Recent News
- Engineering the art of discovering similar song patterns June 22, 2022
The power of merging art with science is beyond our imagination. This amalgamation can pull off things that may seem insurmountable without the assistance of the other. Professor Hiren Deva Sarma, Guest faculty of the Department of Computer Science and Engineering, has developed a computational technique to find the similarity between the given songs in a pool. His paper titled An Approach to Discover Similar Musical Patterns has been published in IEEE ACCESS, a Q1 journal with an impact factor of 3.36.
Abstract
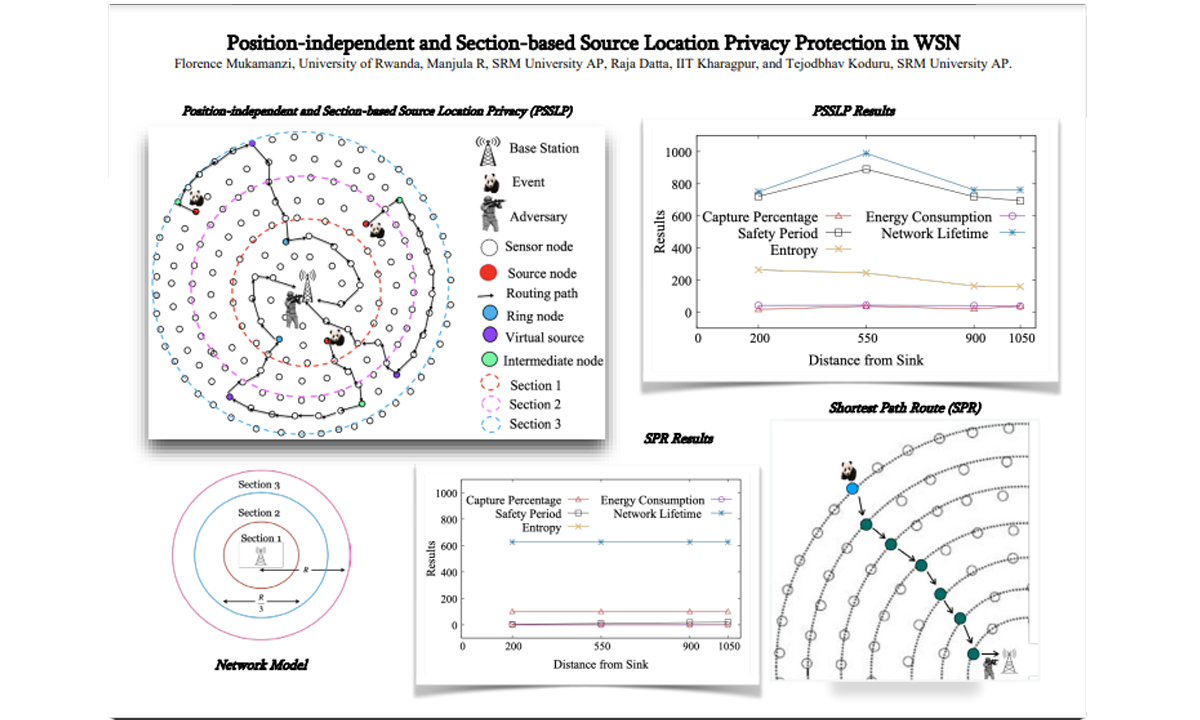
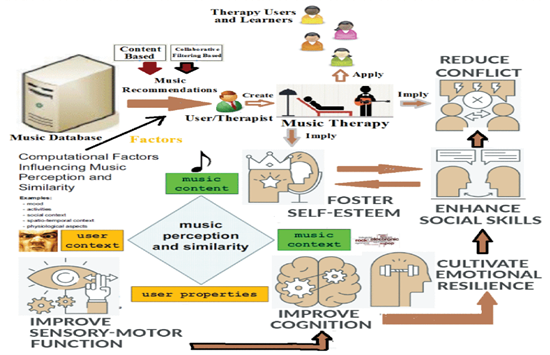 An algorithm has been developed to find the similarity between given songs. The song pattern similarity has been determined by knowing the note structures and the fundamental frequencies of each note of the two songs under consideration. The statistical concept, Correlation of Coefficient, is used in this work. The correlation of Coefficient is determined by applying the 16 Note-Measure Method. If the Correlation of Coefficient is near 1, it indicates that the patterns of the two songs under consideration are similar. Otherwise, there exists a certain percentage of similarity only. This basic principle is used in a set of Indian Classical Music (ICM) based songs. The proposed algorithm can determine the similarity between songs, so alternative songs in place of some well-known songs can be identified in terms of the embedded raga patterns. A digital music library has been constructed as a part of this work. The library consists of different songs, their raga name, and their corresponding healing capabilities in terms of music therapy. The proposed work may find application in the area of music therapy. Music therapy is an area of research that has been explored significantly in recent times. This work can also be exploited for developing an intelligent multimedia tool applicable in the healthcare domain. A multimedia-based mobile app has been developed encapsulating the abovementioned idea that can recommend alternative or similar songs to the existing ICM-based songs. This mobile app-based music recommendation system may be used for different purposes, including entertainment and healthcare. As a result of the applications of the proposed algorithm, similar songs in terms of raga patterns can be discovered from within the pool of a set of songs. A Music Recommendation System built on this algorithm can retrieve an alternative song from within the pool of songs as a replacement to a well-known song, which otherwise may be used for particular music therapy. Results are reported and analysed thoroughly. The future scope of the work is outlined.
