Recent News
- CSE Academic Innovators File Patent for AI-Powered Refrigeration System July 8, 2024
 In a significant development for the field of artificial intelligence and sustainable technologies, Dr Subhankar Ghatak, Dr Aurobindo Behera, Assistant Professor, and Ms Samah Maaheen Sayyad, an undergraduate student from the Department of Computer Science and Engineering, have collectively filed a patent for an “Artificial Intelligence (AI) Enabled Refrigeration System.” The patent, bearing the Application Number 202441036548, has been officially published in the Patent Office Journal, marking a milestone in their academic and research careers.
In a significant development for the field of artificial intelligence and sustainable technologies, Dr Subhankar Ghatak, Dr Aurobindo Behera, Assistant Professor, and Ms Samah Maaheen Sayyad, an undergraduate student from the Department of Computer Science and Engineering, have collectively filed a patent for an “Artificial Intelligence (AI) Enabled Refrigeration System.” The patent, bearing the Application Number 202441036548, has been officially published in the Patent Office Journal, marking a milestone in their academic and research careers.
This innovative refrigeration system promises to enhance efficiency and reduce energy consumption, potentially revolutionising the way we preserve food and other perishables. The team’s dedication to integrating AI into practical applications is a testament to their commitment to advancing technology for the betterment of society. The academic community and industry experts alike are eagerly anticipating further details on the implementation and impact of this patented technology.Abstract
The invention is an advanced smart and AI-enabled refrigerator that seamlessly integrates device and software components. Key features include automatic quantity detection, a reminder system, a spoiler alert system, an inbuilt voice system, an inbuilt barcode scanner, an emotion detection system, and a personalised recipe recommendation system based on user preferences, weather conditions, season, location, and precise quantity measurements.Research in Layperson’s Terms
The invention represents a groundbreaking improvement in traditional refrigerators, providing a new and enriched user experience through AI integration. It addresses food management, user interaction, and personalised recipe recommendations, incorporating user preferences, weather considerations, seasonal variations, location-specific nuances, and accurate quantity measurements.Practical implementation and the social implications associated with it
The practical implementation of the “AN ARTIFICIAL INTELLIGENCE (AI) ENABLED REFRIGERATION SYSTEM ” involves the seamless integration of advanced hardware and sophisticated AI algorithms to create an intelligent and user-friendly refrigerator. The following steps outline the practical implementation:
Hardware Integration:
Sensors: Install advanced sensors, including thermistors for temperature, humidity sensors, barcode scanners, ultrasonic quantity measurement sensors, cameras, spoilage identification sensors, level sensors, defrost sensors, and weight sensors within the refrigerator compartments.
Voice and Emotion Detection Modules: Incorporate a microphone and speaker system for voice interaction and integrate cameras and emotion analysis algorithms for facial recognition and emotion detection.
Connectivity Components: Equip the refrigerator with Wi-Fi or Bluetooth modules to enable seamless data transfer and communication with other smart devices.
Processor and Memory: Utilize a powerful processor and ample memory to support AI algorithms, data processing, and smooth operation.
Display Panel: Implement an LED or touchscreen display for user interaction, providing real-time information and control over the refrigerator’s functionalities.Software Development:
AI Algorithms: Develop and integrate AI algorithms for automatic quantity detection using computer vision, sentiment analysis for emotion detection, and collaborative filtering for personalised recipe recommendations.
Natural Language Processing (NLP): Implement NLP algorithms to enable the inbuilt voice system to understand and respond to user commands effectively.
Image Recognition Software: Utilize image recognition software to accurately read barcodes and analyse visual data from the integrated cameras.
Connectivity Software: Develop software protocols to ensure reliable wireless communication between the refrigerator and other devices or cloud services.
User Interface Software: Design a user-friendly interface for the display panel, allowing users to interact with and manage refrigerator contents easily.Social Implications:
The “AI Enabled Refrigeration System” invention has several profound social implications:1. Reduction in Food Wastage: The automatic quantity detection, reminder system, and spoilage alert system significantly reduce food wastage by ensuring that users are alerted about unused items and potential spoilage. This contributes to more efficient food management and a reduction in household food waste, addressing a critical global issue.
