News and Activities
- Padmashri Prof. Shanti Sinha Discuss Child Labour and Child Rights in India at UDL#20 February 24, 2025
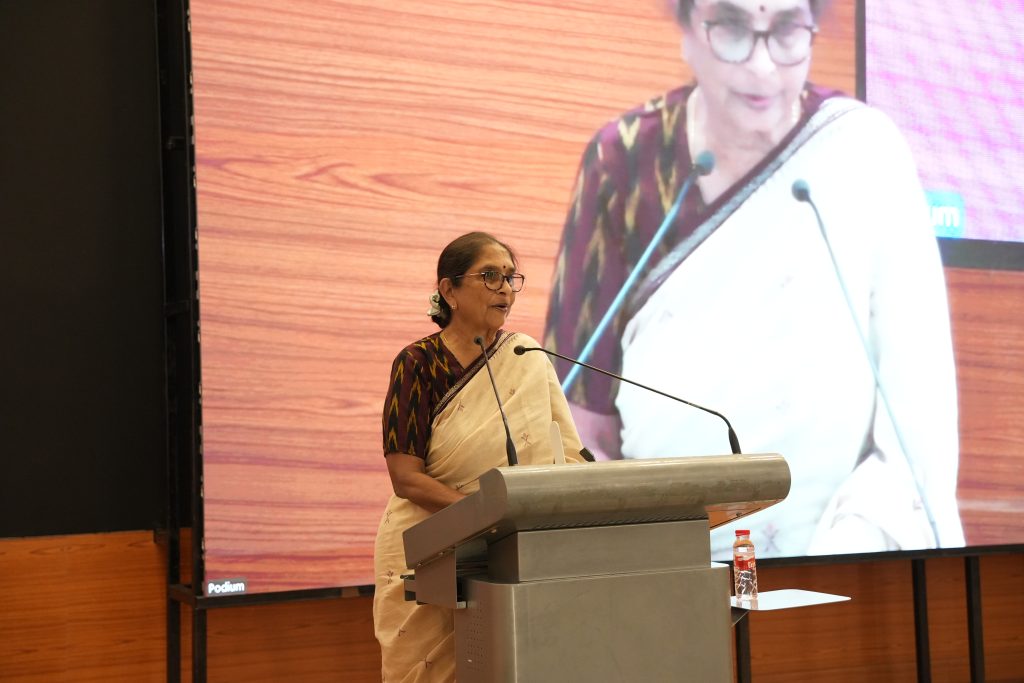

“Every Child Out of School is in Child Labour. Education, Education and Education alone is the Way Forward for a Progressing India.” – Prof. Shanti Sinha
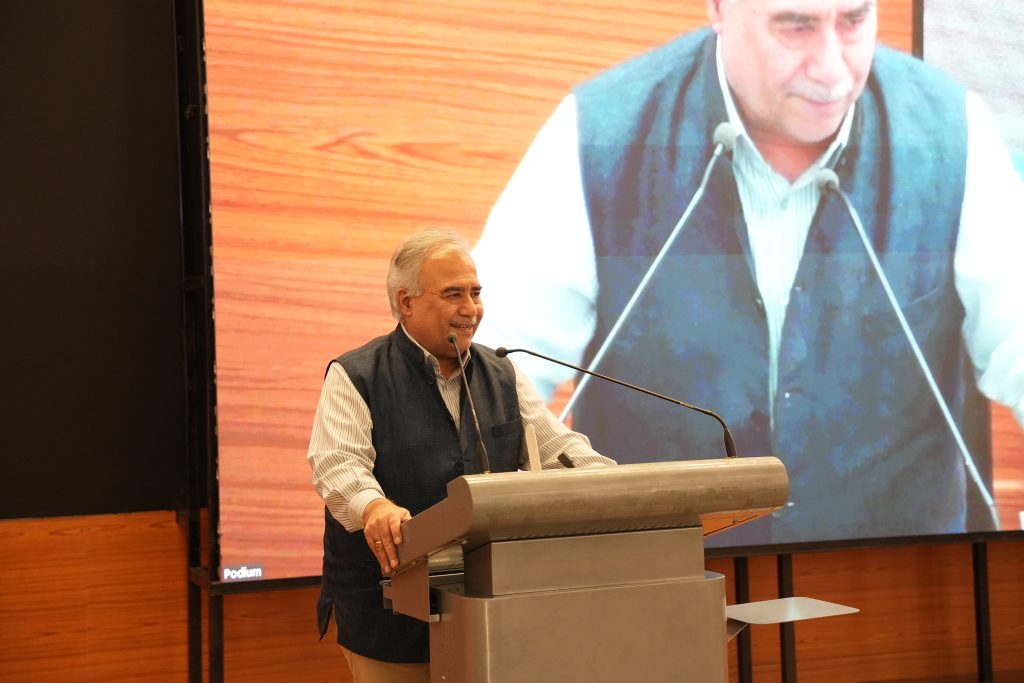
The twentieth edition of the University Distinguished Lecture (UDL) on February 21, 2025, witnessed an invigorating session by the eminent anti-child labour activist Padma Shri Prof. Shanta Sinha, Ramon Magsaysay Awardee, Former Chairperson of the National Commission for Protection of Child Rights (NCPCR), and Professor (Retd.) Dept. of Political Science, Hyderabad Central University. The session on the topic “Making Education a Reality and Ending Child Labour: Experience of M.V. Foundation” gave an overview of the work of M.V. Foundation in the field of child rights in India.
