Events
- Exploring Railway Bridges and Track Structure: Insights from Industry Professionals April 16, 2024

The Department of Civil Engineering is thrilled to host Er. Lakhwant Singh Khalsa for its 3rd Industry Guest Lecture Series. Mr Khalsa, Project Manager at Systra India, Haryana, will deliberate on “Railway Bridges and Track Structure – Practitioner Perspectives”. His lecture will offer deep insights into Railway Track Structure and Components and Railway Bridge Elements and Bridge Types. We Invite all civil engineering students and enthusiasts to join the insightful session on April 22, 2024.
About the Speaker:
Er. Lakhwant Singh Khalsa currently working as a project manager, Systra/PMC for RVNL Vijayawada 3rd line rail project. He has 41 years of rich & extensive experience in railway steel bridge structures, civil bridge works and project management. He is a Life Member of the Institution of Permanent Way Engineers (India)-IPWE and the Indian Institution of Bridge Engineers-IIBE. He holds several prestigious certifications, such as welding inspector from the welding research institute BHEL Trichy and Level II Certification in Non-Destructing Testing for DPT, MPT & UT as per SNT TC IA2006. He is familiar with IS, IRS, EN, and BS Codes, which are relevant to steel and concrete works. Also, he has experience working in hilly terrains in the Himalayan Ranges with critical environmental conditions.
Continue reading → - Research Paper on Reconfigurable Adder Design April 16, 2024
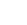
Dr Ramesh Vaddi, and Dr Siva Sankara Yelampalli, Assistant Professors at the Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering, along with research scholars Mr Birudu Venu, Mr Tirumala Rao Kadiyam, and Mr Koteswara Rao Penumalli, have jointly published a paper titled “Computing in-memory reconfigurable (accurate/approximate) adder design with negative capacitance FET 6T-SRAM for energy efficient AI edge devices” The paper introduces Computing in-memory (CiM) as a promising alternative to traditional von-Neumann architectures, focusing on its potential for energy-efficient AI edge computing with CMOS scaling. Additionally, they have explored the advancements in approximate computing in-memory (ACiM) techniques, aiming to further enhance the energy efficiency of these innovative architectures.
Abstract:
Computing in-memory (CiM) is an alternative to von Neumann architectures for energy-efficient AI edge computing architectures with CMOS scaling. Approximate computing in-memory (ACiM) techniques have also been recently proposed to further increase the energy efficiency of such architectures. In the first part of the work, a negative capacitance FET (NCFET) based 6T-SRAM CiM accurate full adder has been proposed, designed and performance benchmarked with equivalent baseline 40 nm CMOS design. Due to the steep slope characteristics of NCFET, at an increased ferroelectric layer thickness, Tfe of 3 nm, the energy consumption of the proposed accurate NCFET-based CiM design is ∼82.48% lower in comparison to the conventional/Non CiM full adder design and ∼85.27% lower energy consumption in comparison to the equivalent baseline CMOS CiM accurate full adder design at VDD = 0.5 V. This work further proposes a reconfigurable computing in-memory NCFET 6T-SRAM full adder design (the design which can operate both in accurate and approximate modes of operation). NCFET 6T-SRAM reconfigurable full adder design in accurate mode has ∼4.19x lower energy consumption and ∼4.47x lower energy consumption in approximation mode when compared to the baseline 40 nm CMOS design at VDD = 0.5 V, making NCFET-based approximate CiM adder designs preferable for energy efficient AI edge CiM based computing architectures for DNN processing.
Future research plans: Implementing reconfigurable computing in-memory (CiM) MAC for energy-efficient AI edge devices.
Continue reading →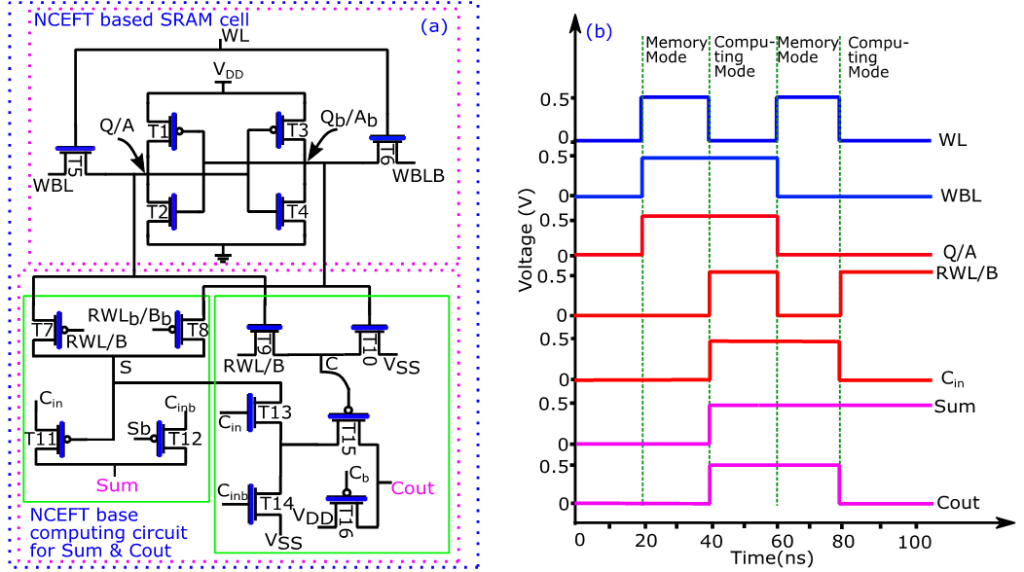
- Examining the Impact of Bifurcation on Agricultural Development in Jharkhand: A Comprehensive Study April 16, 2024