An algorithm has been developed to find the similarity between given songs. The song pattern similarity has been determined by knowing the note structures and the fundamental frequencies of each note of the two songs under consideration. The statistical concept, Correlation of Coefficient, is used in this work. The correlation of Coefficient is determined by applying the 16 Note-Measure Method. If the Correlation of Coefficient is near 1, it indicates that the patterns of the two songs under consideration are similar. Otherwise, there exists a certain percentage of similarity only. This basic principle is used in a set of Indian Classical Music (ICM) based songs. The proposed algorithm can determine the similarity between songs, so alternative songs in place of some well-known songs can be identified in terms of the embedded raga patterns. A digital music library has been constructed as a part of this work. The library consists of different songs, their raga name, and their corresponding healing capabilities in terms of music therapy. The proposed work may find application in the area of music therapy. Music therapy is an area of research that has been explored significantly in recent times. This work can also be exploited for developing an intelligent multimedia tool applicable in the healthcare domain. A multimedia-based mobile app has been developed encapsulating the abovementioned idea that can recommend alternative or similar songs to the existing ICM-based songs. This mobile app-based music recommendation system may be used for different purposes, including entertainment and healthcare. As a result of the applications of the proposed algorithm, similar songs in terms of raga patterns can be discovered from within the pool of a set of songs. A Music Recommendation System built on this algorithm can retrieve an alternative song from within the pool of songs as a replacement to a well-known song, which otherwise may be used for particular music therapy. Results are reported and analysed thoroughly. The future scope of the work is outlined.Explanation of the research
A computational technique has been developed to identify a particular song similar to another in terms of its embedded raga pattern. Indian Classical Music (ICM) based songs are considered in this work. As a result of the application of the proposed technique, it is possible to identify similar songs in terms of their raga patterns from within a pool of songs. Subsequently, a similar alternative song can be recommended for different applications, including music therapy. If we consider music therapy, an alternative medicine (note: here, medicine is the song) is possible to recommend due to the proposed technique. This algorithm will find many applications in the domain of music information retrieval (MIR) and music recommendation systems (MRS).
Practical implementation of the research
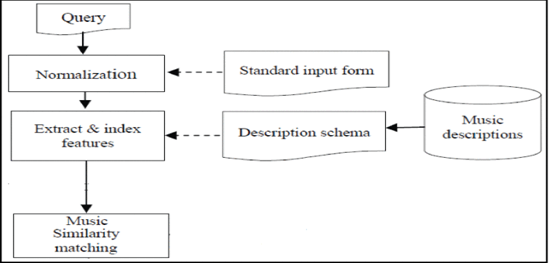 This algorithm may be applied in recommending music in music recommendation systems. Moreover, music information retrieval based on raga patterns can be an important domain where the proposed algorithm may be exploited. Considering the social implications, music therapy has been the intended area of the research; therefore, this algorithm has been developed considering numerous applications of music therapy based on Indian Classical Music. The music therapy community will be benefited from the proposed algorithm.
