Unveiling the Post-Pandemic Tapestry of Mind and Body in Türkiye
 We are thrilled to announce that Dr A Lakshmana Rao, Associate Professor from the Department of Commerce along with Ms Sreya B, a distinguished PhD Scholar, have made a significant contribution to the field of public health with their latest publication.
We are thrilled to announce that Dr A Lakshmana Rao, Associate Professor from the Department of Commerce along with Ms Sreya B, a distinguished PhD Scholar, have made a significant contribution to the field of public health with their latest publication.
Their paper, titled “A Commentary on ‘Sleep Quality, Quality of Life, Fatigue, and Mental Health in COVID-19 post-pandemic Türkiye: A Cross-Sectional Study’,” has been published in the esteemed journal Frontiers in Public Health, which boasts an impressive impact factor of 5.2.
This groundbreaking study delves into the crucial aspects of sleep quality, quality of life, fatigue, and mental health in the aftermath of the COVID-19 pandemic in Türkiye. The research provides insightful commentary and analysis, contributing valuable knowledge to our understanding of the pandemic’s long-term effects on human well-being.
The SRM University-AP community is proud of Dr Rao and Ms Sreya B for their dedication and excellence in research. Their work not only enhances the reputation of our institution but also serves as an inspiration for our students and faculty alike.
We congratulate them on their achievement and encourage our readers to access the full paper to learn more about the study’s findings and implications for public health.
Abstract
This commentary examines the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on mental health and sleep quality among the Turkish population, focusing on socio-demographic disparities and gender-based differences. To investigate the lasting effects of the pandemic, a comprehensive cross-sectional, multi-center-based survey was conducted in 2022. The study used robust sampling strategies and validated assessment tools such as WHOQOL-BREF, PHQ-15, DASS-21, GAD-7, PSQI, and FAS to reveal significant associations between poor sleep quality and worsened mental health.
The findings highlight the need for targeted interventions post-pandemic. The study conducted a detailed analysis, including multivariate regression, to explore the interaction between socio-demographic factors, mental health, and sleep quality, providing valuable insights for future public health interventions that consider both socio-demographic characteristics and lifestyle factors. In conclusion, the study advocates prioritising interventions that enhance sleep quality as a crucial aspect of post-pandemic public health, offering potential avenues for mitigating mental health disorders. Despite acknowledged limitations, the research’s contributions to understanding post-pandemic mental health challenges underscore its relevance in shaping targeted public health interventions.
Explanation of the Research in Layperson’s Terms
This article discusses a research study conducted in Turkey to investigate the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on people’s sleep, quality of life, fatigue, and mental health. The study discovered that numerous individuals experienced sleep problems and mental health disorders following the pandemic, likely due to stress and social isolation. It suggests that enhancing sleep quality could help to improve mental health in the future, emphasising the significance of addressing these issues in public health strategies.
Title of Research Paper in the Citation Format
Sreya B, Lakshmana Rao A, (2024) Commentary: Sleep quality, quality of life, fatigue, and mental health in COVID-19 post-pandemic Türkiye: a cross-sectional study. Front. Public Health 12:1393054. Doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2024.1393054
Practical Implementation or the Social Implications Associated with the Research
The findings of the research have significant practical and social implications for addressing the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on the Turkish population. The study underscores the importance of targeted interventions aimed at improving sleep quality to mitigate long-term mental health challenges. These interventions might involve stress management programs, education on sleep hygiene, and increased access to mental health services. Furthermore, optimising healthcare resource allocation by prioritising mental health services and sleep disorder clinics could enhance support for individuals struggling with mental health issues.
Public health campaigns focusing on the importance of sleep for mental well-being could raise awareness and promote strategies for improving sleep quality across various demographic groups. Additionally, the research helps reduce stigma around mental health by highlighting the prevalence of mental health symptoms and sleep disturbances post-pandemic, encouraging more individuals to seek support without fear of judgment. Moreover, recognising the impact of social isolation on mental health and sleep quality underscores the importance of fostering social support networks and community connections to aid in post-pandemic recovery.
