Recent News
- An Inventive Navigation System for the Visually Impaired May 15, 2024

The Department of Computer Science and Engineering is proud to announce that the patent titled “A System and a Method for Assisting Visually Impaired Individuals” has been published by Dr Subhankar Ghatak and Dr Aurobindo Behera, Asst Professors, along with UG students, Mr Samah Maaheen Sayyad, Mr Chinneboena Venkat Tharun, and Ms Rishitha Chowdary Gunnam. Their patent introduces a smart solution to help visually impaired people navigate busy streets more safely. The research team uses cloud technology to turn this visual information into helpful vocal instructions that the users can hear through their mobile phones. These instructions describe things like traffic signals, crosswalks, and obstacles, making it easier for them to move around independently, making way for an inclusive society.
Abstract
This patent proposes a novel solution to ease navigation for visually impaired individuals. It integrates cloud technology, computer vision algorithms, and Deep Learning Algorithms to convert real-time visual data into vocal cues delivered through a mobile app. The system employs wearable cameras to capture visual information, processes it on the cloud, and delivers relevant auditory prompts to aid navigation, enhancing spatial awareness and safety for visually impaired users.
Practical implementation/Social implications of the research
The practical implementation of the research involves several key components.
- Developing or optimising wearable camera devices that are comfortable and subtle for visually impaired individuals. These cameras should be capable of capturing high-quality real-time visual data.
- A robust cloud infrastructure is required to process this data quickly and efficiently using advanced computer vision algorithms and deep learning algorithms.
- Design and develop a user-friendly mobile application that delivers processed visual information as vocal cues in real-time. This application should be intuitive, customisable, and accessible to visually impaired users.
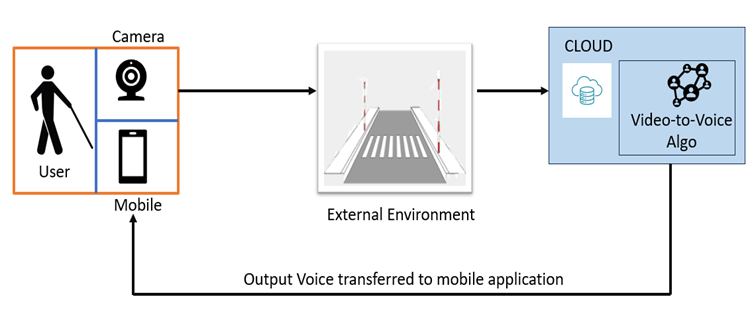
Fig.1: Schematic representation of the proposal
The social implications of implementing this research are significant. We can greatly enhance their independence and quality of life by providing visually impaired individuals with a reliable and efficient navigation aid. Navigating city environments can be challenging and hazardous for the visually impaired, leading to increased dependency and reduced mobility. The research aims to mitigate these challenges by empowering users to navigate confidently and autonomously. This fosters a more inclusive society where individuals with visual impairments can participate actively in urban mobility, employment, and social activities.
In the future, the research cohort plans to further enhance and refine technology to better serve the needs of visually impaired individuals. This includes improving the accuracy and reliability of object recognition and scene understanding algorithms to provide more detailed and contextually relevant vocal cues. Additionally, they aim to explore novel sensor technologies and integration methods to expand the capabilities of our system, such as incorporating haptic feedback for enhanced spatial awareness. Furthermore, we intend to conduct extensive user testing and feedback sessions to iteratively improve the usability and effectiveness of our solution. This user-centric approach will ensure that our technology meets the diverse needs and preferences of visually impaired users in various real-world scenarios.
Moreover, the team is committed to collaborating with stakeholders, including advocacy groups, healthcare professionals, and technology companies, to promote the adoption and dissemination of this technology on a larger scale. By fostering partnerships and engaging with the community, they can maximise the positive impact of their research on the lives of visually impaired individuals worldwide.
Continue reading → - Dr Manjula R and Students Publish Book Chapter on Machine Learning in 6G Networks May 7, 2024
 In an exciting development, Dr Manjula R, Assistant Professor in the Department of Computer Science and Engineering, along with B.Tech. students Mr Adi Vishnu Avula, Mr Jawad Khan, Mr Chiranjeevi Thota, and Ms Venkata Kavyanjali Munipalle, have authored a book chapter titled “Machine Learning Approach to Determine and Predict the Scattering Coefficients of Myocardium Tissue in the NIR Band for In-Vivo Communications – 6G Network in book name “Edge-Enabled 6G Networking: Foundations, Technologies, and Applications”.