The Department of Economics is thrilled to announce the publication of Assistant Professor Dr Ghanshyam Kumar Pandey’s research paper titled, “Bifurcation and Agricultural Development in Jharkhand,” in Economic and Political Weekly. The paper delves into the developmental trajectory of Jharkhand following its bifurcation from Bihar in 2000 and examines the intricacies of agricultural development and the key determinants that have shaped its evolution post-separation.
Abstract:
The cropping pattern in Jharkhand has significantly changed from 2000 to 2016, with shifts from the cultivation of cereals to non-cereals. An increase in the crop area and diversification towards high-value crops have accelerated overall agricultural growth. Capital formation and better infrastructure facilities, along with improved fertiliser consumption and irrigation, will foster agricultural development in Jharkhand
Practical implementation:
This study shows the development path of Jharkhand after bifurcation from Bihar in 2000. The study deals with the process of agricultural development and determinants of agricultural development after its bifurcation.
Continue reading →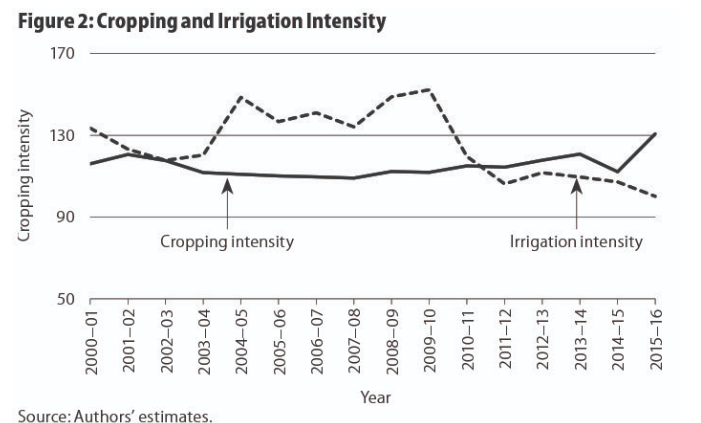
- Ms Boddu Srujana April 16, 2024
- Revolutionising Cooling Technology: Patent Granted for Innovative Fabric Design April 15, 2024
 The Department of Physics is thrilled to announce a remarkable milestone in sustainable technology. Dr Sabyasachi Mukhopadhyay, Associate Professor and Ms Sreelekha Bhuvaneswari, BSc student has been officially granted a patent for their groundbreaking invention: “A fibre material with moisture retention capacity with thermal tolerance and a method for manufacture of the same.”
The Department of Physics is thrilled to announce a remarkable milestone in sustainable technology. Dr Sabyasachi Mukhopadhyay, Associate Professor and Ms Sreelekha Bhuvaneswari, BSc student has been officially granted a patent for their groundbreaking invention: “A fibre material with moisture retention capacity with thermal tolerance and a method for manufacture of the same.”This pioneering material, distinguished by its Application Number 202141023375, stands at the forefront of cooling technology. It promises to enhance thermal regulation while prioritising environmental sustainability.
Dr Mukhopadhyay’s invention is poised to make significant contributions to the field of material science, offering a versatile solution that holds potential applications across various industries. The department extends its heartfelt congratulations to the duo on this significant achievement and looks forward to the positive impact his work will continue to have on our community and beyond.
Abstract:
The project, with the patent application number 202141023375, develops a methodology to design a fabric cloth that would replace the use of air conditioners. This cloth design is inspired by Saharan silver ants which regulate their body temperatures in the scorching desert heat and also from the cooling properties of clay. This research would significantly scale down the usage of AC and other cooling devices in warm places, thus reducing the use of electricity and emission of greenhouse gases to the environment. As this cloth would be environment friendly with long durability and cost-efficiency, Sreelekha hopes that this research would bridge the socioeconomic divide of haves and have-nots between communities.
Explanation of the Research in Layperson’s Terms :
Using room conditioning AC during these times, especially with lower temperatures is very risky. Virus spread with closed circulated air or prolonged cold temperatures while breathing, so thus using air conditioning is bad. With this in mind, we need an efficient way of cooling in the snoring temperatures. We propose developing a fabric that integrates clay (Its primary mineral is kaolinite; clay may be generally described as 40% aluminium oxide, 46% silicon oxide, and 14% water.) in its synthesis; clay is known for its cooling properties given enough water to retail and proper reflection techniques for heat throughout the fabric inspired from uniquely shaped hairs with triangular cross-sections as in arrangement employed by the Saharan silver ants. This model not only conserves energy compared to room cooling but also is very practical, wherein we can dampen the fabric with the least water and retain its cooling for long hours. This Fabric could be employed in a variety of settings, for example, in making carpets and curtains in a house to keep the room temperature regulated.
