Recent News
- Revolutionising LED Lighting: Paper Published in IEEE Transactions on Industry Applications March 12, 2024
 In a significant academic accomplishment, Dr Ramanjaneya Reddy, Assistant Professor in the Department of Electrical and Electronics Engineering, along with UG students Ms Mehataj Syed and Mr Busam Gopichand, have recently published a groundbreaking paper titled “A Three Leg Asymmetrical Voltage Resonant Converter with Independent Dimming Control for Multiple Load LED Lighting Applications” in the esteemed Q1 journal IEEE Transactions on Industry Applications. The journal boasts an impressive impact factor of 4.4, further underscoring the importance of this research contribution.
In a significant academic accomplishment, Dr Ramanjaneya Reddy, Assistant Professor in the Department of Electrical and Electronics Engineering, along with UG students Ms Mehataj Syed and Mr Busam Gopichand, have recently published a groundbreaking paper titled “A Three Leg Asymmetrical Voltage Resonant Converter with Independent Dimming Control for Multiple Load LED Lighting Applications” in the esteemed Q1 journal IEEE Transactions on Industry Applications. The journal boasts an impressive impact factor of 4.4, further underscoring the importance of this research contribution.The paper delves into the development of a novel Three Leg Asymmetrical Voltage Resonant Converter that offers independent dimming control for multiple load LED lighting applications. This innovation holds great promise for enhancing the efficiency and versatility of LED lighting systems, paving the way for more sustainable and adaptable lighting solutions in various industrial applications.
Dr Ramanjaneya Reddy’s leadership and the collaborative efforts of Ms Mehataj Syed and Mr Busam Gopichand have culminated in this significant publication, which not only adds to the body of knowledge in the field but also showcases the talent and dedication of the researchers at the department.
This achievement highlights the commitment to excellence and innovation within the Department of Electrical and Electronics Engineering, positioning it as a hub for cutting-edge research and academic prowess. The impact of this research is expected to reverberate across the industry, contributing to advancements in LED lighting technology and its applications.
The publication of this paper underscores the quality and rigour of the research solidifying their reputation as leaders in the field. This accomplishment is a testament to the department’s commitment to pushing boundaries and making meaningful contributions to the field of electrical engineering.
Congratulations to Dr Ramanjaneya Reddy, Ms Mehataj Syed, and Mr Busam Gopichand on this remarkable achievement, and we look forward to seeing the continued impact of their research in the field.
Abstract
This work proposes a three-leg asymmetrical voltage resonant converter for multiple load Light Emitting Diode (LED) lighting applications. The proposed converter is developed with a common leg-1 for both load-1 and load-2. The load-1 is powered from asymmetrical voltage between leg-1 and leg-2. Similarly, load-2 is powered from asymmetrical voltage between leg-1 and leg-3. The proposed circuit provides the following major contributions: (1) Independent dimming control of LED loads; (2) Zero Voltage Switching (ZVS) of all power switches; (3) High efficiency; and (4) Asymmetrical voltage regulation. To achieve independent dimming control, the voltages between legs are made zero by dimming leg-2 and leg-3 independently. Two resonant circuits are connected in the proposed circuit. Owing to this all the power switches operate with ZVS, which reduces the switching losses. Further, two LED lamps are connected in series with battery sources to supply the threshold voltage to lamps which in turn results in a lower power processing of the converter.
Explanation of Research in Layperson’s Terms
This work proposes a three-leg asymmetrical voltage resonant converter with independent dimming control for multiple load LED lighting applications. The proposed converter drives multiple loads independently with a dimming feature. The converter is developed with leg-1 is common for both LED loads. The major contributions of the proposed LED driver are independent dimming control, asymmetrical voltage regulation, zero voltage switching of all the power switches, and high efficiency. The threshold voltage of LED loads is supplied by batteries connected in series with LED loads, which will help in lower power processing of the proposed converter. Further, due to soft switching technology implemented in this converter, it reduces the losses in the system considerably increasing efficiency.
Title of Research Paper in the Citation Format
A Three Leg Asymmetrical Voltage Resonant Converter with Independent Dimming Control for Multiple Load LED Lighting Applications.
