Predicting Biogas Production Using Time Series Algorithms
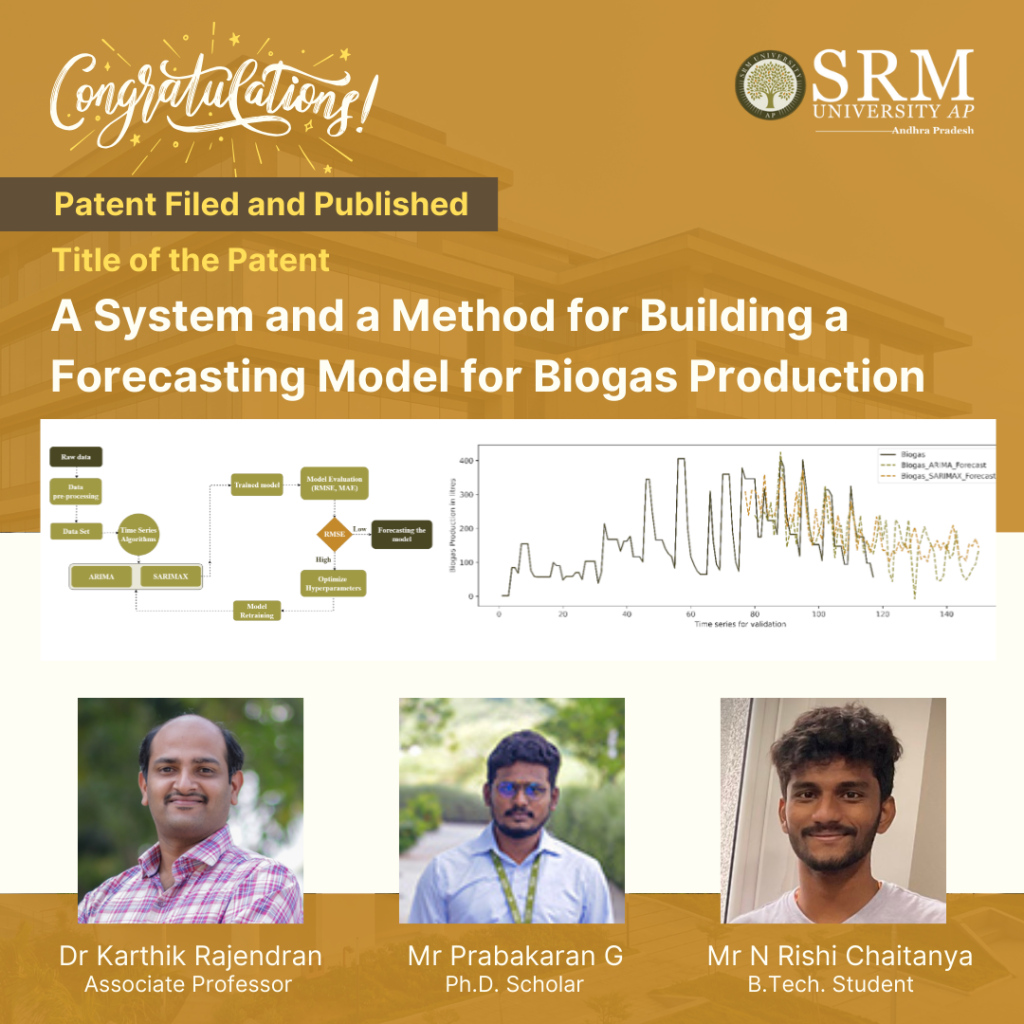
With the advent of the climate crisis, the use of the latest scientific technologies to develop methods for sustainable energy usage is pivotal. Dr Karthik Rajendran, Associate Professor, Department of Environmental Science and Engineering, his PhD scholar Mr Prabakaran G & UG Student Mr Nalluri Rishi Chaitanya Sri Prasad have filed and published a patent titled “A System and a Method for Building a Forecasting Model for Biogas Production” with Application No.: 202341074196, on their radical invention of predicting future biogas production using advanced Machine Learning techniques.
