- Effects of Covid-19 on mental health March 19, 2022
The Department of Economics is delighted to announce that Dr Ghanshyam Kumar Pandey and his research group; Sheeba Moghal, Rakshit Barodia, and William Carey have published an article titled “COVID-19 and its effects on the mental health of people living in urban slums in India” in the ‘Journal of Information and Knowledge Management’, having an Impact Factor of 1.3.
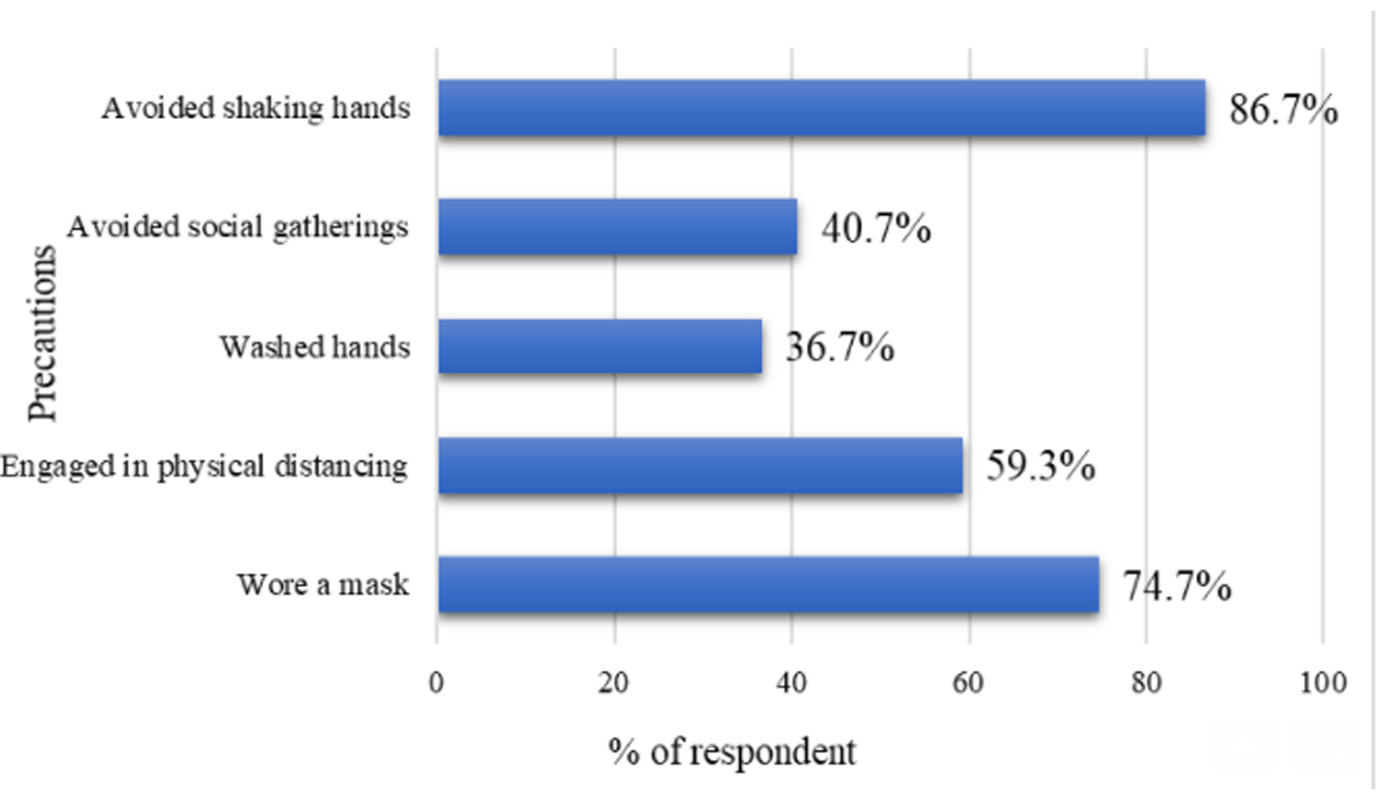
The study confirms that more than three-fourth of the population suffer from mental stress due to the spread of COVID-19 and the lockdown imposed by the government. Eighty per cent of those surveyed stated that the stress had affected their decision-making. The study also confirms that the number of dependents, monthly income, number of living rooms, maintenance of physical distancing norms, avoidance of social gatherings, government support, health insurance, and living in a rented house are significantly related to the mental stress of people living in slums in Andhra Pradesh in India.
Abstract of the Research
The COVID-19 pandemic has had a devastating effect on the mental health of people from different backgrounds; these effects have been particularly acute among lower-income households and in slums. There has been a steep rise in mental illness and behaviours associated with it since 2020, especially in slums characterized by poverty, poor housing, high density, and unhealthy environments. This paper aims to examine the effect of COVID-19 on the mental health of people living in the slums of Vijayawada and Visakhapatnam in the state of Andhra Pradesh in India.