Policy development informed by the research findings could address broader social determinants of health, such as housing insecurity and access to healthcare, to create a more supportive environment for mental health and sleep quality improvement initiatives. Overall, integrating mental health and sleep quality considerations into post-pandemic recovery efforts is crucial for promoting the overall well-being of the Turkish population.
- Published in Commerce Current Happenings, Departmental News, News, Research News
Triumphant Trio: Dr Soumyajyoti and Scholars Make Strides in Physics
 In a significant academic achievement, Dr Soumyajyoti Biswas, Assistant Professor and Scholars Ms Diksha and Mr Gunnemeda Eswar in the Department of Physics, has published an insightful paper in the prestigious Q1 journal, Physical Review E. The paper, titled “Prediction of depinning transitions in interface models using Gini and Kolkata indices,” presents a novel approach to understanding the complex phenomena of depinning transitions in physical systems.
In a significant academic achievement, Dr Soumyajyoti Biswas, Assistant Professor and Scholars Ms Diksha and Mr Gunnemeda Eswar in the Department of Physics, has published an insightful paper in the prestigious Q1 journal, Physical Review E. The paper, titled “Prediction of depinning transitions in interface models using Gini and Kolkata indices,” presents a novel approach to understanding the complex phenomena of depinning transitions in physical systems.
The research introduces the use of Gini and Kolkata indices as predictive tools, offering a fresh perspective that could pave the way for new discoveries in the field. This publication not only underscores Dr. Biswas’s expertise but also enhances the university’s reputation as a hub for cutting-edge research.
The Department of Physics congratulates Dr. Biswas on this remarkable accomplishment and looks forward to the continued impact of his work on the scientific community.
Abstract
The intermittent dynamics of driven interfaces through disordered media and its subsequent depinning for large enough driving force is a common feature for a myriad of diverse systems, starting from mode-I fracture, vortex lines in superconductors, and magnetic domain walls to invading fluid in a porous medium, to name a few. In this work, we outline a framework that can give a precursory signal of the imminent depinning transition by monitoring the variations in sizes or the inequality of the intermittent responses of a system that are seen prior to the depinning point. In particular, we use measures traditionally used to quantify economic inequality, i.e., the Gini index and the Kolkata index, for the case of the unequal responses of precritical systems.
The crossing point of these two indices serves as a precursor to imminent depinning. Given a scale-free size distribution of the responses, we calculate the expressions for these indices, evaluate their crossing points, and give a recipe for forecasting depinning transitions.We apply this method to the Edwards-Wilkinson, Kardar-Parisi-Zhang, and fiber bundle model interface with variable interaction strengths and quenched disorder. The results are applicable for any interface dynamics undergoing a depinning transition.
Explanation of Research in Layperson’s Terms
Many different physical systems, from cracking in materials to the movement of magnetic fields, share a common underlying behavior – they all involve an “interface” or boundary that moves through a disordered, or irregular, medium. As this interface moves, it often gets “pinned” or stuck in place by the disorder in the medium. However, as the driving force on the interface increases, there comes a point where the interface suddenly “depins” and starts moving much more freely. This transition from a pinned to a depinned state is called the “depinning transition” and it’s an important phenomenon in many areas of science and engineering.
In this work we have found a way to detect when this depinning transition is about to happen, before it actually occurs. We do this by looking at the sizes or magnitudes of the intermittent, or irregular, responses of the system as the driving force increases. Specifically, we use two measures that are traditionally used to quantify economic inequality – the Gini index and the Kolkata index. These give a way to track how “unequal” or unevenly distributed the sizes of the responses are. We found that when these two inequality measures cross each other, it serves as a precursor or early warning sign that the depinning transition is imminent. This is a powerful result because being able to predict when depinning will happen is very useful in fields like material science, superconductivity, and fluid dynamics, where controlling these phase transitions is important. By monitoring these inequality measures, one can may be able to forecast depinning events before they occur, which could lead to better design and control of these systems.