Abstract
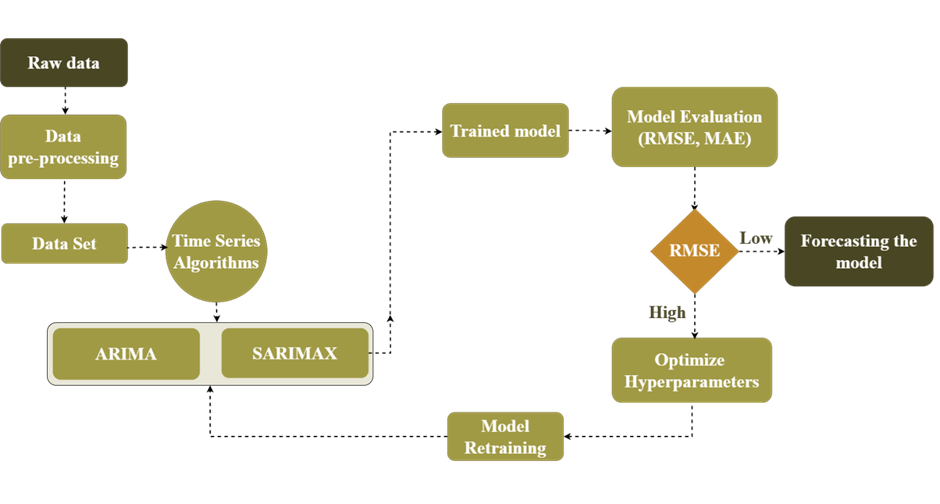
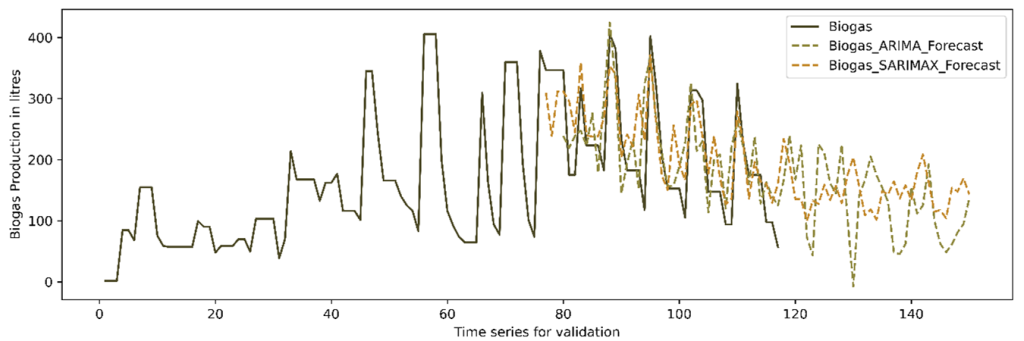
The anaerobic digestion (AD) process poses challenges in maintaining process stability and time series-based prediction and forecasting due to the intricate nature of the system. Process instability is a consequence of the unpredictability in the raw material received at the facility, as well as temperature fluctuations and pH changes resulting from microbiological processes. Consequently, it is necessary to implement constant monitoring and control measures for higher biogas production. The challenges associated with anaerobic digestion (AD) systems can be effectively addressed through the integration of advanced machine learning (ML) algorithms and industry 4.0 systems within biogas facilities. This integration holds the potential to enhance system efficiency and enable on-site control capabilities. Machine learning (ML) based solutions have the potential to enhance process performance in AD facilities, leading to improved system operation and maintenance. The present study focuses on advanced ML techniques, specifically time series algorithms (ARIMA and SARIMAX), which have been employed to forecast daily biogas production. These algorithms are trained to discern critical process parameters and forecast daily biogas production rates, measured in Liters. For forecasting, 117 days of experimental data were used and ARIMA was identified as the best algorithm to forecast the daily production. This algorithm excelled not only in predicting biogas production but also in forecasting yield, resulting in a Root Mean Square Error (RMSE) of 3.26. Furthermore, a comparison between the forecasted values of both ARIMA and SARIMAX was conducted. The predictive ARIMA model underwent statistical validation with unknown data, resulting in a P-value is >0.05.