2. Enhanced Food Safety and Health: By providing real-time alerts about food spoilage and precise quantity measurements, the invention ensures that users consume fresh and safe food. This minimizes health risks associated with consuming spoiled food and promotes overall well-being.
3. Personalized Dietary Support: The personalized recipe recommendation system caters to individual dietary preferences and requirements, promoting healthier eating habits. By suggesting recipes based on user preferences, weather conditions, seasonality, and location, the system encourages balanced and nutritious meal planning.
4. Convenience and Efficiency: The inbuilt voice system, emotion detection, and intuitive user interface enhance the convenience and efficiency of managing refrigerator contents. Users can easily access information, receive reminders, and interact with the refrigerator, making food storage and preparation more streamlined.
5. Technological Advancements: The integration of advanced AI technologies in everyday appliances like refrigerators represents a significant step forward in smart home innovation. This can drive further advancements in the field, encouraging the development of more intelligent and interconnected household devices.
6. Environmental Impact: By promoting efficient food management and reducing wastage, the invention indirectly contributes to environmental sustainability. Less food waste translates to lower carbon footprints and reduced strain on food production resources, aligning with global efforts to combat climate change.
Overall, the “AI Enabled Refrigeration System” invention not only offers practical benefits in terms of food management and user convenience but also holds significant social implications by promoting health, reducing waste, and advancing technological innovation in household appliances.
Future Research Plans
Building on the innovative foundation of the “AN ARTIFICIAL INTELLIGENCE (AI) ENABLED REFRIGERATION SYSTEM, ” future research plans involve enhancing the AI algorithms for even greater accuracy in food quantity detection, spoilage prediction and personalised recipe recommendations. This includes exploring more advanced machine learning techniques and incorporating real-time feedback mechanisms to continuously refine the system’s performance. Additionally, research will focus on integrating the refrigerator with broader smart home ecosystems, allowing for seamless interaction with other smart appliances and IoT devices to create a fully connected kitchen experience. Investigations into more sustainable and energy-efficient sensor technologies will also be pursued to further reduce the environmental footprint of the device. Finally, extensive user studies will be conducted to gather feedback and insights, ensuring that the next iterations of the refrigerator are even more aligned with consumer needs and preferences, ultimately driving widespread adoption and maximising the social benefits of this technology.
Pictures Related to the Research
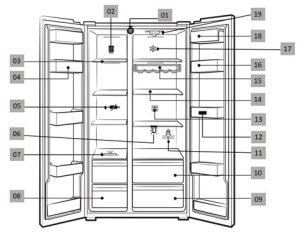
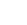
Fig 1: Schematic Arrangement of various Components for adequate operation of the proposed scheme
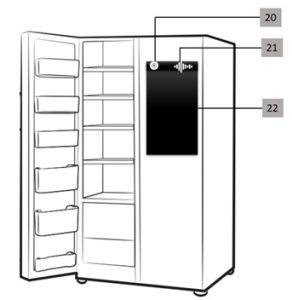
Fig 2: Schematic Arrangement of various Components for user interaction
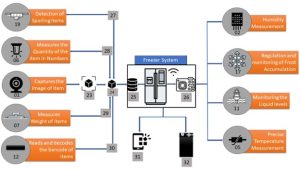
Fig 3: Schematic representation of working of various components in the freezer system
• Pointer Number-27: Spoilage Detection Sensor (19) detects the item that is being spoiled and maps to particular item for alerting the user with the help of the capturing Device (01) and the info associated with that particular item like Expiry date etc.
Continue reading →
• Pointer Number-28: The Ultra Sonic Quantity Measurement Sensor (06) senses the quantity of the ITEM “x” (24), and the camera (01) is used to identify what is ITEM “x” through (23).
• Pointer Number-29: Weight Sensor (07), using newly captured item ITEM “x” (24) by capturing device (01), identifies the weight of that item by subtracting the weight obtained after the addition of that item with the initial holding by the cabinet and attaching the value with corresponding ITEM “x” (24).
