Recent News
- A Discourse on Multiscale Modelling of Complex Systems May 11, 2023

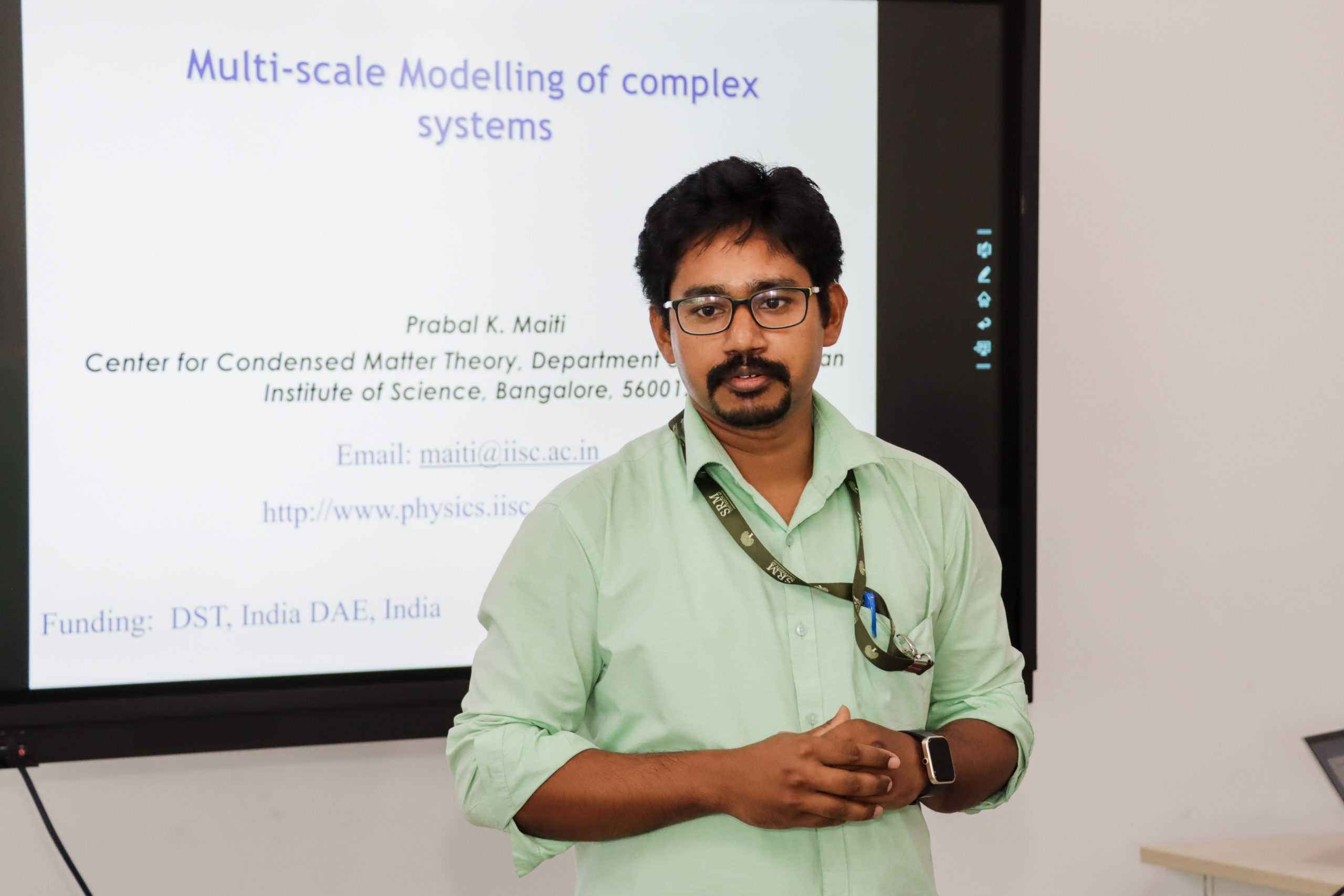
The Department of Physics, SRM University–AP organised the 8th lecture of the “Eminent Guest Lecture Series: An Odyssey of Physics” on May 10, 2023. Prof. Prabal K Maiti from the Department of Physics, Indian Institute of Science (IISc) Bangalore visited the university campus and delivered a talk on “Multiscale Modelling of Complex Systems”. The seminar was held at colloquium level to motivate and encourage young undergraduates and graduates.