- Tenancy and Credit: Exploring Facts below the Crust in AP February 19, 2022
 SRM University-AP is proud to announce that Dr Ghanshyam Kumar Pandey, Department of Economics, has received the prestigious NABARD (National Bank for Agriculture and Rural Development) grant of Rs 14.85 lacs for a duration of 10 months of active research on “Tenancy and Credit: Exploring Facts below the Crust in AP”.
SRM University-AP is proud to announce that Dr Ghanshyam Kumar Pandey, Department of Economics, has received the prestigious NABARD (National Bank for Agriculture and Rural Development) grant of Rs 14.85 lacs for a duration of 10 months of active research on “Tenancy and Credit: Exploring Facts below the Crust in AP”.About the Research
The study will attempt to identify different possible sources of credit of agriculture households in the Guntur district of AP and then an analysis of the impact at the macro level will be carried out. The role of self-help groups and microfinance on agriculture and livelihood will be one important component of this analysis. Transaction cost, cascading effect, and loan waiver impact will be estimated across tenant and owner cultivators, and social groups.
The study will help to understand the improvement in the life of tenants due to the adoption of the ‘Model Tenancy Act’ and provide feedback on the Tenancy Certificate introduced in AP for enabling farmers to access bank/formal credit and whether the formation of JLGs has led to increase in the credit availability to tenants or not.
The project will help understand the sociological impact of economic decisions by the governance and help direct policies to more beneficial outcomes especially in terms of Tenancy and Credit.
- Budget Panel Discussion 2022-23 February 10, 2022
 The Department of Economics of SRM University-AP, Andhra Pradesh, conducted a Panel Discussion on February 09, 2022, for the much needed and relevant in-depth analysis of the Union Budget proposed by the Finance Minister in the parliament on February 01, 2022.
The Department of Economics of SRM University-AP, Andhra Pradesh, conducted a Panel Discussion on February 09, 2022, for the much needed and relevant in-depth analysis of the Union Budget proposed by the Finance Minister in the parliament on February 01, 2022. Professor Bandi Kamaiah was the moderator of the event, and Dr Anandarao Suvvari, the faculty coordinator of the Department of Economics in the University, organised this discussion, inviting four eminent public finance economists of India, Prof N R Bhanu Murthy, Vice-Chancellor, BASE University, Bengaluru; Prof K R Shanmugam, Director, Madras School of Economics, Chennai; Prof K Gayathri, Professor, Institute for Social and Economic Change (ISEC), Bengaluru; Dr Shri Hari Naidu, Economist, National Institute of Public Finance and Policy (NIPFP), New Delhi. The co-convenors of the event were Dr Ghanshyam Pandey, Dr Manzoor Hassan Malik, Dr Kamal Sai Erra, Dr Hari Venkatesh from the Department of Economics SRM-AP.
The discussion started with a brief overview and essence of the Union budget by Dr Anandarao Suvvari, followed by Prof Bandi Kamaiah. Then first panellist Prof N R Bhanu Murthy, who our Indian Finance Minister also quoted, spoke about how the current budget is a continuation of the previous budget and emphasised more on the capital expenditure, which is the route to growth. He highlighted that the government should bring efficiency in public expenditure and expressed that the public policymakers side-lined the public debt number to GDP ratio at both central and state levels. An issue identified by Prof Murthy was bringing in many commodities under the customs tariff line and how doing this will have a negative impact on the exports. Further, he mentioned the ignorance towards the health and education sectors by a reduction in the allocation of expenditure for the same.
The second panellist Prof K R Shanmugam, gave a very detailed look at the budget, sector by sector, pointing out the benefits and the concerns related to each of them. He gave us a brief look at how the Indian economy has been doing for the past few years and gave an analysis taking this into consideration and stated that the budget had provided necessary fiscal stimuli through an increase in capital expenditure for the revival of the economy.
The third panellist Prof K Gayathri highlighted the philosophy of policy implications of budget and the need for a continuous process for analysing it. She also focused on the need for scientificity for estimates and the need for a sustainable approach for the budget. She pointed out that the current budget was future-looking in line with the vision for India 100 and that it put thorough emphasis on capacity building inclusive development by involving all stakeholders and modern infrastructure while expressing concern over effective implementation of policies.
The final panellist, Dr Shri Hari Naidu, discussed the revenue side of the budget thoroughly while focusing on the new taxation regime, other and legitimising crypto assets and digital Indian currency. In addition to this, Dr Naidu commented on the budget that the tax GDP ratio has been stagnant for the past two decades also, it has not been addressed in the budget, and despite the fact that there were a lot of tax reforms, the tax bases needed to be expanded.
