 Dr Satish Anamalamudi, Assistant Professor, in the Department of Computer Science and Engineering has published a research paper titled “Cooperative Caching Scheme for Machine-to-Machine Information-Centric IoT Networks” in the IEEE Canadian Journal of Electrical and Computer Engineering. The research paper is co-authored by Dr Mohammed Saeed Alkatheiri and Dr Eesa Al Solami of University of Jeddah, Saudi Arabia and Dr Abdur Rashid Sangi of Yibin University, China.
Dr Satish Anamalamudi, Assistant Professor, in the Department of Computer Science and Engineering has published a research paper titled “Cooperative Caching Scheme for Machine-to-Machine Information-Centric IoT Networks” in the IEEE Canadian Journal of Electrical and Computer Engineering. The research paper is co-authored by Dr Mohammed Saeed Alkatheiri and Dr Eesa Al Solami of University of Jeddah, Saudi Arabia and Dr Abdur Rashid Sangi of Yibin University, China.
According to the authors, Information-centric networks (ICNs), a foreseen future Internet architecture, focuses on the application content rather than its hosting location. With this, the existing Internet protocol (IP)-based host-centric communication model can be transformed into a content-centric communication model with the support of in-network caching, name-based routing, and location-independent content domain names. Recently, ICN is proposed to be a potential Internet architecture for Internet-of-Things (IoT) networks due to minimal retrieval delays and reduced load on the data producer. Content retrieval from IoT nodes plays a prominent role in enhancing the performance of the ICN-IoT networks. The in-network caching of ICN enhances the data availability in the network, overcome the issue of single-point failure, and improve IoT devices power efficiency. In this work, the authors explore a cooperative caching scheme for information-centric-IoT networks to optimize the cache hit with the support of a caching network topology model, a content popularity model, and an exogenous request access model.
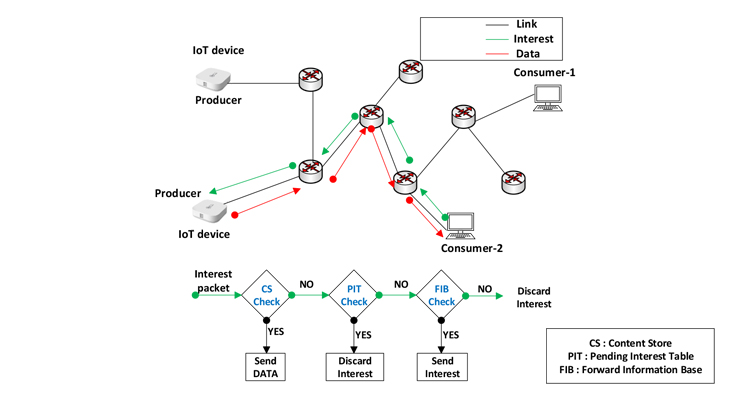 Dr Satish says that ICN proposes to shift the existing complex Internet model to a simple and generic one. This approach considers the content as the first-class network citizen. In ICN, contents are addressed and routed by their unique names and are decoupled from the address of the node storing it. In this way, consumers ask for information by its name rather than its locality address. In ICN, every content is identified by using a unique, persistent and location-independent name. A wide set of IoT applications is inherently information-centric. In fact, the majority of IoT applications target data regardless of its source. For instance, environmental monitoring applications are oblivious to the information origin. ICN is a promising candidate for IoT environments. It can natively support IoT scenarios while improving data dissemination and reducing network complexity.
Dr Satish says that ICN proposes to shift the existing complex Internet model to a simple and generic one. This approach considers the content as the first-class network citizen. In ICN, contents are addressed and routed by their unique names and are decoupled from the address of the node storing it. In this way, consumers ask for information by its name rather than its locality address. In ICN, every content is identified by using a unique, persistent and location-independent name. A wide set of IoT applications is inherently information-centric. In fact, the majority of IoT applications target data regardless of its source. For instance, environmental monitoring applications are oblivious to the information origin. ICN is a promising candidate for IoT environments. It can natively support IoT scenarios while improving data dissemination and reducing network complexity.
Dr Satish Anamalamudi had been a Research Engineer with Huawei Technologies, Beijing, China. He also worked with the Huaiyin Institute of Technology (HYIT), Huai’an, China, until February 2018. He is currently an Assistant Professor with the Department of Computer Science and Engineering, SRM University-AP, Andhra Pradesh. His research interests include the common-control-channel design for MAC and routing protocols in cognitive radio ad hoc networks, MAC, and routing protocol design of Internet of Things (IoT) and 5G networks.
Read the full paper here: https://doi.org/10.1109/ICJECE.2020.3046844

