Smart algorithm to optimize performance of the heterogeneous multi-cloud network
 Dr Sambit Kumar Mishra
Dr Sambit Kumar Mishra
As the world goes more digital in the future, the dependability on cloud computing is going to be more. The availability of high-capacity networks, low-cost computers and storage devices as well as the widespread adoption of hardware virtualization, service-oriented architecture and autonomic and utility computing has led to growth in cloud computing. But is it enough? How to improve its performance? How to make it more reliable with high-end technology and impeccable performance quality? Dr Sambit Kumar Mishra’s research has an answer to that.
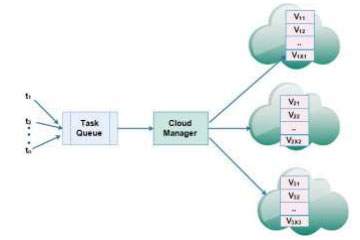 System Model for Multi-cloud Networks Dr Sambit Kumar Mishra, Assistant Professor, Computer Science and Engineering has published a paper “Energy-Aware Task Allocation for Multi-Cloud Networks” in renowned journal IEEE ACCESS with an Impact Factor: 3.745. The research was done in collaboration with Dr Sonali Mishra, SOA (Deemed to be) University Bhubaneswar, India; Dr Ahmed Alsayat, College of Computer and Information Sciences Jouf University, Al-Jouf, Saudi Arabia; Dr N Z Jhanjhi and Dr Mamoona Humayun, School of Computer Science and Engineering (SCE), Taylor’s University, Malaysia; Dr Ashish Kr. Luhach, The PNG University of Technology, Papua New Guinea Lae, Morobe; Dr Kshira Sagar Sahoo, VNRVJIET, Hyderabad, India.
System Model for Multi-cloud Networks Dr Sambit Kumar Mishra, Assistant Professor, Computer Science and Engineering has published a paper “Energy-Aware Task Allocation for Multi-Cloud Networks” in renowned journal IEEE ACCESS with an Impact Factor: 3.745. The research was done in collaboration with Dr Sonali Mishra, SOA (Deemed to be) University Bhubaneswar, India; Dr Ahmed Alsayat, College of Computer and Information Sciences Jouf University, Al-Jouf, Saudi Arabia; Dr N Z Jhanjhi and Dr Mamoona Humayun, School of Computer Science and Engineering (SCE), Taylor’s University, Malaysia; Dr Ashish Kr. Luhach, The PNG University of Technology, Papua New Guinea Lae, Morobe; Dr Kshira Sagar Sahoo, VNRVJIET, Hyderabad, India.
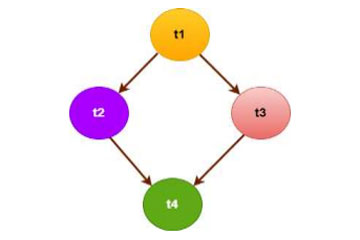 Example of Direct Acyclic Graph (DAG)with four TasksIn recent years, the growth rate of Cloud computing technology is exponentially, mainly for its extraordinary services with expanding computation power, the possibility of massive storage and all other services with the maintained quality of services (QoS). The task allocation is one of the best solutions to improve different performance parameters in the cloud, but when multiple heterogeneous clouds come into the picture, the allocation problem becomes more challenging. This research work proposed a resource-based task allocation algorithm. The same is implemented and analysed to understand the improved performance of the heterogeneous multi-cloud network. The proposed task allocation algorithm (Energy-aware Task Allocation in Multi-Cloud Networks (ETAMCN)) minimizes the overall energy consumption and also reduces the makespan. The results show that the makespan is approximately overlapped for different tasks and does not show a significant difference. However, the average energy consumption improved through ETAMCN is approximately 14%, 6.3%, and 2.8% in opposed to the random allocation algorithm, Cloud Z-Score Normalization (CZSN) algorithm, and multi-objective scheduling algorithm with Fuzzy resource utilization (FR-MOS), respectively. An observation of the average SLA-violation of ETAMCN for different scenarios is performed.
Example of Direct Acyclic Graph (DAG)with four TasksIn recent years, the growth rate of Cloud computing technology is exponentially, mainly for its extraordinary services with expanding computation power, the possibility of massive storage and all other services with the maintained quality of services (QoS). The task allocation is one of the best solutions to improve different performance parameters in the cloud, but when multiple heterogeneous clouds come into the picture, the allocation problem becomes more challenging. This research work proposed a resource-based task allocation algorithm. The same is implemented and analysed to understand the improved performance of the heterogeneous multi-cloud network. The proposed task allocation algorithm (Energy-aware Task Allocation in Multi-Cloud Networks (ETAMCN)) minimizes the overall energy consumption and also reduces the makespan. The results show that the makespan is approximately overlapped for different tasks and does not show a significant difference. However, the average energy consumption improved through ETAMCN is approximately 14%, 6.3%, and 2.8% in opposed to the random allocation algorithm, Cloud Z-Score Normalization (CZSN) algorithm, and multi-objective scheduling algorithm with Fuzzy resource utilization (FR-MOS), respectively. An observation of the average SLA-violation of ETAMCN for different scenarios is performed.
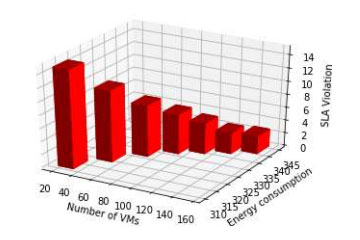 Energy Consumption Vs SLA Violation when
Energy Consumption Vs SLA Violation when
the number of VMs varies and the number of Task is 100.The multi-cloud strategy offers flexibility to service providers. It allows businesses to be productive while using the proper set of services to optimize their opportunities. Adopting a multi-cloud network enables an enterprise to implement a “best of breed” model for the services. Organizations’ ability to choose the vendor that offers the best price for their workload is added significant advantage of multi-cloud. Thus, the optimization of energy consumption in a multi-cloud environment is necessary for the current generation.
However, this proposed work has not considered any priority-oriented users, such as task execution through reserve resource in the network, which will be considered as his future work. The future work also aims to propose a task cum resource-aware scheduling approach that will exploit the nature of the presented workload and efficiently map on the available Cloud resources so that energy consumption will optimize.
Link to the research paper: Please Click Here