More than 60 participants attended the seminar across the disciplines and interacted with the eminent speaker. During his visit, Prof. Maiti also had one-to-one interaction sessions with the faculty members and research scholars. The speaker also enthusiastically interacted with many students informally over breakfast at the university mess hall. Dr Debabrata Pramanik from the Department of Physics coordinated the event with Dr Amit Chakraborty and with active participation from the research scholars, faculty members and supporting staff. Department of Physics plans to conduct more such events where eminent and distinguished scientists will visit the campus and encourage young talents.
Continue reading → - Two-Dimensional Transition Metal Oxide Layers and A method for Their Synthesis May 8, 2023
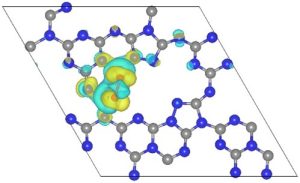
 Researchers at the Department of Physics have successfully developed large-area ultra-thin 2D transition metal oxide (TMO) layers using a cost-effective and straightforward method through proximity evaporation under ambient conditions. Associate Professor Dr Jatis Kumar Dash and his students Shaik Md. Abzal, Kurapati Kalyan, and Sai Lakshmi Janga have secured a patent for their research in Two-Dimensional Transition Metal Oxide Layers and A method for their Synthesis (application no: 202241005220). They have integrated the 2D TMO layers with various other 2D materials to create nano-electronic devices. Their work demonstrates the immense potential of ultra-thin TMOs in 2D-material-based flexible electronics.
Researchers at the Department of Physics have successfully developed large-area ultra-thin 2D transition metal oxide (TMO) layers using a cost-effective and straightforward method through proximity evaporation under ambient conditions. Associate Professor Dr Jatis Kumar Dash and his students Shaik Md. Abzal, Kurapati Kalyan, and Sai Lakshmi Janga have secured a patent for their research in Two-Dimensional Transition Metal Oxide Layers and A method for their Synthesis (application no: 202241005220). They have integrated the 2D TMO layers with various other 2D materials to create nano-electronic devices. Their work demonstrates the immense potential of ultra-thin TMOs in 2D-material-based flexible electronics.Patent Background
The two-dimensional (2D) ultrathin hetero-stacked layers show unusual physiochemical properties when reduced to a few atoms in thickness. These 2D heterostructures offer significant benefits for next-generation devices. Firstly, their atomically thin 2D nanosheets provide a larger surface area due to the complete exposure of surface atoms. Secondly, edge sites in 2D nanosheets are chemically more reactive than their basal planes, and open gaps allow for the intercalation of electrolyte ions. In addition, the high mechanical strength and flexibility at atomic dimensions make them suitable for use in next-generation wearable electronics. However, growing and stacking 2D materials is challenging, and existing growth tools are complex and costly.
Future Prospects
2D materials are critical for making flexible, wearable, foldable and transparent self-powered smart electronic devices. The next generation smart electronic devices will be
Continue reading →
made of 2D materials heterostructures which will need less operating power, fewer materials consumption and will have ultimate scalability. - One-Day Workshop on Powder X-ray Diffraction May 3, 2023
 A One-Day Workshop on Powder X-ray Diffraction was conducted on April 28, 2023, by the Department of Physics in association with Malvern Panalytical, a division of Spectris Technologies. The workshop was intended to train users on the foundation of the X-ray diffraction technique in solids, the equipment’s hardware, data collection and analysis by software and advanced applications on thin-film and battery measurements.
A One-Day Workshop on Powder X-ray Diffraction was conducted on April 28, 2023, by the Department of Physics in association with Malvern Panalytical, a division of Spectris Technologies. The workshop was intended to train users on the foundation of the X-ray diffraction technique in solids, the equipment’s hardware, data collection and analysis by software and advanced applications on thin-film and battery measurements.More than 60 participants attended the workshop from eight different institutes, including SRM University-AP, VIT-AP, KL University, Vignan’s Foundation for Science, Technology & Research, PB Siddhartha College, VR Siddhartha Engineering College, Raghu Institute of Technology – Visakhapatnam and NIT Andhra Pradesh. Four members from the Panalytical team visited, and the experts, Dr Mangesh Mahajan and Dr Sandeep Nagar, presented technical presentations on the topics.