Citation: Ramanjaneya Reddy Udumula, et. al, “A Three Leg Asymmetrical Voltage Resonant Converter with Independent Dimming Control for Multiple Load LED Lighting Applications,” IEEE Transactions on Industry Applications, Feb 2024. doi: 10.1109/TIA.2024.3363676
Practical and Social Implementation of Research
To achieve effective and efficient use of energy resources under the sustainable development goals, Light Emitting Diodes (LEDs) have emerged as a global lighting industry solution. Over the conventional lighting sources such as incandescent lamps, fluorescent lamps, and high intensity discharge lamps, LEDs are i) more efficient, ii) eco-friendly due to absence of toxic gases, iii) have longer life span up to one lakh year, iv) high luminous intensity and v) good colour rendering index. LED’s requires low voltage direct current supply and the V-I characteristics of LEDs which is like Shockley diode represents the exponential growth of current over a small voltage variation which may damage the LED or effects the illumination. Hence, an LED driver is necessary in an LED system to supply LEDs with constant current. DC fed LED drivers are more reliable due to absence of AC-DC conversion stage and power factor correction stage which are crucial in AC fed LED drivers. Therefore, DC fed LED drivers are paid more attention in recent times in the majority of battery-powered/solar-powered applications. Given its features of high power, exceptional efficiency, cost-effectiveness, and flicker-free operation, this innovation is well-suited for streetlight/stadium lighting applications.
Collaborations
Dr. Kasi Ramakrishna Reddy, Assistant Professor
Department of Electrical and Electronics Engineering, Vasavi College of Engineering, HyderabadFuture Research Plans
The future work is on PV/battery fed LED driver topologies suitable for streetlighting/stadium lighting applications with low component count, high efficiency, reduced device stress, and flicker free lighting system
Continue reading → - Advances in Electric Vehicle Technology: A Study on Bi-Directional Converters March 12, 2024
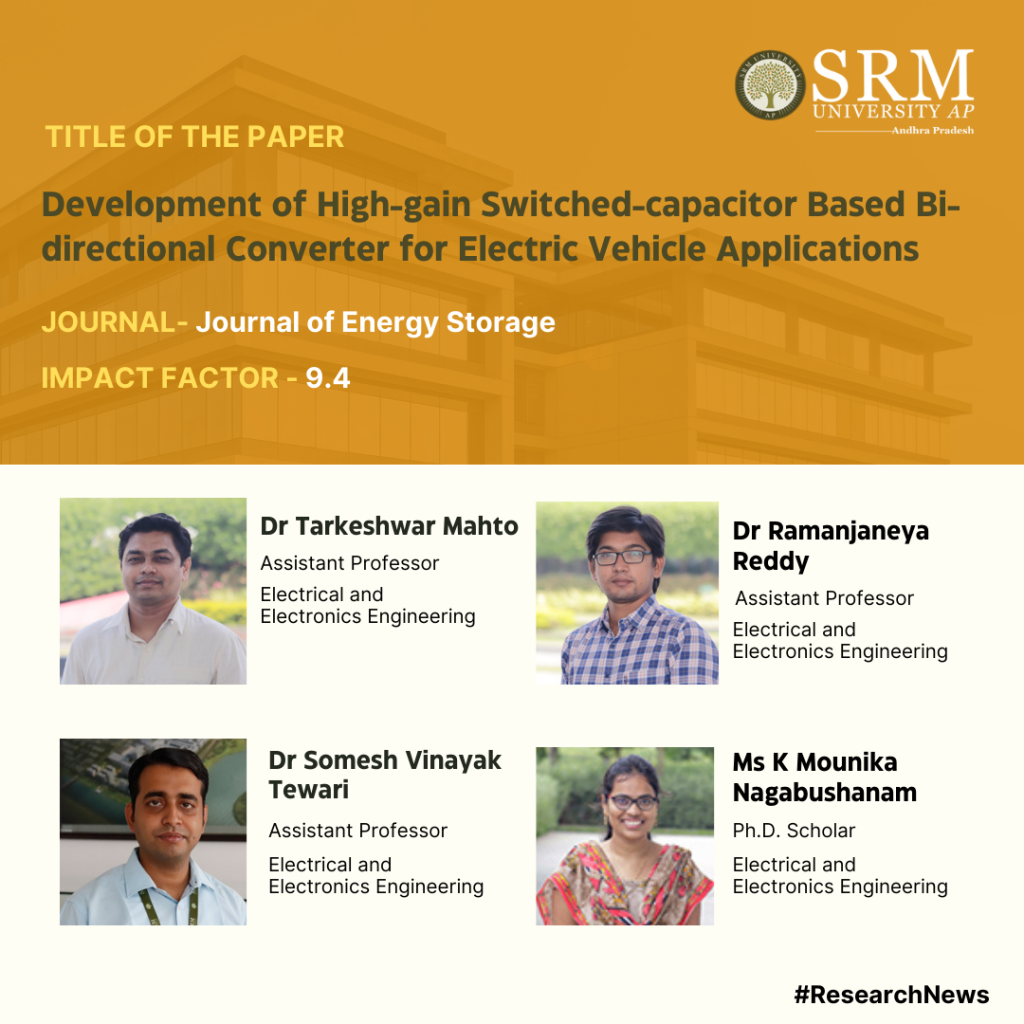