Practical Implementation and Social Implications:
The research would significantly scale down the usage of AC and other cooling devices in warm places, thus reducing the use of electricity and emission of greenhouse gases to the environment. As this cloth would be environment friendly with long durability and cost-efficiency, Sreelekha hopes that this research would bridge the socioeconomic divide of haves and have-nots between communities.
The Title of Patent in the Citation Format
“A fibre material with moisture retention capacity with thermal tolerance and a method for manufacture of the same” with Application Number: 202141023375
Collaborations:
Prof. Seeram Ramakrishna, Professor of Materials, National University of Singapore
Future Research Plans:
The forthcoming endeavour encompasses the commercialisation of this pioneering concept to render it widely accessible and applicable on a larger scale.
Continue reading → - 1st Research Scholar’s Summit: A Symposium of Ideas and Innovation April 15, 2024
“The very idea of a platform such as this is to promote multidisciplinary collaborative research,” emphasised Prof. K Hemachandra Reddy, Chairman, Andhra Pradesh State Council of Higher Education (APSCHE), encapsulating the spirit of the 1st Research Scholar’s Summit hosted at SRM University-AP in partnership with the Government of Andhra Pradesh. The event was staged to reinforce research within academic circles and herald a new phase of learning. The summit was attended by esteemed dignitaries like Prof. Korukonda Babji, Vice Chancellor Dr Y S R University of Health Sciences; Prof. Ramesh Srikonda, Director-School of Planning and Architecture; Dr M Balakrishnan, IIT, Delhi, along with Vice Chancellor, Prof. Manoj K Arora; Registrar, Dr R Premkumar, Deans, Faculty, and Students.
In his keynote address, Vice Chancellor Prof. Arora emphasised the pivotal role of such summits in fostering a conducive environment. He stated, “We live in a world of collaborations, and a summit like this gives an opportunity to interact, establish partnerships and forge scholarly excellence”. He highlighted the varsity’s research acumen in the form of patents, technology transfers, research publications, start-ups, and incubations. He also declared that the varsity would be open to sharing its state-of-the-art research infrastructure among the broader demography in order to foster a research mindset among all.
Prof. Ranjit Thapa, Dean-Research at the university, highlighted the participation of 150 PhD scholars from diverse institutions. His speech reflected the tireless commitment to building the university’s scientific fortitude. Prof. Srikonda underscored the significance of technological advancement and innovation. He praised the summit for being a stage that will offer pragmatic solutions to societal challenges and commended its tagline – “Inspire, Ignite, Innovate,” for aligning with its core objectives.
Prof. Korukonda Babji and Prof. M Balakrishnan, pivotal figures in academia, articulated the transformative role of cutting-edge research in elevating society. They emphasised the potential of such forums in catalysing groundbreaking changes in research.
The summit showcased presentations from doctoral scholars, encompassing 60 poster presentations and 90 oral presentations, organised across 8 thematic areas. The summit concluded with a valedictory function, and tokens of appreciation were presented to the dignitaries by the Vice Chancellor, Registrar, Deans, and convenors, Dr Ramanjaneya Reddy and Dr Sabyasachi Chakrabortty, and members of the organising committee.
Continue reading → - Revolutionising Energy Harvesting: Dr Banee Banadana Receives Patent for Innovative System April 15, 2024