Advanced features of the HighScore Plus software application and in-situ Powder X-ray diffraction measurement on battery charge-discharge were vital highlights. The external members interacted with participants during the technical sessions and during X-ray diffraction laboratory demonstrations. Participants were awarded a certificate by the varsity and Malvern Panalytical.
Dr Pranab Mandal, Head of the Department of Physics and Mr Soumik Mahapatra from Panalytical coordinated the event. The workshop witnessed active participation from research scholars and faculty from the Department of Physics. The Department plans to conduct more events on advanced research techniques and hands-on training for young researchers.
Continue reading → - Maximising Electrochemical NH3 Production March 21, 2023

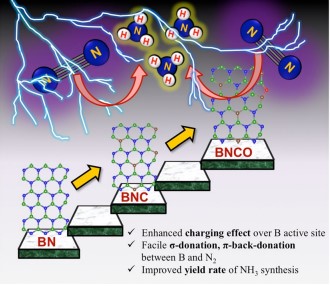
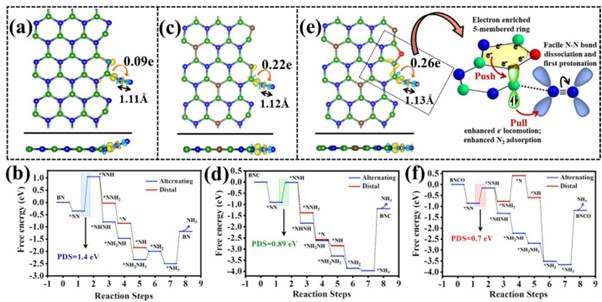
Significant measures have been undertaken to synthesise ammonia proficiently, the future renewable energy fuel for its wide range of applications in various sectors. On this account, a research paper titled “Oxygen functionalization-induced charging effect on boron active sites for high-yield electrochemical NH3 production” has been published by Prof. Ranjit Thapa, Professor, Department of Physics and his research scholar Mr Samadhan Kapse in the journal Nano-Micro Letters having an impact factor of 23.655.
Abstract
Ammonia has been recognized as the future renewable energy fuel because of its wide-ranging applications in H2 storage and transportation sector. In order to avoid the environmentally hazardous Haber–Bosch process, recently, the third-generation ambient ammonia synthesis has drawn phenomenal attention and thus tremendous efforts are devoted to developing efficient electrocatalysts that would circumvent the bottlenecks of the electrochemical nitrogen reduction reaction (NRR) like competitive hydrogen evolution reaction, poor selectivity of N2 on the catalyst surface. Herein, we report the synthesis of an oxygen-functionalised boron carbonitride matrix via a two-step pyrolysis technique. The conductive BNCO(1000) architecture, the compatibility of B-2pz orbital with the N-2pz orbital and the charging effect over B due to the C and O edge-atoms in a pentagon altogether facilitate N2 adsorption on the B edge-active sites. The optimum electrolyte acidity with 0.1 M HCl and the lowered anion crowding effect aid the protonation steps of NRR via an associative alternating pathway, which gives a sufficiently high yield of ammonia (211.5 μgh−1 mgcat−1) on the optimized BNCO(1000) catalyst with a Faradaic efficiency of 34.7% at −0.1 V vs RHE. This work thus offers a cost-effective electrode material and provides the contemporary idea about reinforcing the charging effect over the secured active sites for NRR by selectively choosing the electrolyte anions and functionalizing the active edges of the BNCO(1000) catalyst.