Explanation of the Research in Layperson’s Terms
This paper focuses on predicting future biogas production using advanced mathematical methods. The researchers used data collected over 117 days of biogas experiments, divided into three periods. They kept track of important factors like methane production, consumed volatile solids, methane percentage in biogas, and initial and final pH levels. To make the predictions more accurate, the researchers addressed missing data and fine-tuned certain parameters using a process called hyperparameter tuning. They wanted to find the best settings for the mathematical models they used, which are called ARIMA and SARIMAX. These models consider patterns and relationships in the data to make predictions. The researchers checked their models’ using measures like AIC and BIC values and examined certain plots to ensure they were getting good results. After applying the models to the data, they were able to predict future biogas production. The accuracy of their predictions was assessed using a metric called RMSE, and they found values of 3.26 for ARIMA and 24.02 for SARIMAX. In simpler terms, these values help us understand how close their predictions were to the actual values. The researchers also did some statistical analysis, and the results showed that both methods (ARIMA and SARIMAX) were equally good at predicting biogas production. Therefore, they concluded that these mathematical models are reliable tools for forecasting biogas production in the future.
Practical Implementation/ Social Implications of the Research
The integration of advanced machine learning (ML) algorithms and Industry 4.0 systems within anaerobic digestion (AD) facilities holds significant promise in addressing the challenges associated with process instability and unpredictability in biogas production. The utilization of ML techniques, particularly time series algorithms like ARIMA (AutoRegressive Integrated Moving Average) and SARIMAX (Seasonal AutoRegressive Integrated Moving Average with eXogenous factors), to forecast daily biogas production presents a practical solution to enhance system efficiency and control.
- Real-time Decision Making
- Reduced Operational Costs
- Published in Departmental News, ENVS News, News, Research News
Understanding the Inflation-Unemployment Dynamics in Canada

The rate of inflation has been termed to be directly proportionate to economic activity, with the increase in economic activity leading to higher levels of inflation. Central Banks have used this relationship to formulate interest rates and understand the inflation–unemployment dynamics in many countries. Dr Adviti Devaguptapu, Assistant Professor from the Department of Economics, has published an interesting study in her paper titled “Phillips Curve in Canada: A Tale of Import Tariff and Global Value Chain”, where she examines the relationship between inflation-economic activity in Canada to better understand the correlation between inflation and unemployment rates.
Abstract
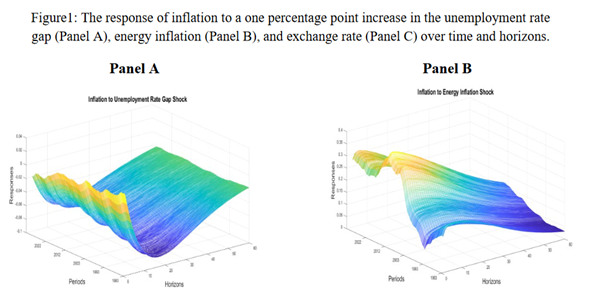
The paper examines the Phillips curve for Canada from June 1976 to October 2022 in a time-varying manner. The findings reveal that the impulse response of inflation to the changes in the unemployment rate gap has reduced over time till 2010 and strengthened thereafter. The response of inflation to the changes in the unemployment rate gap has increased in short and medium horizons after 2010. On further examination, it is found that the changes in both average import tariff and forward participation in the global value chain have reduced the inflation response to the changes in the unemployment rate gap.
Social Implications of the Research
Inflation-targeting central banks should have to put more (less) effort into achieving price stability in the medium run when the change in the level of inflation to the changes in the unemployment rate gap is more (less).
Dr Adviti’s research works towards developing quality-adjusted inflation in India – the need for it and the challenges in recording it.
Link to the article
- Published in Departmental News, Economics Current Happenings, Economics News, News, Research News
Unveiling a Realm of Possibilities in the Field of Material Science
 Dr Sabyasachi Mukhopadhyay, Associate Professor in the Department of Physics at SRM University-AP recently published a paper, titled “Polarity-Induced Morphological Transformation with Tunable Optical Output of Terpyridine–Phenanthro[9,10-d] imidazole-Based Ligand and Its Zn(II) Complexes with I–V Characteristics,” in the prestigious journal “ACS Omega.” Notably, “ACS Omega” is a Q1 journal with an impact factor of 4.1. This groundbreaking work delves into the polarity-induced morphological transformations and tunable optical outputs of Terpyridine–Phenanthro[9,10-d] imidazole-based ligands and their Zn(II) complexes. The study also explores their I–V characteristics, contributing valuable insights to the realms of materials science and chemistry.