• Pointer Number-30: Barcode Scanner (12) scans the Barcode associated with the item and maps the corresponding information with that particular item with the help of the capturing device (01).
• Port Number-31: Mobile Application. - A System for Visually Impaired Navigation June 25, 2024

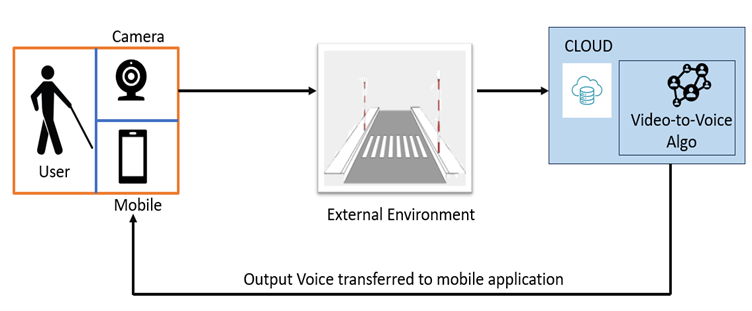
A dedicated team of researchers and professors have developed an innovative patent titled “System and a Method for Assisting Visually Impaired Individuals” that uses cutting-edge technology to significantly improve the navigation experience for visually impaired individuals, fostering greater independence and safety.
The team, comprising Dr Subhankar Ghatak and Dr Aurobindo Behera, Assistant Professors from the Department of Computer Science and Engineering, and students Ms Samah Maaheen Sayyad, Mr Chinneboena Venkat Tharun, and Ms Rishitha Chowdary Gunnam, has designed a system that transforms real-time visual data into vocals via a mobile app. It will utilise wearable cameras, cloud processing, computer vision, and deep learning algorithms. Their solution captures visual information and processes it on the cloud, delivering relevant auditory prompts to users.
Abstract
This patent proposes a novel solution entitled, “System and a method for assisting visually impaired individuals aimed at easing navigation for visually impaired individuals. It integrates cloud technology, computer vision algorithms, and Deep Learning Algorithms to convert real-time visual data into vocal cues delivered through a mobile app. The system
employs wearable cameras to capture visual information, processes it on the cloud, and deliver relevant auditory prompts to aid navigation, enhancing spatial awareness and safety for visually impaired users.Practical implementation/Social implications of the research
The practical implementation of our research involves several key components. Firstly, we need to develop or optimise wearable camera devices that are comfortable and subtle for visually impaired individuals to wear. These cameras should be capable of capturing high-quality real-time visual data. Secondly, we require a robust cloud infrastructure capable of processing this data quickly and efficiently using advanced computer vision algorithms and Deep Learning Algorithms. Lastly, we need to design and develop a user-friendly mobile application that delivers the processed visual information as vocal cues in real-time. This application should be intuitive, customisable, and accessible to visually impaired users.
The social implications of implementing this research are significant. By providing visually impaired individuals with a reliable and efficient navigation aid, we can greatly enhance their independence and quality of life. Navigating city environments can be challenging and hazardous for the visually impaired, leading to increased dependency and reduced mobility. Our solution aims to mitigate these challenges by empowering users to navigate confidently and autonomously. This fosters a more inclusive society where individuals with visual impairments can participate actively in urban mobility, employment, and social activities.
In the future, we plan to further enhance and refine our technology to better serve the needs of visually impaired individuals. This includes improving the accuracy and reliability of object recognition and scene understanding algorithms to provide more detailed and contextually relevant vocal cues. Additionally, we aim to explore novel sensor technologies and integration methods to expand the capabilities of our system, such as incorporating haptic feedback for enhanced spatial awareness.
Furthermore, we intend to conduct extensive user testing and feedback sessions to iteratively improve the usability and effectiveness of our solution. This user-centric approach will ensure that our technology meets the diverse needs and preferences of visually impaired users in various real-world scenarios.
Moreover, we are committed to collaborating with stakeholders, including advocacy groups, healthcare professionals, and technology companies, to promote the adoption and dissemination of our technology on a larger scale. By fostering partnerships and engaging with the community, we can maximize the positive impact of our research on the lives of visually impaired individuals worldwide.
Continue reading →