In an exciting development, Dr Manjula R, Assistant Professor in the Department of Computer Science and Engineering, along with B.Tech. students Mr Adi Vishnu Avula, Mr Jawad Khan, Mr Chiranjeevi Thota, and Ms Venkata Kavyanjali Munipalle, have authored a book chapter titled “Machine Learning Approach to Determine and Predict the Scattering Coefficients of Myocardium Tissue in the NIR Band for In-Vivo Communications – 6G Network in book name “Edge-Enabled 6G Networking: Foundations, Technologies, and Applications”.This achievement highlights the innovative research and collaboration showcase the dedication and expertise of both faculty and students in the field of computer science and engineering. The book chapter explores the cutting-edge advancements in 6G networking and its potential applications, shedding light on the future of communication technologies.
We congratulate Dr Manjula R and the team of talented students on this significant accomplishment and look forward to seeing more groundbreaking research from them in the future. Stay tuned for more updates on their work and achievements.
Abstract
The accurate calculation of the scattering coefficient of biological tissues (myocardium) is critical for estimating the path losses in prospective 6-G in-vivo Wireless Nano sensor networks (i-WNSN). This research explores machine learning’s potential to promote non-invasive procedures and improve in-vivo diagnostic system’s accuracy while determining myocardium’s scattering properties in the Near Infrared (NIR) frequency. We begin by presenting the theoretical model used to estimate and calculate scattering coefficients in the NIR region of the EM spectrum. We then provide numerical simulation results using the scattering coefficient model, followed by machine learning models such as Linear Regression, Polynomial Regression, Gradient Boost and ANN (Artificial Neural Network) to estimate the scattering coefficients in the wavelength range 600-900 nm.
We next contrast the values provided by the analytical model with those predicted via machine learning models. In addition, we also investigate the potential of machine learning models in producing new data sets using data expansion techniques to forecast the scattering coefficient values of the unavailable data sets. Our inference is that machine learning models are able to estimate the scattering coefficients with very high accuracy with gradient boosting performing better than other three models. However, when it comes to the prediction of the extrapolated data, ANN is performing better than other three models.
Keywords: 6G, In-vivo, Dielectric Constant, Nano Networks, Scattering Coefficient, Machine Learning.
Significance of Book Chapter
The human heart is a vital organ of the cardiovascular system and is very crucial for any living being. However, this organ is prone to several diseases—Cardiovascular Disease (CVD)—an umbrella term. CVDs are the set of the heart diseases that comprises heart attack, cardiac arrest, arrhythmias, cardiomyopathy, atherosclerosis to name a few. CVD alone account for most of the deaths across the globe and is estimated reach 23.3 million deaths due to CVD by 2030. Early detection and diagnosis of CVD is the ultimate solution to mitigate these death rates. Current diagnostic tests include, however not the exhaustive list, ECG, blood test, cardiac x-ray, angiogram.
The limitations of these techniques include bulkiness of the equipment, cost, tests are suggested only when things are in critical stage. To alleviate these issues, we are now blessed with on-body or wearable devices such as smart watches that collect timely information about the cardiac health parameters and notify the user in a real-time. However, these smart watches do not have the capability to directly detect the presence of plaque in the arteries that leads to atherosclerosis. These devices have the capability to track certain health parameters such as heart rate, blood pressure, other activity levels, any deviation in the measured values of these parameters from the normal values might give an indication of cardiac health issues. This requires a formal diagnostics test such as cardiac catheterization or cardiac x-ray leading to the original problem.
Therefore, in this work we aim to mitigate these issues by proposing the usage of prospective medical grade nanorobots—called nanosurgeons, that can provide real-time live information on the health condition of the internal body. Particularly, our work assumes that these tiny nanobots are injected into the cardiovascular system that keep circulating along with the blood to gather health information. Such nanosized robots are typically expected to work in the terahertz band owing to their size. At such high frequency, the terahertz signals are prone to high path losses due to spreading, absorption and scattering of the signal during propagation. Our work aims at understanding these losses, especially the scattering losses, of the terahertz signal in the NIR band (600-900 nm) using the existing models, analytically. Further, to understand the strength of machine learning in predicting these scattering losses, we also carryout simulation work to estimate and predict the scattering losses using Linear Regression, Polynomial Regression, Gradient Boost and Artificial Neural Network (ANN) models.
Our preliminary investigation suggests scattering losses are minimal in NIR band and machine learning can be seen as a potential candidate for perdiction of scattering losses using the available experimental data as well as using data augmentation techniques to predict the scattering losses at those frequencies for which either experimental data is not available or can prevent the use of costly equipment to determine these parameters.
Continue reading →