Dr Sabyasachi Mukhopadhyay, Associate Professor in the Department of Physics at SRM University-AP recently published a paper, titled “Polarity-Induced Morphological Transformation with Tunable Optical Output of Terpyridine–Phenanthro[9,10-d] imidazole-Based Ligand and Its Zn(II) Complexes with I–V Characteristics,” in the prestigious journal “ACS Omega.” Notably, “ACS Omega” is a Q1 journal with an impact factor of 4.1. This groundbreaking work delves into the polarity-induced morphological transformations and tunable optical outputs of Terpyridine–Phenanthro[9,10-d] imidazole-based ligands and their Zn(II) complexes. The study also explores their I–V characteristics, contributing valuable insights to the realms of materials science and chemistry.
Abstract
Self-assembled nanostructures obtained from various functional π-conjugated organic molecules have been able to draw substantial interest due to their inherent optical properties, which are imperative for developing optoelectronic devices, multiple-color-emitting devices with color-tunable displays, and optical sensors. These π-conjugated molecules have proven their potential employment in various organic electronic applications. Therefore, the stimuli-responsive fabrication of these π-conjugated systems into a well-ordered assembly is extremely crucial to tuning their inherent optical properties for improved performance in organic electronic applications.
To this end, herein, we have designed and synthesized a functional π-conjugated molecule (TP) having phenanthrol [9,10-d] imidazole with terpyridine substitution at the 2 position and its corresponding metal complexes (TPZn and (TP)2Zn). By varying the polarity of the self-assembly medium, TP, TPZn, and (TP)2Zn are fabricated into well-ordered superstructures with morphological individualities. However, this medium polarity-induced self-assembly can tune the inherent optical properties of TP, TPZn, and (TP)2Zn and generate multiple fluorescence colors.
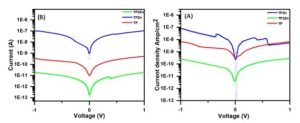
Particularly, this property makes them useful for organic electronic applications, which require adjustable luminescence output. More importantly, in a 10% aqueous-THF medium, TPZn exhibited H-type aggregation-induced white light emission and behaved as a single-component white light emitter. The experimentally obtained results of the solvent polarity-induced variation in optical properties as well as self-assembly patterns were further confirmed by theoretical investigation using density functional theory calculations. Furthermore, we investigated the I− V characteristics, both vertical and horizontal, using ITO and glass surfaces coated with TP, TPZn, and (TP)2Zn, respectively, and displayed maximum current density for the TPZn-coated surface with the order of measured current density TPZn > TP > (TP)2Zn.
This observed order of current density measurements was also supported by a direct band gap calculation associated with the frontier molecular orbitals using the Tauc plot. Hence, solvent polarity-induced self-assembly behavior with adjustable luminescence output and superior I−V characteristics of TPZn make it an exceptional candidate for organic electronic applications and electronic device fabrication.
Research Explanation
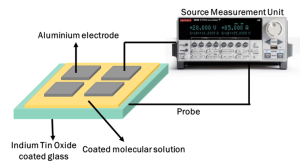
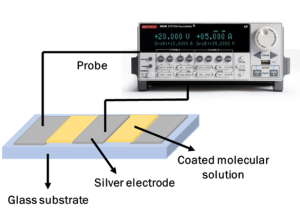
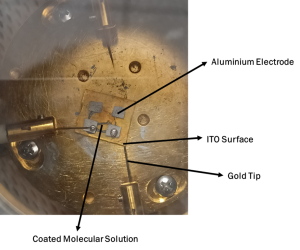
Our investigation is based on the electron transport characteristics of molecules (voltage vs. current), which allows us to ascertain the molecule’s conductive capacities. The Janis probe station, which has four gold tips total is the primary instrument utilized in this investigation. To investigate the properties of electron transport, two gold tips were used: one in contact with an aluminum electrode and the other with an ITO surface. The current measurements for a given voltage of given molecules have been studied using a source measuring unit.
Application
- Our research study can be applicable to predict the good electron and hole transport layers for the Organic Light Emitting Diode (OLED) application.
- Organic field effect transistor (OFET) applications.