Title of Research paper in the Citation Format
Diksha, G. Eswar, and S. Biswas, Prediction of depinning transitions in interface models using Gini and Kolkata indices, Physical Review E 109, 044113 (2024).
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevE.109.044113
Practical Implementation or the Social Implications Associated with it
Prediction of imminent transition has implications in a wide range of disciplines, including stability of mechanical structures (buildings, aircraft, bridges, etc.), extraction of oil (fracking) to the largest scale of mechanical failure i.e., earthquakes.
Collaborations
This work is done with the PhD student Ms Diksha and the BSc student Mr Gunnemeda Eswar.
Future Research Plans
Future research plans include applications of the methods developed here to be applied to real-life physical structures for their stability analysis and predictions of impending catastrophes.
Pictures Related to the Research
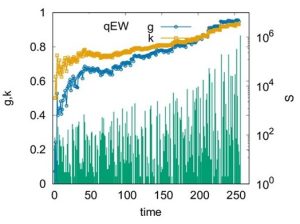
In this fig. the time series of avalanche sizes is shown along with the time variations of g and k for the quenched Edwards-Wilkinson model as a prototype. Here the crossing of g and k occurs prior to the depinning transition point (the last avalanche in the series). Therefore, the crossing of g and k can serve as a good indicator of an imminent depinning transition.
- Published in Departmental News, News, Physics News, Research News
Research Paper on Reconfigurable Adder Design
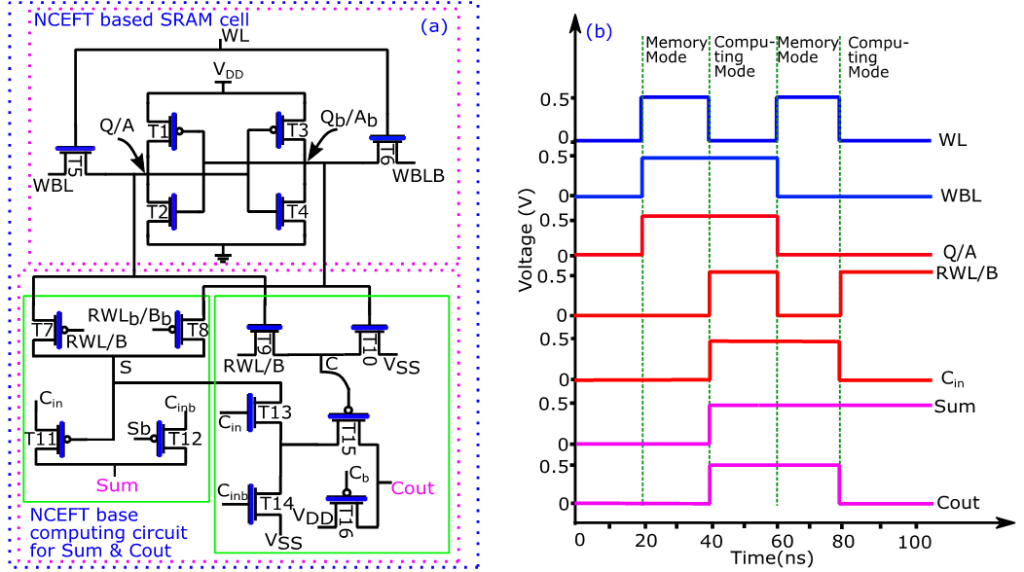
Prof. Siva Sankar Yelampalli and Dr Ramesh Vaddi, Associate Professor, from the Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering, along with research scholars Mr Birudu Venu, Mr Tirumala Rao Kadiyam, and Mr Koteswara Rao Penumalli, have jointly published a paper titled “Computing in-memory reconfigurable (accurate/approximate) adder design with negative capacitance FET 6T-SRAM for energy efficient AI edge devices” The paper introduces Computing in-memory (CiM) as a promising alternative to traditional von-Neumann architectures, focusing on its potential for energy-efficient AI edge computing with CMOS scaling. Additionally, they have explored the advancements in approximate computing in-memory (ACiM) techniques, aiming to further enhance the energy efficiency of these innovative architectures.