Electric Vehicles are in vogue today, thanks to the heightened environmental concerns, greater availability of models, increased cost competitiveness and improved vehicle ranges. To contribute to the growing field of electric vehicle technology, Assistant Professors, Dr Tarkeshwar Mahto, Dr Somesh Vinayak Tewari and Dr Ramanjaneya Reddy from the Department of Electrical and Electronics Engineering at SRM University-AP along with the research scholar, Ms K Mounika Nagabushanam, conducted a study and published a research paper titled “Development of High-Gain Switched-Capacitor Based Bi-Directional Converter for Electric Vehicle Applications.” The team’s research focuses on creating a bi-directional DC-DC converter that enables power flow from the battery to the motor and vice versa while maintaining necessary voltage gains and ensuring improved efficiency and low cost.
Abstract
High efficiency, high voltage transfer ratio (VTR), and low input ripple current are required in any bidirectional DC-DC converter (BDC) that plays a major role in interfacing batteries in applications like DC microgrids and electric vehicles (EVs). To meet these requirements, a switched capacitor-based BDC is proposed to interface the battery with a propulsion system via a DC Link. It has a simple circuit with only a set of switching operations, High VTR, and lesser ripple current on the low voltage (LV) side, which are advantages of the proposed High Gain Switched-Capacitor Bi-directional DC-DC Converter (SC-BDC), making it appropriate for use in EVs. The steady-state analysis, design consideration of passive components, loss and efficiency analysis are presented. Finally, the proposed High Gain SC-BDC is compared with a few of the existing BDCs in the literature. The feasibility of the converter was demonstrated by simulating a 200 W converter and validating results produced in a MATLAB environment.
Practical implementation of your research or the social implications associated with it.
The developed converter can be used in Electric Vehicle for integration of battery to traction motor.
Collaborations.
1. Majed A. Alotaibi, Department of Electrical Engineering, College of Engineering, King Saud University, 11421, Saudi Arabia.
2. Hasmat Malik, Department of Electrical Power Engineering, Faculty of Electrical Engineering, University Technology Malaysia (UTM), Johor Bahru 81310, Malaysia.
3. Fausto Pedro García Márquez, Ingenium Research Group, Universidad Castilla-La Mancha, 13071 Ciudad Real, Spain.
As part of their future research plans the team plans of working on noise reduction methods that are brought on by regeneration action and to incorporate various control techniques to keep the DC link voltage of the propulsion system constant.
We wish the team all success in their future endevours!