A brief summary of the research in layman’s terms
In summary, this work displayed the significant role of O and C doping within BN architecture to promote NRR on the edge B sites via an associative alternating mechanism. The gradual formation of the ideal structure was systematically studied by means of XPS and the electronic properties was investigated from NEXAFS. A greater impact was found on the charging effect of B centres due to O-functionalized edges that induced a greater charge density from B to the adsorbed N2, overcoming the potential determining steps for NRR. This work simultaneously highlighted the importance of the choice of electrolyte, where in 0.1 M HCl our catalyst BNCO(1000) yielded 211.5 μg h−1mgcat−1 of ammonia at −0.1 V vs RHE with a FE of 34.7%. It was experimentally found and theoretically supported that the bulky anions in H2SO4 and H3PO4 blocked the B active sites by a Lewis acid-base interaction between the B sites and the O ends of the anions, hence not suitable for this class of materials. Thus, the present work offered an overall idea of catalyst designing and the medium to retain a high and consistent NRR performance.
Social implications of the research
Nitrogen reduction reaction (NRR) performed electrochemically is regarded as a green and legitimate approach to ammonia synthesis and it has been intrinsically brought into the limelight by the worldwide research community, not only because of the immense use of ammonia in the agriculture and transportation sector but also due to urge to resolve the fallacies associated with the process. Primarily, the eternal problem persisting with NRR is the predominance of the combative hydrogen evolution reaction (HER) at the same potential range, which overpowers NRR over most of the catalyst surfaces, resulting in poor yield and Faradaic efficiency (FE) of ammonia production. Researchers thus majorly focus on varied catalyst development, which includes several strategies: (a) Selectivity of elements that would prefer binding with N2 over protons, (b) Blocking the HER active sites, (c) Phase-selective material designing, inhibiting HER at the active surface, (d) interface-engineering that would deviate the HER pathway inducing better Faradaic efficiency for NRR. Although either 1st-row transition metals or semimetals are regarded as more suitable candidates for NRR, a metal-free approach is rather preferred for the cost-effectiveness and simplicity of the process. Boron (B)-based electrocatalyst in this respect can act as a strong contender. The research also posits that Density functional theory is useful for the molecular level understanding to unveil the performance of different catalytic reactions.
Collaborations
- Ms Ashmita Biswas, Institute of Nano Science and Technology (INST), Sector-81, Mohali, Punjab 140306, India
- Mr Ramendra Sundar Dey, Institute of Nano Science and Technology (INST), Sector-81, Mohali, Punjab 140306, India
- Synergistic Effects of CN in Sonophotocatalytic Degradation February 21, 2023
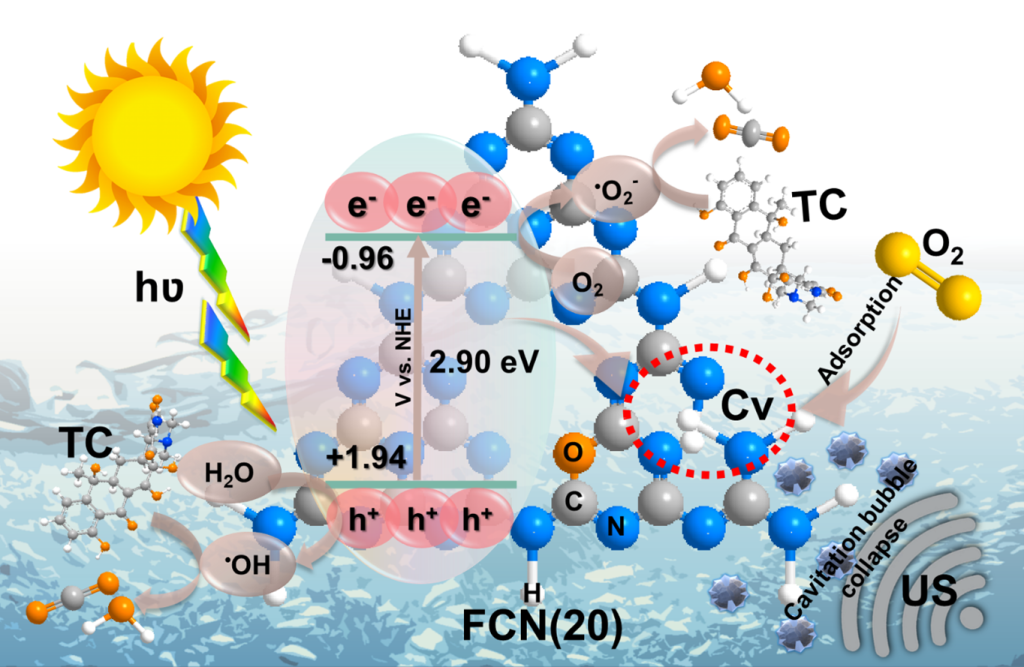
The Department of Physics is pleased to announce that Professor Ranjit Thapa, Dean-School of Engineering and Sciences (SEAS) and Professor of Physics along with his PhD scholar, Mr E S Erakulan, has published a groundbreaking paper titled “Scrutinizing the Role of Tunable Carbon Vacancies in g-C3N4 Nanosheets for Efficient Sonophotocatalytic Degradation of Tetracycline in Diverse Water Matrices: Experimental study and theoretical calculation” in the prestigious Chemical Engineering Journal with an impact factor of 16.744. The paper offers crucial insights into the role of controllable defects in the sonophotocatalytic degradation of tetracycline (TC) antibiotics from polluted water.