Collaborations
Dr. Priyadip Das, Associate Professor, Department of Chemistry,SRMIST
Pictures related to research
- Published in Departmental News, News, Physics News, Research News
Scholarly Exploration into Nuanced Portrayal of Human Experiences
 Dive into the realms of contemporary literature as our esteemed faculty members, Dr Partha Bhattacharjee and Dr Bidisha Pal from the Department of Literature and Languages presented their latest research endeavor. Their collaborative paper, titled “Transcending the Trouble, Trauma, and Pain of Failed Marriage and Closeted Sexuality in Indian Web Series Made in Heaven,” has found its home in the prestigious journal “Quarterly Review of Film and Video” (Scopus Q2).This scholarly exploration take into the portrayal of human experiences in the context of failed relationships and concealed identities within the framework of Indian web series. Join us in celebrating their insightful contributions to the literary discourse, reflecting SRM AP’s commitment to advancing knowledge and fostering academic excellence.
Dive into the realms of contemporary literature as our esteemed faculty members, Dr Partha Bhattacharjee and Dr Bidisha Pal from the Department of Literature and Languages presented their latest research endeavor. Their collaborative paper, titled “Transcending the Trouble, Trauma, and Pain of Failed Marriage and Closeted Sexuality in Indian Web Series Made in Heaven,” has found its home in the prestigious journal “Quarterly Review of Film and Video” (Scopus Q2).This scholarly exploration take into the portrayal of human experiences in the context of failed relationships and concealed identities within the framework of Indian web series. Join us in celebrating their insightful contributions to the literary discourse, reflecting SRM AP’s commitment to advancing knowledge and fostering academic excellence.
Abstract
Premiered as a television web series on Amazon Prime Video on 8th March 2019, Made in Heaven (2019) simultaneously unmasks the hypocrisies and lies of the big fat Indian weddings and breaks the taboo of homosexuality. In consecutive nine episodes, the plots and the subplots are beaded together to initiate a sensory sensitization towards the hypocrisy of marriages and insensitive homophobia. Carefully analyzing postulates from theorists this short article attempts to decode the trouble, trauma, and pain encoded in messy lifestyles, marriages, and relationships characterizing and wielding the lives as well as the sexuality of the characters in the web series
Explanation in Layperson’s Terms
The research revolves around the concept of marriage in Indian society as well as homosexuality in the Indian Hindi web series Made in Heaven (2019). The research shows how the various episodes of the web series showcase different aspects of marriage and the actual reality behind the pomp and pleasure of high-profile weddings within society. On the other hand sexuality and sexual desire are often hidden and do not get proper channelization in a person’s life. The desire thus remains suppressed and results in crisis in many forms. There are other intertwined concerns such as the dowry system, social disparity, impotency, virginity, and sexual molestations which weave a meta-narrative on the popular medium and raise consciousness regarding how people should react to those hazards and behave accordingly.
Practical Implementation and Social Implications of the Research
The research involves practical aspects such as the dowry system, social disparity, impotency, virginity, and sexual molestations which are part of our social lives. Many people have to face such things in their day-to-day lives. This research brings out such realities of society while analyzing the mental condition and psychology behind these. Moreover, this research also shows marriage is an important decision in a person’s life, it should be made in terms of love and respect, not based upon money and social status. The research visits practical examples and revisits the laws to substantiate the arguments. Popular media such as web series is not just a form of entertainment, but it can be a medium for building awareness.
- Published in English Current Happenings, News, Research News
A Research On Examining Stress Among Adolescents

The research paper titled “The Adolescence Stress Scale: Development and Standardization” is a significant contribution to the field of psychology. The paper by Dr Sandra Roshni Monteiro, Assistant Professor at the Department of Psychology in SRM University-AP featured in The Journal of Indian Association for Child and Adolescent Mental Health and provides a detailed account of the development and standardisation of the scale, highlighting its importance and relevance. Dr Monteiro has developed a comprehensive stress scale that aims to evaluate the psychometric issues faced by school-going adolescents.
Here’s a brief extract of the paper.
Abstract
Background/Aim
The objective of the paper was to develop a comprehensive “Adolescence Stress Scale” and to examine different psychometric issues in the development, initial validation, and standardization of this scale.
Method
Exploratory factor analysis was conducted on the data procured from a sample of 634 (11–18 years) school-going adolescents in India.
Results
An exploratory analysis provided a 10-factor structure, namely, major loss-induced stress, enforcement or conflict-induced stress, phobic stress, interpersonal conflict-induced stress, punishment-induced stress, illness and injury-induced stress, performance stress, imposition-induced stress, insecurity-induced stress, and unhealthy environment-induced stress. The 10 oblique factor solutions are found to be interrelated and interdependent with good indices of internal consistency, and content validity.
