Recent News
- Introducing decentralized security system using blockchain technology March 10, 2022
The Department of Computer Science and Engineering is delighted to announce that Dr Rajiv Senapati and his research group; Abhiram Chakravadhanula, Jaswanth Kolisetty, Karthik Samudrala and Bharat Preetham have published a research article titled “A Novel Decentralized Security Architecture for the Centralized Storage System in Hadoop using Blockchain Technology” in the Scopus indexed IEEE 7th I2CT (The premier conference for the latest discoveries in Convergence in Technology in Asia Pacific).
Over the past decades, the Big Data ecosystem is experiencing a humungous explosion in the generation and exchange of information. Trading such delicate information can serve as a profitable knowledge resource in the present economy. However, serious concerns have been raised about the security and assurance of delicate data as the conventional safety architecture in centralized storage systems does not meet its nuanced requirements. Blockchain technology offers a promising solution for big data protection due to its decentralized nature. Through this research article, Dr Rajiv Senapati and his students intend to introduce a decentralized security architecture in centralized storage systems such as Hadoop to address its existing vulnerabilities.
Abstract of the Research
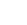
Big Data is huge in volume, diverse in information, and growing at flourishing rates. The major distributed file systems in the current market in Big Data Analysis include Apache Hadoop, Storm, Cassandra, Flink, Cloudera, and many more. Hadoop is an open-source framework divided into Hadoop Distributed File System (HDFS) and Map-Reduce. Hadoop plays a leading role in storing and processing Big Data in contemporary society as it is cost-effective and can manage large volumes of data in low-cost commodity hardware. HDFS is a type of Data Warehouse which is scalable and has fast access to information.
Metadata is the information about the data, such as which block is storing on what datanode, how many replications that block has, and on which datanodes those replications reside. In HDFS, this metadata is stored at a fixed place in namenode, and attackers can access the metadata and modify it without notice. Also, metadata is mutable, which means the attacker can erase his presence easily.
In this paper, to resolve this issue, we have provided a mechanism using blockchain technology that follows a decentralized architecture against the centralized architecture followed by HDFS. Hyperledger Fabric (HLF) is the blockchain proposed to be effective and trusted for such a purpose. HLF is a private blockchain with a distributed immutable ledger. The metadata will be stored in the ledger. If an attacker tries to modify the data, he cannot erase his presence as the ledger is immutable, unlike HDFS. Further, the work proposed in this paper can be extended in real-time HDFS with a secure ledger and multiple nodes.
- Security Framework using Blockchain Technology February 24, 2022
The Department of Computer Science Engineering is proud to announce that Dr Sriramulu Bojjagani has published a paper titled “Blockchain-Based Security Framework for Sharing Digital Images using Reversible Data Hiding and Encryption” in the journal Multimedia Tools and Applications (MTAP) having an impact factor of 2.757.
The paper is published in collaboration with D.R Denslin Brabin from the Department of Computer Science and Engineering, DMI College of Engineering, Tamil Nadu and Christo Ananth from the Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering, St. Mother Theresa Engineering College, Tamil Nadu.
Abstract of the Research
Security is an important issue in current and next-generation networks. Blockchain will be an appropriate technology for securely sharing information in next-generation networks. Digital images are the prime medium attacked by cyber attackers. In this paper, a blockchain-based security framework is proposed for sharing digital images in a multi-user environment. The proposed framework uses reversible data hiding and encryption as component techniques. A novel high-capacity reversible data hiding scheme is also proposed to protect digital images. Reversible data hiding in combination with encryption protects the confidentiality, integrity and authentication of digital images. In the proposed technique, the digital image is compressed first to create room for data hiding, then the user signature is embedded; afterwards, the whole image is encrypted. For compression, JPEG lossy compression is used to create high capacity. For encryption, any symmetric block cipher or stream cipher can be used. Experimental results show that the proposed blockchain-based framework provides high security and the proposed reversible data hiding scheme provides high capacity and image quality.
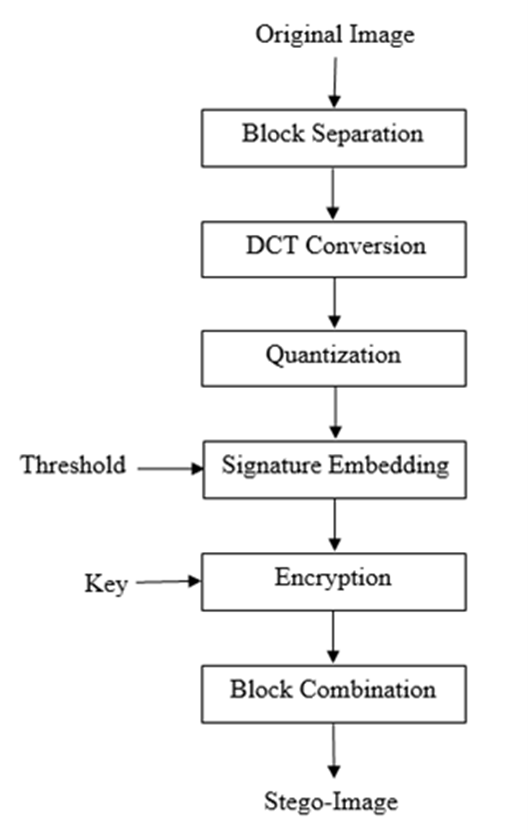
Fig 1: The process of encoding during reversible data hiding
Dr Sriramulu Bojjagani also intends to work on the development of block-chain based solutions to intelligent transport systems and on addressing the challenges of security issues involved in connected and autonomous vehicles.