Recent News
- Revolutionising Energy Harvesting: Dr Banee Banadana Receives Patent for Innovative System April 15, 2024

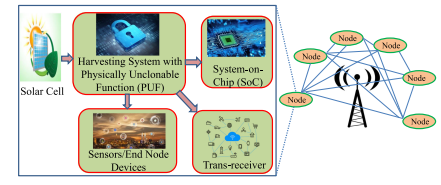
Dr Banee Bandana Das, Assistant Professor in the Department of Computer Science and Engineering, has achieved a remarkable milestone. The invention titled “An Energy Harvesting System for Node Devices and a Method Thereof” has been granted a patent by the Patent Office Journal, under Application Number: 202241066526. This achievement marks a significant leap forward in the realm of energy harvesting systems, promising a brighter and more secure future for IoT applications.
Abstract
The present invention is broadly related to design of secure and Trojan Resilient energy harvesting system (EHS) for IoT end node devices. The objective is to develop a state-of-the-art energy harvesting system which can supply uninterrupted power to the sensors used in IoT. The EHS is self-sustainable. The higher bias voltages are generated on chip. The system is mainly consisting of security module, power conditioning module, Trojan Resilient module, and load controller module. The power failure of the sensors used in IoT may leads to information loss thereby causing catastrophic situations. An uninterrupted power supply is a must for smooth functioning of the devices in IoT. This invention caters secure power requirements with security issues of IoT end node devices.
Practical Implementation:
The IoT end node devices needs 24*7 power supply and are very sensitive to attacks made by adversaries before and after fabrication. This invention takes care of the power requirement of end node devices with green energy and secure the EHS-IC from adversaries and attacks and therefore can be used by individuals, as powering sensors at remote locations and as part of smart agriculture.
Future research plans:
Design more secure and reliable design for making a IoT smart node smarter and self-Sustainable. Exploring more circuit level techniques and find new way to design more power efficient designs.
Continue reading → - April 15, 2024
Dr Banee Bandana Das, Assistant Professor in the Department of Computer Science and Engineering, has achieved a remarkable milestone. The invention titled “An Energy Harvesting System for Node Devices and a Method Thereof” has been granted a patent by the Patent Office Journal, under Application Number: 202241066526. This achievement marks a significant leap forward in the realm of energy harvesting systems, promising a brighter and more secure future for IoT applications.
Abstract
The present invention is broadly related to design of secure and Trojan Resilient energy harvesting system (EHS) for IoT end node devices. The objective is to develop a state-of-the-art energy harvesting system which can supply uninterrupted power to the sensors used in IoT. The EHS is self-sustainable. The higher bias voltages are generated on chip. The system is mainly consisting of security module, power conditioning module, Trojan Resilient module, and load controller module. The power failure of the sensors used in IoT may leads to information loss thereby causing catastrophic situations. An uninterrupted power supply is a must for smooth functioning of the devices in IoT. This invention caters secure power requirements with security issues of IoT end node devices.
Practical Implementation:
The IoT end node devices needs 24*7 power supply and are very sensitive to attacks made by adversaries before and after fabrication. This invention takes care of the power requirement of end node devices with green energy and secure the EHS-IC from adversaries and attacks and therefore can be used by individuals, as powering sensors at remote locations and as part of smart agriculture.
Future research plans:
Design more secure and reliable design for making an IoT smart node smarter and self-Sustainable. Exploring more circuit level techniques and find new way to design more power efficient designs.
Continue reading →