Conclusions
This scale development is a novel and powerful measure that taps onto various aspects of stress experienced by school-going adolescents. The scale can facilitate researchers, clinicians, and teachers to identify and quantify the significant sources of stress in adolescents in school, or clinic settings.
- Published in Departmental News, News, Psychology News, Research News
SLP-E: Enhancing Privacy and Lifespan in WSNs for IoT
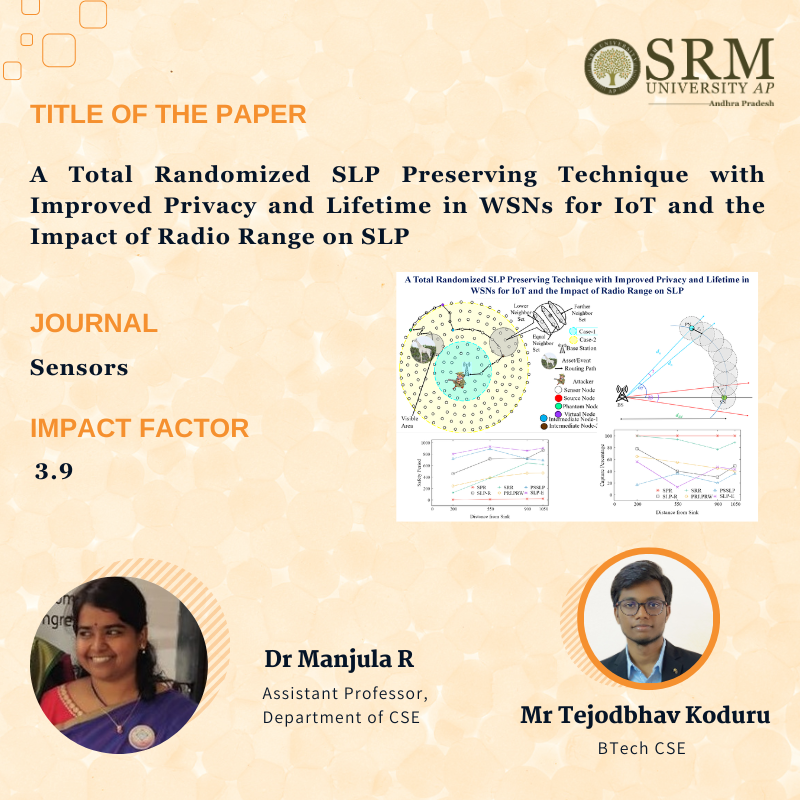
The Department of Computer Science and Engineering is thrilled to share that the paper titled, “A Total Randomized SLP Preserving Technique with Improved Privacy and Lifetime in WSNs for IoT and the Impact of Radio Range on SLP” has been published by Dr Manjula R, Assistant Professor, Department of CSE, and BTech-CSE Student Mr Tejodbhav Koduru in “Sensors“, a Q2 journal, having an Impact Factor of 3.9. Their research addresses the critical need for improved source location privacy and extended network longevity, presenting a pioneering solution known as Source Location Privacy with Enhanced Privacy and Network Lifetime (SLP-E).
Abstract
SLP-E utilises a unique combination of techniques, including a reverse random walk, a walk on annular rings, and min-hop routing, to diversify routing pathways within the network. Unlike existing SLP techniques that either prioritize privacy over network lifetime or vice versa, this approach aims to simultaneously enhance safety period, network lifetime, and privacy uniformly. Notably, this research also explores the impact of sensor radio range on Network Lifetime metrics and privacy strength within the context of SLP in WSN.
Practical Implementation/Social Implications of the research
This research holds real-world significance, especially in scenarios like protecting a lone white giraffe in Kenya fitted with a GPS tracker. Poachers pose a serious threat to such animals, hacking GPS devices to locate and harm them. This solution offers a viable approach to mitigate these threats, providing practical implications for the conservation of endangered species.
Collaborations
- Mr Tejodbhav Koduru from SRM University-AP
- Prof. Raja Datta from IIT Kharagpur
- Ms Florence Mukamanzi, Dr Damien Hanyurwimfura and Prof. Mukanyiligira Didacienne from the African Center of Excellence in the Internet of Things, University of Rwanda
- Published in CSE NEWS, Departmental News, News, Research News
Paper Presented at the NIAS Conference in Amsterdam

Dr Bikku, Assistant Professor, Department of Liberal Arts has presented a paper titled “Mobile Pastoralism and Conservation in the 21st Century: A Case Study from India” at the NIAS Conference on Belonging & Mobility, held at the Netherlands Institute for Advanced Study (NIAS), Amsterdam, Netherlands on October 18-20, 2023 (online).