In a society ravaged by poverty, where children were forced to join the bonded labour workforce, Prof. Sinha remarked that it was not poverty that led to child labour but child labour that led to poverty. Prof. Sinha elucidated on the non-negotiable principle adopted by the M.V. Foundation, that ‘no child must work, and every child must attend full-time formal day school,’ which broke the societal norms of Indian society.
She briefly spoke about the impact that the M.V. Foundation had and the ripple it created in the field of child rights. “M.V. Foundation has withdrawn over 15 lakh children in the age group of 5-14 years from child labour; stopped over 20,000 child marriages and pioneered a program for mainstreaming children to schools through residential bridge courses. The MVF’s mission to abolish child labour also led to the Closure of Night Schools and the creation of necessary amendments in the Child Labour Act of 1986,” stated Prof. Sinha.
The session also discussed Prof. Sinha’s Journey at the National Commission for Protection of Child Rights (NCPCR), and the various challenges faced in addressing key issues such as violation of children’s rights in relation to child labour and child trafficking, rights of children in areas of civil unrest, juvenile justice system, corporal punishment, child abuse and violence on children, and child malnutrition.
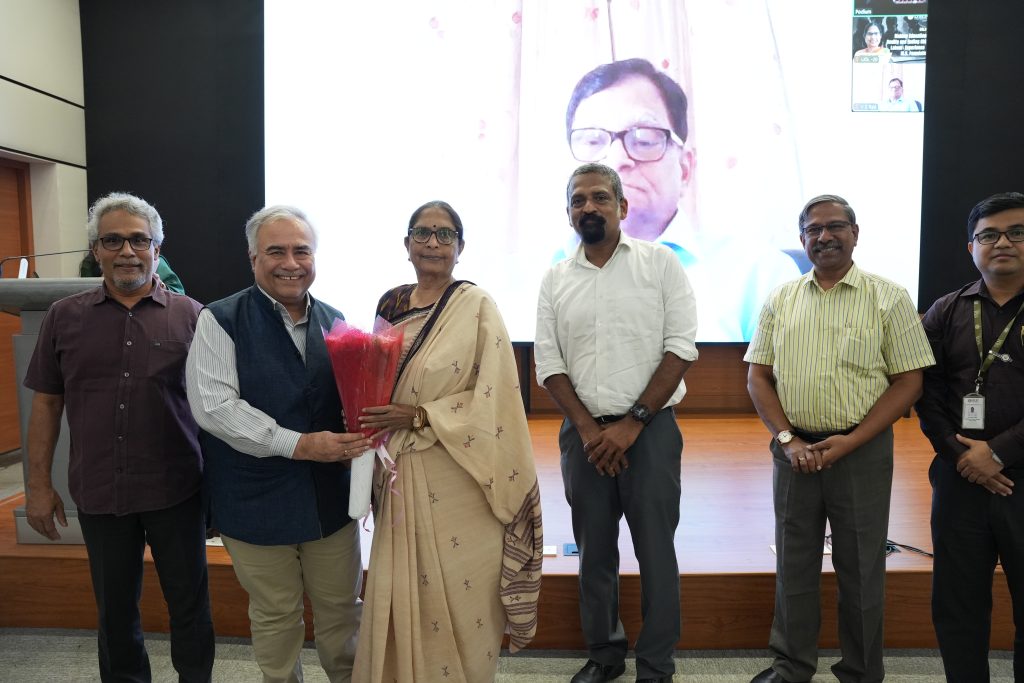

The UDL 20 was a mind opener and a lens into the reality of child labour still prevalent in India. Prof. Manoj K Arora, Vice Chancellor of SRM University-AP, expressed his gratitude