Continue reading →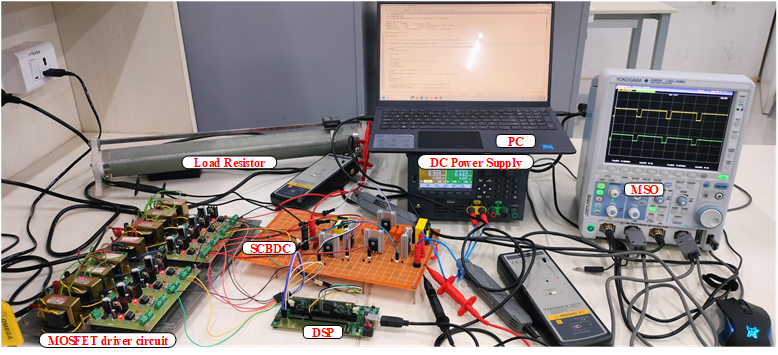
- Elected as General Secretary of ACDOS NMO-IFAC July 11, 2023

The Department of Electrical and Electronics Engineering is glad to announce that Dr Tousif Khan, Associate Professor and HOD, has been selected as the General Secretary of the Prestigious Automatic Control and Dynamic Optimization Society (ACDOS), National Member Organisation of the International Federation of Automatic Control (IFAC), at the Governing Council meeting held on June 22, 2023.
Automatic Control & Dynamic Optimization Society (ACDOS) was established in 2011 with the noble objective to promote automatic control and dynamic optimization discipline in academia and industry across India. The society aims to host international conferences and technical workshops regularly in order to promote close interaction between industry and academia. The society also participates in curriculum development for graduate and undergraduate studies and facilitates productive research in this field. The society also volunteers to honour eminent persons who excelled in this field in industry and academic circles.
Congratulations to Dr Tousif for this remarkable accomplishment and for further contributing to the university’s rising reputation among national and international frontiers!
Continue reading → - EEE students venture into Entrepreneurship June 6, 2023

HatchLab Research Centre, SRM University-AP aims at facilitating a conducive atmosphere where all types of businesses can grow and prosper especially in a socially backward place. Hatchlab has helped in developing multiple projects, but here’s a unique venture by fourth year
Electrical and Electronics Engineering students, Gopichand and Avinash.Whilst the rest of their batch mates are awaiting lucrative offers from top-tech companies, this duo has decided to venture into Entrepreneurship. Gopichand and Avinash, despite societal pressure, have decided to live their dreams and co-founded Virxon Private Limited. These final year engineering students have developed an AI-based digital platform that would enable schools to post job openings for teachers, along with fully automated ERP and learning solutions for students. After surveying around 400+ schools. Virxon found that, there is a huge gap in the demand and supply which can be automated through AI tools and provide a complete solution which is missing in the market right now.
Thrilled about their decision of swimming against the tide to choose a rather difficult path, these entrepreneur duo said -“It may appear that we might be slogging for 18 hours, and stay awake till 2 am in the morning, balancing our studies and our aspirations, but that is not the case. Our dreams keep us awake and our goals keep us going. We are definitely going to make a difference in society.”
Currently, the students are being mentored on the business model and the marketing strategies by Mr. Jayaprakash Narayan, from HatchLab Research Centre, SRM University- AP.
Continue reading → - Agricultural Utility Vehicle: Patent Granted to Inventors from the Department of EEE April 19, 2023
 Conventional agricultural utility vehicles used for crop cultivation involve complex operations such as ploughing and seeding, require trained personnel, and are expensive and not affordable to many farmers, especially in developing countries. Thus, there is a need for an agricultural utility vehicle for carrying out crop cultivation activities that alleviate the drawbacks of conventional practices.
Conventional agricultural utility vehicles used for crop cultivation involve complex operations such as ploughing and seeding, require trained personnel, and are expensive and not affordable to many farmers, especially in developing countries. Thus, there is a need for an agricultural utility vehicle for carrying out crop cultivation activities that alleviate the drawbacks of conventional practices.Researchers at the Department of Electrical and Electronics Engineering have been granted a patent for an invention entitled An Agricultural Utility Vehicle for Crop Cultivation Activities (Application number 202241051059). Assistant Professor Dr Somesh Vinayak Tewari and his students Gundrevula Sisir Srivastav, Kolisetty Jayanth, Tempalli Pallavi Sri, and Jayana Keerthi Tanvita have accomplished this milestone through their dedicated research.
Abstract
The present disclosure discloses an agricultural utility vehicle (1000) for carrying out crop cultivation activities comprising a framed structure (200) having wheels configured to be driven in an open plot of land. An agricultural implement (400) is configured to be attached to the vehicle. An electric drive system (100) is configured to drive the framed structure, and a battery (300) is coupled to the electric drive system to provide power.
Continue reading →