After individual reviews by the panellists, questions posed by the students and the co-convenors were answered, followed by an interactive and engaging discussion among panellists, moderator, convenor and co-convenors on various issues spanning from the way of analysing the budget, trade-offs between debt and capital expenditure, debt sustainability, control mechanisms, the process of allocation, outcome evaluation or impact of the budget and the need for reality and effectiveness of planned budget on the ground level.
The session, after a thorough discussion on the union budget, was concluded by a vote of thanks proposed by Asst. Prof. Dr Hari Venkatesh to the esteemed panellists, moderator, convenor, co-convenors and all the people who made this session successful for contributing their precious time and valued efforts.
Continue reading → - CRIDAP appoints Dr Ghanshyam Pandey as an expert for agriculture September 3, 2021
 Dr Ghanshyam Pandey, Assistant Professor of Economics, SRM University – AP has been appointed as an expert for agriculture, rural development, livelihood issues, and climate change and agriculture by The Centre of Integrated Rural Development for Asia and Pacific (CRIDAP). CRIDAP is an intergovernmental and autonomous organization and has 15 member countries. The member countries are Afghanistan, Bangladesh, Fiji, India, Indonesia, Iran, Lao PDR, Malaysia, Myanmar, Nepal, Pakistan, Philippines, Sri Lanka, Thailand, and Vietnam. His tenure of appointment will be up to 2024.
Dr Ghanshyam Pandey, Assistant Professor of Economics, SRM University – AP has been appointed as an expert for agriculture, rural development, livelihood issues, and climate change and agriculture by The Centre of Integrated Rural Development for Asia and Pacific (CRIDAP). CRIDAP is an intergovernmental and autonomous organization and has 15 member countries. The member countries are Afghanistan, Bangladesh, Fiji, India, Indonesia, Iran, Lao PDR, Malaysia, Myanmar, Nepal, Pakistan, Philippines, Sri Lanka, Thailand, and Vietnam. His tenure of appointment will be up to 2024.Dr Ghanshyam Pandey’s role in the organisation:
- CIRDAP resource person to participate in project proposal development and consultancy.
- CIRDAP resource person for flagship training courses.
- Reviewer of Asia-Pacific Journal on Rural Development (APJORD).
- Part of CIRDAP Think Tank for knowledge sharing and solutions to IRD and PA.
- To expand CIRDAP Think Tank Networks.
- To advise on refining CIRDAP Strategic Plan 2020-2024.
About the organisation:
Continue reading →
The Centre on Integrated Rural Development for Asia and the Pacific (CIRDAP) is a regional, intergovernmental and autonomous organisation. It was established on 6 July 1979 at the initiative of the countries of the Asia-Pacific region and the Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) of the United Nations with support from several other UN bodies and donors. The Centre came into being to meet the felt needs of the developing countries at that time as an institution for promoting integrated rural development in the region. From the original six members, CIRDAP has now grown up as a Centre of 15 member countries. The member countries are Afghanistan, Bangladesh (Host State), Fiji, India, Indonesia, Iran, Lao PDR, Malaysia, Myanmar, Nepal, Pakistan, Philippines, Sri Lanka, Thailand and Vietnam. Operating through designated contact ministries and link institutions in member countries, CIRDAP promotes regional cooperation. It plays a supplementary and reinforcing role in supporting and furthering the effectiveness of integrated rural development programmes in Asia and the Pacific. - Dr Balaga Mohana Rao receives Best PhD Thesis award from IIT Bombay August 19, 2021
 Dr Balaga Mohana Rao, Assistant Professor from the Department of Economics has been awarded the best PhD thesis award in the 59th IIT Bombay convocation held on August 07, 2021. The thesis titled The Early Warnings of the Impending Currency Crises and the Ensuing Macroeconomic Costs aims to develop an Early Warning System to identify the Currency Crises that would help in preventing an impending crisis and also in mitigating the devastating aftermath effects if that occurred.
Dr Balaga Mohana Rao, Assistant Professor from the Department of Economics has been awarded the best PhD thesis award in the 59th IIT Bombay convocation held on August 07, 2021. The thesis titled The Early Warnings of the Impending Currency Crises and the Ensuing Macroeconomic Costs aims to develop an Early Warning System to identify the Currency Crises that would help in preventing an impending crisis and also in mitigating the devastating aftermath effects if that occurred.The financial crises have enthused a huge theoretical and empirical debate in current times due to their recurrent nature in the history of economics. To highlight the importance of an economic crisis among various sections, Kaminsky et al. (1998) quote Kindleberger (1978) saying that academics are interested in a crisis as they have had a history of fascination for the crises, policymakers are interested because they want to prevent the crisis, and financial market participants are interested as they can make money out of it. The financial crises can be divided into two broad categories—currency and sudden stop crises, and debt and banking crises. The currency crises have not only swept away Argentina (2001), Brazil (1998–1999), Latin America (the 1980s), Russia (1998), Southeast Asia (1997) and UK (1992) (to name a few) but they also have caused serious economic adversities to India and BRICS in the recent past. A currency crisis encompasses one of the following four features or a combination of them owing to a speculative attack—both successful and unsuccessful attacks—on a currency: A sharp depreciation of a currency (possibly followed by devaluation) and/or huge depletion of foreign exchange reserves or an increase in interest rates by the central bank or imposing restrictions on capital flows. In this context, Dr Balaga Mohana Rao’s thesis focuses on developing an early warning system to identify the impending crises, finding the common determinants of currency crises and the aftermath effects on macroeconomic indicators.