to have the presence of a torchbearer of social reform at the UDL. He stated, “Prof. Sinha is a stalwart whose work has created a magnitudinal shift in the societal norm, significantly contributing to the abolition of child labour in India. We are grateful to imbibe from her knowledge and experience as a social leader.” Dean of Easwari School of Liberal Arts, Prof. Vishnupad, also expressed his heartfelt appreciation for Prof. Sinha’s presence and her work. He stated that the thought-provoking and inspiring session will ignite students to think in a ‘non-conventional’ way and offer courage to make a change.
The 20th UDL was organised under the aegis of the Office of Dean-Research, the UDL committee, and the Easwari School of Liberal Arts. It witnessed the presence of Registrar Dr R Premkumar, Dean of the School of Engineering and Sciences, Prof C V Tomy, Dean of Research, Prof. Ranjit Thapa, and Faculty and students of the varsity. The signature lecture series is the university’s flagship initiative to impart global exposure and quality education to its students.
Continue reading → - Field Trip to Hyderabad: A Journey of Education, Culture, and Adventure February 11, 2025
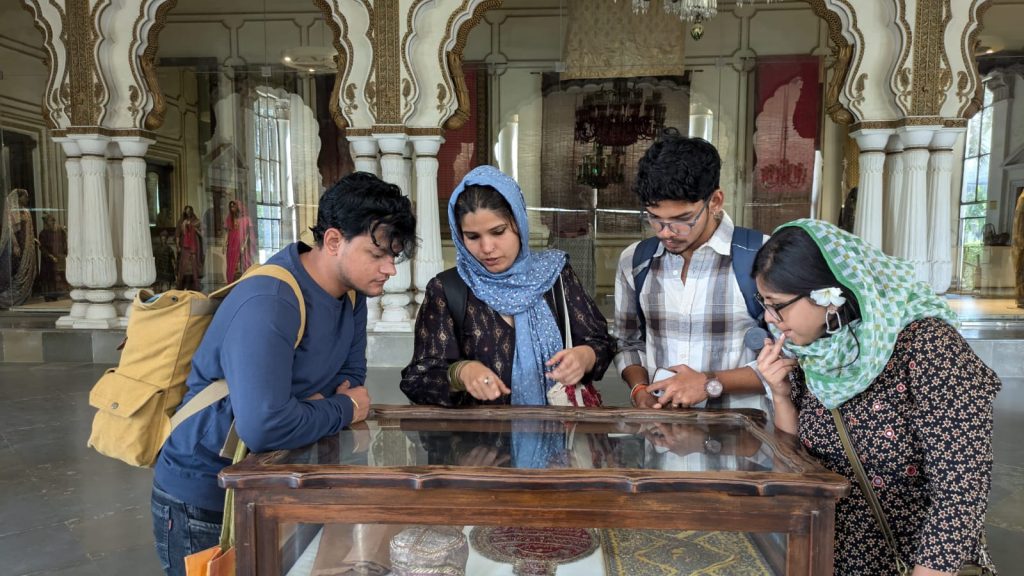

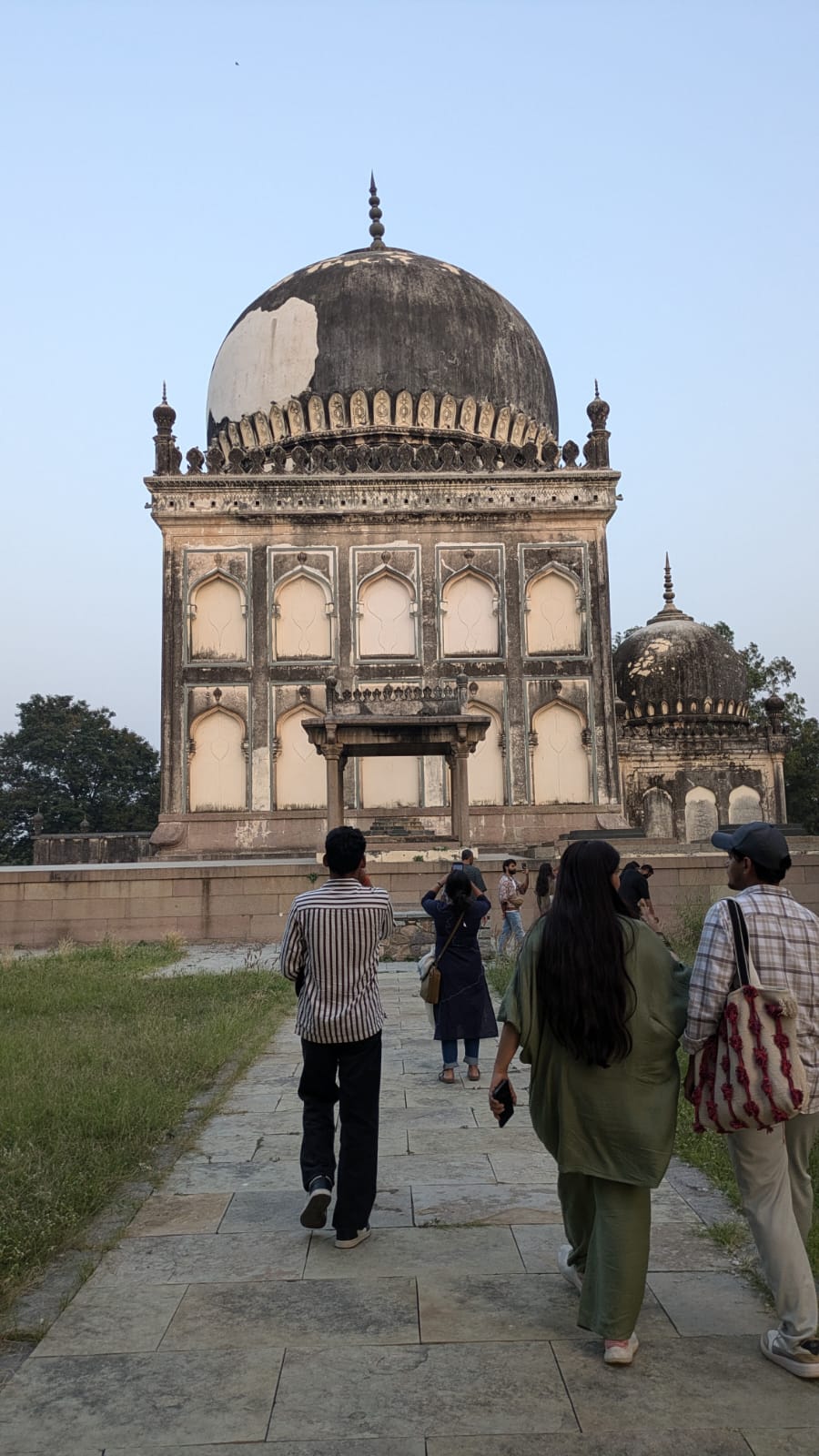
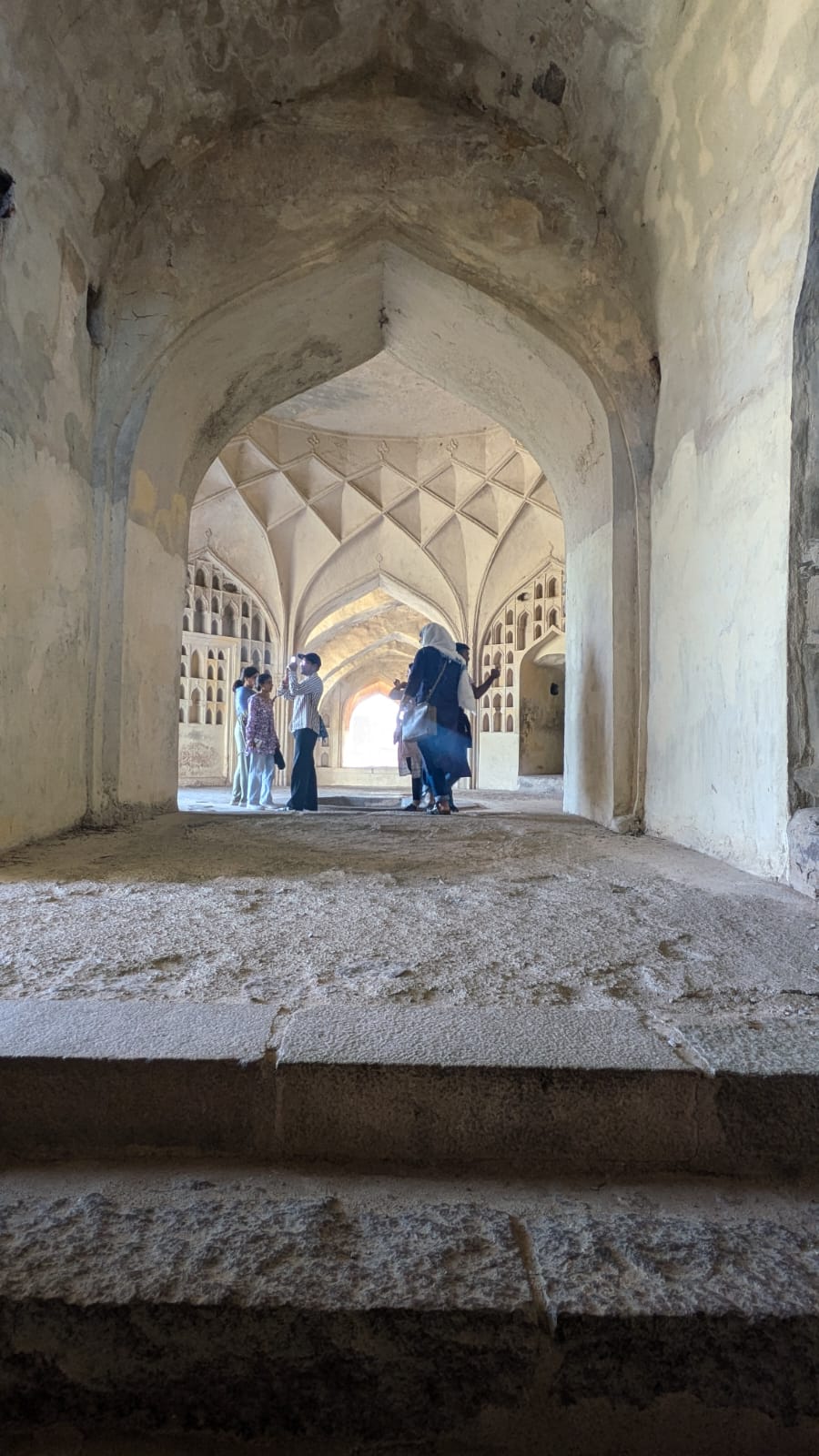
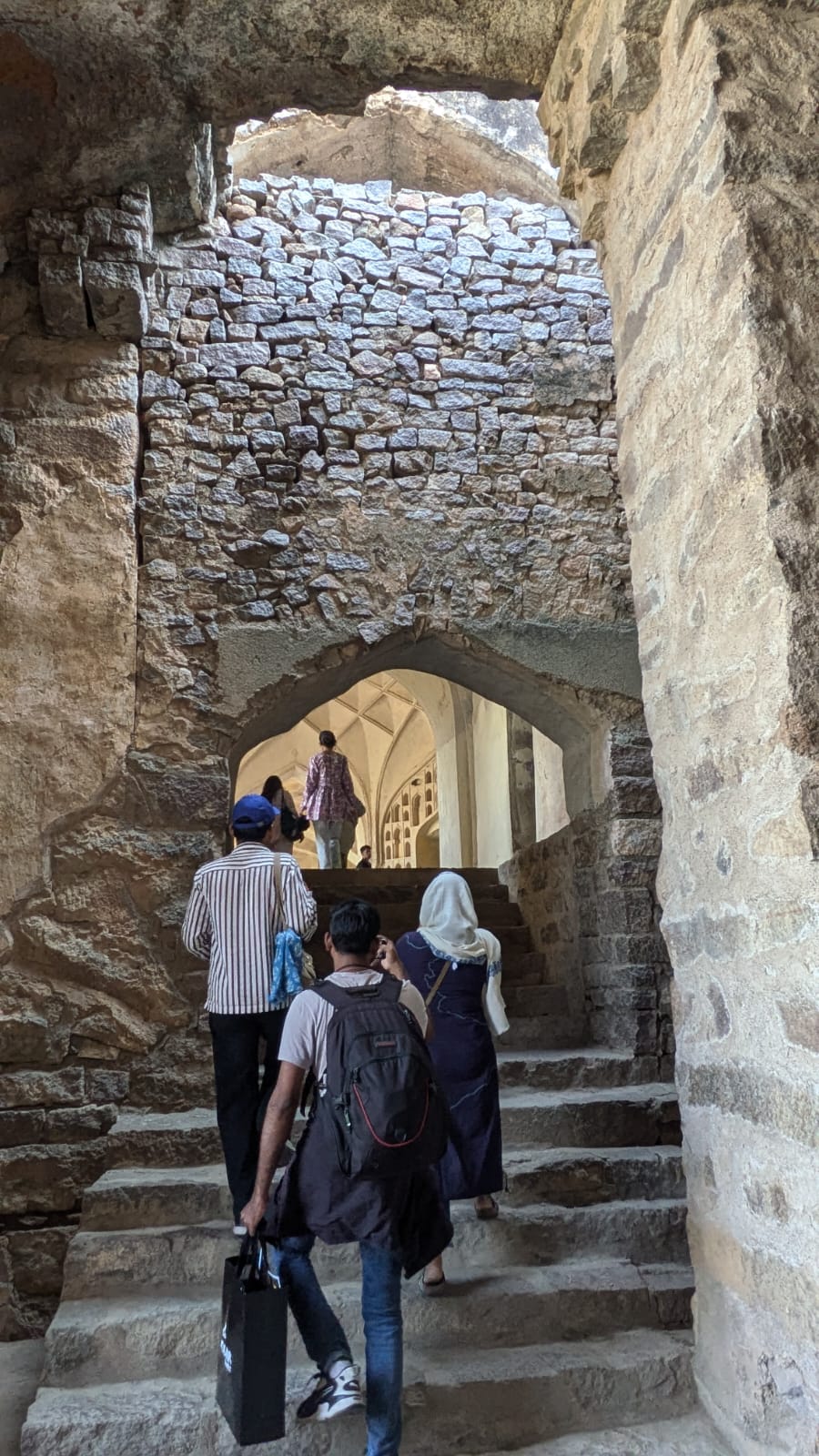
The 5th Semester B.A. History students went on a field trip to Hyderabad as part of their courses ‘Medieval India’ and the ‘Eighteenth Century in Indian History’. Dr Aqsa Agha, Course Coordinator, and Dr Manaswini Sen led the study group to explore the city’s historical and cultural significance, enhancing their learning outside the classroom for the two courses.
The group visited Charminar, exploring the iconic monument and its surrounding bazaars, Golconda Fort, discussing its history and architecture with a Heritage Walk Practitioner from Hyderabad, and finally the Qutb Shahi Tombs and gardens, a standing testament of Indo-Persian architectural excellence.
The field trip provided students with a refined exposure to the diverse culture and history of Hyderabad and the historical context of the evolution of the culture of the city. The students had a wonderful chance to visit the important historical monuments and urban morphology that mark the period of study in the courses on Medieval and Eighteenth-century Indian History.
The field trip fostered a deep understanding of the respective courses, inspiring students to explore beyond books and classrooms.
Continue reading →