Congratulations to Dr Bikku for this remarkable achievement. SRM AP immense pride in the success of its faculty and scholars and applauds their unwavering commitment to scientific excellence and societal impact!
Abstract
The study focuses on the struggle of nomadic pastoralists to continue their traditional occupation of raising livestock at different landscapes in the face of the shifting political ecology in India. Pastoralism is a traditional subsistence livelihood pattern that involves raising domestic animals in different pastures. For pastoralists to use continually shifting resources in a variety of ecological landscapes, mobility is an effective strategy. However, the current conservation approach has colonial roots and reinforces biodiversity conservation by establishing and enforcing protected areas in several countries around the globe. Scientific conservationists and states have often seen pastoralism responsible for environmental degradation and wildlife decline through over-grazing and resource competition, respectively. As a result, the customary rights of the various pastoralist groups have been denied inside and outside the protected areas.
The paper investigates the current global conflicts between pastoralism and conservation. It also emphasises the changing dimensions of mobile pastoralism and conservation policies in India. By challenging the conservationists’ and the state’s preconceived notions about pastoralism, the Raika mobile pastoralists of Rajasthan, India, provide sustainable pastoralism and nature conservation through evidence of the coexistence of pastoralism and multispecies.
- Published in Departmental News, Liberal Arts News, News, Research News
Using Nonlinear Differential Equations to Formulate a Novel Approach to Combat HIV-1

The combat against HIV, the virus responsible for AIDS has witnessed consistent advancements and studies put forward by researchers in various fields. To identify a more intelligent and effective approach to combat HIV-1 and enhance the understanding of the workings of its treatments, Dr Koyel Chakravarty, Assistant Professor, Department of Mathematics has published a paper titled “Mathematical modelling of HIV-1 transcription inhibition: a comparative study between optimal control and impulsive approach” in the Q2 journal, Journal of Computational and Applied Mathematics.
Abstract
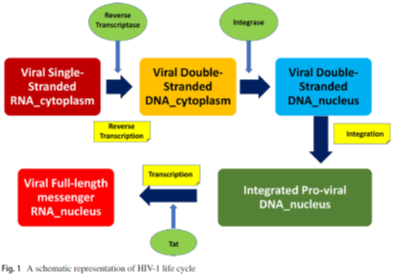
By adopting a proactive strategy, this study facilitates the interaction with human immunodeficiency virus type I (HIV-1), successfully navigating its sequential fusion stages. This approach enables efficient infiltration of the virus into a target CD4+T helper cell within the host organism, initiating the virus’s replication cycle. As a retrovirus, HIV-1 orchestrates the conversion of its single-stranded viral RNA genome into a more stable double-stranded DNA structure. The newly formed DNA integrates with the host cell’s genetic material, and the pro-viral DNA transforms into functional messenger RNA (mRNA) with the assistance of the host enzyme RNA polymerase II (Pol II).
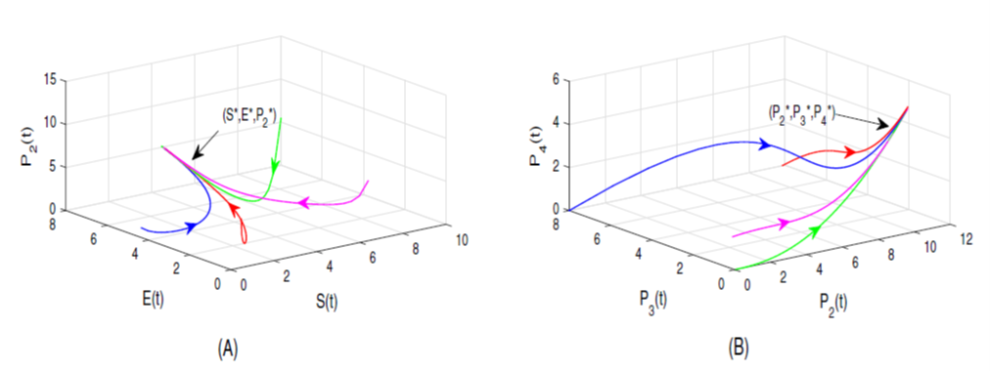
The ongoing research focuses on constructing a meticulous mathematical framework using a system of nonlinear differential equations. The investigation aims to assess the impact of a Tat inhibitor on suppressing the transcriptional activity of HIV-1, treating it as an optimal control problem. The study also evaluates the Tat inhibitor’s efficacy as a potential therapeutic intervention for HIV-1 infection. Employing a one-dimensional impulsive differential equation model to determine the mathematically derived maximum concentration of the elongating complex (P2), the research considers the crucial aspect of optimal timing between successive dosages. A comparative analysis contrasts the effects of continuous dosing with impulse dosing of the Tat inhibitor, using numerical analysis to evaluate outcomes. The findings underscore the superior effectiveness of impulsive dosing over continuous dosing in inhibiting HIV-1 transcription. Visual representations of the model’s parameter sensitivities enhance understanding of the intricate physiological and biochemical processes within the system.