“One may wonder why the crisis should be prevented or mitigated. The reason is that a full-blown crisis will not be just confined to the foreign exchange market or some other segment, but it will affect the whole economy” Dr Balaga said. He plans to extend his PhD work on Currency Crises and see it in the context of the International Price System.
Continue reading →

The Department of Economics is inviting Distinguished Visiting Professor, Prof. Rathinasamy Maria Saleth for two esteemed seminars on novel topics of social relevance. Prof. Saleth will talk on “Climate Change, Water, and Adaptation” on November 29, 2023, and “Social Science Research: Theories, Models, and Empirical Analysis” on November 30, 2023.
Join the sessions and gain insights from the seasoned academician!
About the Speaker
Prof. Rathinasamy Maria Saleth is currently a Distinguished Visiting Professor at the Department of Economics, Easwari School of Liberal Arts, SRM University-AP. He is regularly affiliated as an Honorary Professor at the Madras School of Economics, Chennai.
Prof. Saleth received his MA from Madurai Kamaraj University, Madurai (1979), MPhil from Jawaharlal Nehru University, New Delhi (1981), and PhD from University of Illinois, Urbana-Champaign, USA (1989). He works in the areas of water resource management, institutional change, development policy, and impact assessment and has published three books, six edited volumes, and over 100 research papers in journals and edited volumes related to these areas.
Prof. Saleth has also won awards for some of his papers, books, and works from professional organisations such as the Indian Society of Agricultural Economics, the American Water Resources Association, the International Water Association, and the University of South Australia. He has also been a consultant to the World Bank, Food and Agriculture Organisation, Asian Development Bank, UN Economic and Social Council for the Asia and the Pacific, and UN Environment Programme.
Talk 1: Climate Change, Water, and Adaptation
Abstract: This presentation covers the nature and magnitude of the impacts of climate change on water resources and possible coping and adaptation options both from global and national perspectives. The presentation starts with a discussion on the leading causes of climate change, especially the cumulative effects of global warming caused by greenhouse gases and related environmental consequences from human-induced economic activities and ecological disturbances. It, then, shows how the impacts of climate change are manifested both at the global and national scale in terms of the spatial and temporal patterns of precipitation and water availability and the resultant implications for water, agriculture, and economy. Although climate change is caused essentially by non-hydrological factors, the water sector continues to be the main medium through which most of its impacts are transmitted to the agricultural sector in particular and other economic sectors in general. As such, it is but natural for the adaptation/coping strategies also to be designed at the point of the impacted sectors, though, admittedly, general mitigation strategies go far beyond these sectors. The presentation, finally, concludes by delineating feasible adaptation strategies for the water sector, which include not just demand management options but also supply management avenues, especially those involving institutional changes and infrastructural developments.
Talk 2: Social Science Research: Theories, Models, and Empirical Analysis
Abstract: This presentation covers the theoretical, methodological, and empirical aspects of social science research, especially from the perspective of young research scholars. It starts with a discussion on the nature, rationale, features, and types of building blocks of social science theories. After an analytical description of three broad types of models, i.e., simple, interactive, and path-based models, the presentation provides concrete illustrations, particularly for the interactive and path-based models using a few empirical case studies. These illustrative case studies will show how to conceptualize, operationalize, and empirically evaluate the research problems in different contexts. The presentation, finally, concludes with the discussion on some of the additional methodological, practical, and data-related aspects of importance in social science research.

Pandey, G. (2020). “Sources and Drivers of Agricultural Growth in Jharkhand” Paper is awarded with Gold medal on Research Day at SRM University held on 29th January 2020.
Articles
Dr Ghanshyam Pandey - Budget 2023-24 is not a complete package for the Agricultural sector
Prof Balaji Vejju - Union Budget 2023: A big push for MSME sector development
Dr Manozor Hassan - Budget 2023-24 And India’s Imports, Exports, And Current Account Deficit
Md Murtaza & J vineesh Prakash - Is Gobardhan Scheme A Lasting Solution To Stubble Burning?