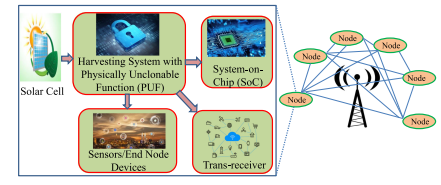
Dr Banee Bandana Das, Assistant Professor in the Department of Computer Science and Engineering, has achieved a remarkable milestone. The invention titled “An Energy Harvesting System for Node Devices and a Method Thereof” has been granted a patent by the Patent Office Journal, under Application Number: 202241066526. This achievement marks a significant leap forward in the realm of energy harvesting systems, promising a brighter and more secure future for IoT applications.
Abstract
The present invention is broadly related to design of secure and Trojan Resilient energy harvesting system (EHS) for IoT end node devices. The objective is to develop a state-of-the-art energy harvesting system which can supply uninterrupted power to the sensors used in IoT. The EHS is self-sustainable. The higher bias voltages are generated on chip. The system is mainly consisting of security module, power conditioning module, Trojan Resilient module, and load controller module. The power failure of the sensors used in IoT may leads to information loss thereby causing catastrophic situations. An uninterrupted power supply is a must for smooth functioning of the devices in IoT. This invention caters secure power requirements with security issues of IoT end node devices.
Practical Implementation:
The IoT end node devices needs 24*7 power supply and are very sensitive to attacks made by adversaries before and after fabrication. This invention takes care of the power requirement of end node devices with green energy and secure the EHS-IC from adversaries and attacks and therefore can be used by individuals, as powering sensors at remote locations and as part of smart agriculture.
Future research plans:
Design more secure and reliable design for making a IoT smart node smarter and self-Sustainable. Exploring more circuit level techniques and find new way to design more power efficient designs.
Continue reading → - 1st Research Scholar’s Summit at SRM University-AP A Symposium of Ideas and Innovation April 15, 2024
The Hindu
Continue reading →