Abstract of the paper
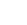
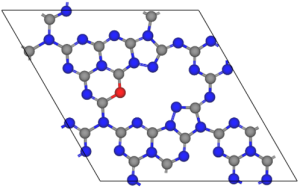
Metal-free polymeric graphitic carbon nitride (CN) materials are robust and stable visible-light-driven photocatalysts that have recently piqued interest in photocatalytic applications. Its photocatalytic performance is restricted remarkably due to moderate oxidation ability and fast charge carrier recombination rate. To address these issues, we engineered carbon-vacant CN (FCN) using a facile formalin-assisted thermal polymerization of molten CN precursor in which the carbon vacancies (C v ) were regulated by altering formalin dosage. Consequently, FCN catalysts revealed C v concentration-dependent sonophotocatalytic degradation of Tetracycline (TC) antibiotics over diverse water matrices. The optimal FCN exhibited complete TC degradation efficiency within 60 min with a synergy index of 1.4, which is approximately 2.6 times higher than that of pristine CN. The enhanced sonophotocatalytic performance was mainly due to the synergistic effect of ultrasound and light irradiation. The C v formation also resulted in enhanced charge carrier transportation and facilitated oxygen adsorption at the C V site of FCN – supported by both experimental study and theoretical calculation. Subsequently, FCN generated abundant reactive active oxygen species including, •O 2 –, as well as indirectly •OH which played a significant role in the degradation pathway and mineralisation of the TC molecules. This study provides insight into understanding the correlation between controllable defects and sonophotocatalytic degradation properties of the self-doped and deficient FCN.
In this research, Prof. Thapa and his team utilised a facile formalin-assisted thermal polymerization technique to fabricate metal-free polymeric graphitic carbon nitride (CN) materials. These materials have been gaining increasing interest as photocatalysts, although their photocatalytic performance has been restricted due to moderate oxidation ability and fast charge carrier recombination rate. To address these issues, the researchers engineered carbon-vacant CN (FCN) by regulating carbon vacancies (Cv) with formalin dosage. The optimal FCN catalyst exhibited complete TC degradation within 60 minutes with a synergy index of 1.4, which is approximately 2.6 times higher than pristine CN.
Emerging pollutants, such as antibiotics discharged from pharmaceutical companies, have detrimental effects on living organisms and can cause drug resistance through gene transmission. The removal of TC from water requires efficient and sustainable strategies. A detailed understanding of the synergistic effects of the defect and self-doped CN in sonophotocatalytic degradation could pave the way for the destruction of various recalcitrant pollutants in an aqueous environment.
Collaborations
- Ms Mani Preeyanghaa, Department of Physics and Nanotechnology, SRM Institute of Science and Technology, Kattankulathur, Chennai.
- Prof. Bernaurdshaw Neppolian, Department of Physics and Nanotechnology, SRM Institute of Science and Technology, Kattankulathur, Chennai.
Overall, the research presents exciting possibilities for future projects in the field of sonophotocatalytic degradation and provides a significant contribution to the scientific community’s understanding of controllable defects in CN materials.
Continue reading →