bridging facet assembly (BFA), validated by TEM analysis. This unique BFA was observed for the first time and not reported before to the best of our knowledge. Elemental mapping confirms the good adsorption of TRM over Au NRs, and FT-IR, Raman, SERS, and XPS analysis confirm the adsorption of TRM on Au NRs through Au-S bond. A uniformity study was performed for the TRM-Au NRs sample using 25 random places and obtained an RSD of ≤ 10% for each peak in SERS. This shows TRM is uniformly adsorbed on Au NRs. LOD and EF were achieved at 10 pM and 2.8 ×106, respectively. Hence, Au NRs are considered an excellent substrate for the detection of TRM. The unique assembly of BFA may play a significant role in the research community to further study the facet-dependent interactions of nanostructures. The computational study was performed to know the reason behind SSA and BFA. The density functional theory (DFT) was carried out using the Vienna Ab-initio Simulation Package (VASP). The Perdew-Burke-Ernzerhof (PBE) functional within Generalized Gradient Approximation (GGA) is adopted to treat the exchange-correlation interactions. These studies confirm the formation of a strong bond between Au and S, as well as the SSA and BFA for higher and lower TRM concentrations with Au NRs. The binding energy of TRM in SSA and BFA is -3.81 eV and 3.19 eV respectively. From the theory, it shows that TRM of lower concentration form BFA and higher concentration of TRM, due to high barrier energy for TRM diffusion, Au NRs form SSA. In this respect, we calculated the activation barrier for thiram migration from edge site (BFA) to in between site (SSA). Results indicate that TRM needs 2.40 eV energy to migrate from the edge site to in between site to form side-by-side assembly. Therefore, for diffusion from edge to in between (SSA) site high-energy barrier is required i.e. higher concentration is required for such configuration. Hence, at low concentration, TRM will form bridge facet assembly and due to high barrier energy for TRM diffusion, the side-by-side assembly is possible only at high concentration.
Practical implementation/social implications
Concerns have grown in recent years about the widespread use of the pesticide thiram (TRM), which has been linked to negative effects on local ecosystems. This highlights the critical need for quick and accurate point-of-need pesticide analysis tools for real-time applications. The detection of TRM using gold nanorods (Au NRs) with a limit of detection (LOD) of 10-11 M (10 pM) and an enhancement factor (EF) of 2.8 × 106 along with 6.2% of signal homogeneity (with respect to peak at 1378 cm-1) achieved through surface-enhanced Raman scattering (SERS). The interaction of Au NRs with TRM is sensitive, and ultra-low detection of hazardous TRM through SERS makes an ideal technique for environmental protection, real-time applications, and analysis of one-of-a-kind materials.
Collaborations
Bhavya M. B, Akshaya K. Samal
Continue reading →
Institute: Centre for Nano and Material Sciences, Jain University, Jain Global Campus
Ramanagara, Bangalore 562112, India