This algorithm may be applied in recommending music in music recommendation systems. Moreover, music information retrieval based on raga patterns can be an important domain where the proposed algorithm may be exploited. Considering the social implications, music therapy has been the intended area of the research; therefore, this algorithm has been developed considering numerous applications of music therapy based on Indian Classical Music. The music therapy community will be benefited from the proposed algorithm.In this research project, Professor Hiren Deva Sarma has collaborated with; Assistant Professor Sudipta Chakrabarty, Techno India, Salt Lake at the Department of Master of Computer Application; Mr Ruhul Islam, IT Consultant, Cloud Shine Global LLP; and Emil Pricop, Associate Professor in the Department of Automatic Control, Computers and Electronics, Petroleum-Gas University of Ploiesti, Romania.
In the future, the researchers look forward to exploring the music therapy capabilities of Indian Folk Music (IFM) like Kamrupia Lokgeet, Goalparia Lokgeet, and Baul Geet. Understanding the similarity and dissimilarity of the above-mentioned folk songs with Indian Classical Music (ICM) from computational musicology perspectives is another objective of the proposed research work. The researchers also aim to develop Music Recommendation Systems (i.e., applications) considering the songs mentioned above (ICM + IFM) and the different requirements of the users.
Continue reading → - Tackling the menace of cyber poaching June 21, 2022
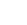
Wireless Sensor Networks (WSNs) and their derivatives such as Internet of Things (IoT) and the Internet of Industrial Things (IIOT) are no longer confined to traditional applications such as smart homes and transportation. It has already marked its presence in Industrial applications and extended even to wildlife conservation. The impending concerns associated with such wireless networks are their privacy and security. One such menace afflicting wildlife is cyber poaching. Taking this into consideration, Dr Manjula R, Assistant Professor, and her student Mr Tejodbhav Koduru, from the Department of Computer Science and Engineering, have published a paper, “Position-independent and Section-based Source Location Privacy Protection in WSN” in the journal, ‘IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics’ having an Impact Factor of 10.215. The article is published in collaboration with Ms Florence Mukamanzi from the University of Rwanda, Rwanda, Africa and Prof Raja Datta from IIT Kharagpur, West Bengal, India.
The sensors collect data about these endangered animals and report it to the central controller which is connected to the Internet. Over the period, the hunters have also evolved and are equipped with smart devices that help them to easily locate the animal with minimal effort. In the simplest form, the attacker or the hunter just eavesdrops on the communication links to know the message’s origin and backtrack to the source of information. Once the source of information i.e., the location is identified then the endangered animal is captured. To overcome such backtracking issues, their work aims at delaying the information disclosure to the attacker through traffic obfuscation.
Although it may not act as an ultimate solution, the research work focuses on contextual privacy, unlike traditional content privacy. The attacker collects only contextual information such as packet rate, traffic intensities, routing paths, time correlations etc., to determine the source of information. The work focuses on mitigating traffic correlation i.e., hop-by-hop backtrack attacks and protecting the assets that are monitored using WSNs. The performance metrics include safety period and network lifetime amongst other metrics. The proposed random-walk-based routing solution achieves an improved safety period and network lifetime compared to the existing schemes. The work was simulated using a custom-designed simulation tool and was validated with the numerical results obtained using mathematical models.
The proposed solutions could be seamlessly used in monitoring endangered animals such as rhinoceros or in military applications to track soldiers. In addition, the routing algorithm could also be used in delaying tolerant networks to improve the efficiency and lifetime of the network, in designing the random trajectories of bio-nano bots for intrabody monitoring etc. Their future research plan includes developing improved source location privacy preservation techniques for terrestrial and underwater wireless sensor networks using the benefits of Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning. In addition, they also aims at the development of data collection and routing protocols for intrabody nanonetwork operating at tera hertz frequencies— next-generation networks, envisioned networks.