Abstract:
Computing in-memory (CiM) is an alternative to von Neumann architectures for energy-efficient AI edge computing architectures with CMOS scaling. Approximate computing in-memory (ACiM) techniques have also been recently proposed to further increase the energy efficiency of such architectures. In the first part of the work, a negative capacitance FET (NCFET) based 6T-SRAM CiM accurate full adder has been proposed, designed and performance benchmarked with equivalent baseline 40 nm CMOS design. Due to the steep slope characteristics of NCFET, at an increased ferroelectric layer thickness, Tfe of 3 nm, the energy consumption of the proposed accurate NCFET-based CiM design is ∼82.48% lower in comparison to the conventional/Non CiM full adder design and ∼85.27% lower energy consumption in comparison to the equivalent baseline CMOS CiM accurate full adder design at VDD = 0.5 V. This work further proposes a reconfigurable computing in-memory NCFET 6T-SRAM full adder design (the design which can operate both in accurate and approximate modes of operation). NCFET 6T-SRAM reconfigurable full adder design in accurate mode has ∼4.19x lower energy consumption and ∼4.47x lower energy consumption in approximation mode when compared to the baseline 40 nm CMOS design at VDD = 0.5 V, making NCFET-based approximate CiM adder designs preferable for energy efficient AI edge CiM based computing architectures for DNN processing.
Future research plans: Implementing reconfigurable computing in-memory (CiM) MAC for energy-efficient AI edge devices.
- Published in Departmental News, News, Research News
Examining the Impact of Bifurcation on Agricultural Development in Jharkhand: A Comprehensive Study

The Department of Economics is thrilled to announce the publication of Assistant Professor Dr Ghanshyam Kumar Pandey’s research paper titled, “Bifurcation and Agricultural Development in Jharkhand,” in Economic and Political Weekly. The paper delves into the developmental trajectory of Jharkhand following its bifurcation from Bihar in 2000 and examines the intricacies of agricultural development and the key determinants that have shaped its evolution post-separation.
Abstract:
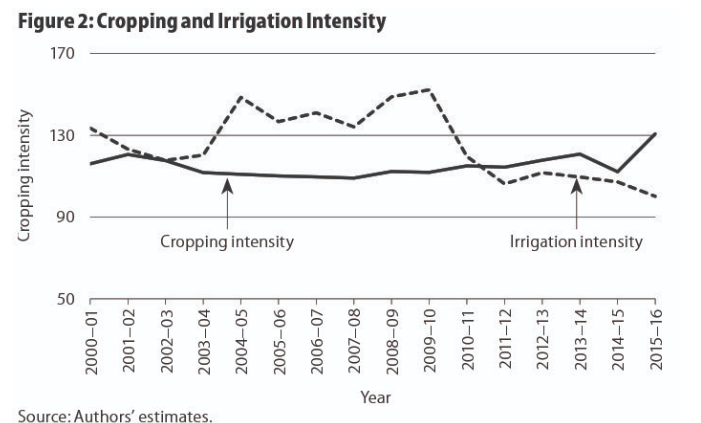
The cropping pattern in Jharkhand has significantly changed from 2000 to 2016, with shifts from the cultivation of cereals to non-cereals. An increase in the crop area and diversification towards high-value crops have accelerated overall agricultural growth. Capital formation and better infrastructure facilities, along with improved fertiliser consumption and irrigation, will foster agricultural development in Jharkhand
Practical implementation:
This study shows the development path of Jharkhand after bifurcation from Bihar in 2000. The study deals with the process of agricultural development and determinants of agricultural development after its bifurcation.
- Published in Departmental News, News, Research News