The New Indian Express

The Hans India

Andhra Jyothi

Andhra Patrika

Eenadu

Visalaandhra

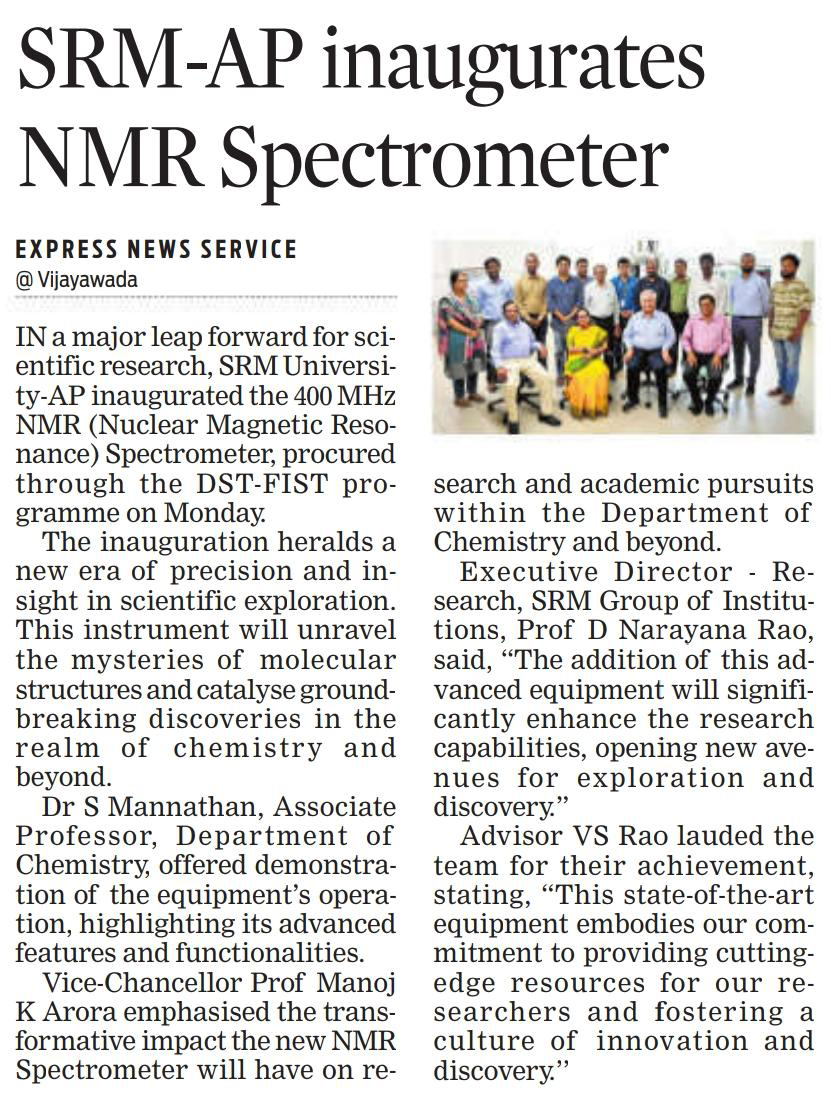
- Inauguration of NMR Spectrometer Marks a Milestone in SRM University-AP’s Research Capabilities April 15, 2024
The Hindu
Continue reading →

The Hans India

The Pioneer

The New Indian Express
Andhra Jyoti

Andhra Patrika

Vartha

Vasalaandhra

Prajasakthi

Surya

- April 15, 2024
Dr Banee Bandana Das, Assistant Professor in the Department of Computer Science and Engineering, has achieved a remarkable milestone. The invention titled “An Energy Harvesting System for Node Devices and a Method Thereof” has been granted a patent by the Patent Office Journal, under Application Number: 202241066526. This achievement marks a significant leap forward in the realm of energy harvesting systems, promising a brighter and more secure future for IoT applications.
Abstract
The present invention is broadly related to design of secure and Trojan Resilient energy harvesting system (EHS) for IoT end node devices. The objective is to develop a state-of-the-art energy harvesting system which can supply uninterrupted power to the sensors used in IoT. The EHS is self-sustainable. The higher bias voltages are generated on chip. The system is mainly consisting of security module, power conditioning module, Trojan Resilient module, and load controller module. The power failure of the sensors used in IoT may leads to information loss thereby causing catastrophic situations. An uninterrupted power supply is a must for smooth functioning of the devices in IoT. This invention caters secure power requirements with security issues of IoT end node devices.
Practical Implementation:
The IoT end node devices needs 24*7 power supply and are very sensitive to attacks made by adversaries before and after fabrication. This invention takes care of the power requirement of end node devices with green energy and secure the EHS-IC from adversaries and attacks and therefore can be used by individuals, as powering sensors at remote locations and as part of smart agriculture.
Future research plans:
Design more secure and reliable design for making an IoT smart node smarter and self-Sustainable. Exploring more circuit level techniques and find new way to design more power efficient designs.
Continue reading →