Practical implementation/social implications of the research
1. Treatment Optimization:
• Practical Implementation: Develop personalized treatment plans for individuals with HIV-1 based on the optimal control and impulsive approaches identified in the study.
• Social Implication: Improve the effectiveness of HIV-1 treatments, potentially leading to better health outcomes and a higher quality of life for individuals living with the virus.
2. Drug Administration Guidelines:
• Practical Implementation: Provide guidelines for healthcare professionals on the timing and dosage of Tat inhibitors using insights from the comparative study.
• Social Implication: Enhance the efficiency of drug administration, potentially reducing side effects and improving patient adherence to treatment regimens.
3. Public Health Planning:
• Practical Implementation: Incorporate the study’s findings into public health planning, considering the optimal and impulsive control strategies in broader HIV-1 prevention and treatment programs.
• Social Implication: Contribute to more effective and resource-efficient public health interventions, potentially reducing the overall burden of HIV-1 in communities.
4. Drug Development Strategies:
• Practical Implementation: Inform pharmaceutical companies and researchers about the comparative study results to guide the development of new HIV-1 inhibitors or improvements to existing drugs.
• Social Implication: Accelerate the development of more potent and targeted therapies, offering new options for managing HIV-1 infections.
5. Patient Education:
• Practical Implementation: Develop educational materials for individuals with HIV-1, explaining the importance of adherence to optimized treatment plans based on the study’s findings.
• Social Implication: Empower patients to actively participate in their treatment, potentially leading to better treatment outcomes and reduced transmission rates.
6. Policy Recommendations:
• Practical Implementation: Present policy recommendations to healthcare institutions and government agencies based on the study’s outcomes.
• Social Implication: Influence health policies to integrate the most effective strategies for HIV-1 transcription inhibition, potentially contributing to more efficient resource allocation and improved public health outcomes.
7. Global Health Impact:
• Practical Implementation: Collaborate with international health organizations to disseminate the study’s findings globally.
• Social Implication: Contribute to global efforts in controlling the HIV-1 pandemic, fostering collaboration and knowledge-sharing among nations.
8. Reduced Healthcare Costs:
• Practical Implementation: If the impulsive approach proves more cost-effective, healthcare systems can implement this strategy to potentially reduce the overall cost of HIV-1 treatment
• Social Implication: Alleviate financial burdens on both individuals and healthcare systems, making HIV-1 treatment more accessible
In summary, the practical implementation and social implications of this study extend from optimizing individual treatment plans to influencing global health policies, ultimately contributing to more effective HIV-1 management and improved public health outcomes.
Collaborations
- Prof. D C Dalal, Professor, Department of Mathematics, IIT Guwahati
- Prof. A K Sarkar, Professor, Centre for Mathematical Biology and Ecology, Department of Mathematics, Jadavpur University
- Dr L N Guin, Associate Professor, Department of Mathematics, Visva-Bharati
Future Prospects of the Research
- Mathematical Modelling of Cholesterol Dynamics.
- Mathematical Modelling of Muscle Regeneration.
- Mathematical Modelling of Bone Remodelling
- Mathematical Modelling of Glucose-Insulin Dynamics.
- Mathematical Modelling on HIV-1 Transcription.
- Mathematical Modelling of Population Dynamics for Patients suffering from Diabetes.
- Published in Departmental News, Math News, News, Research News
Intellectual realm of Vaishnava Philosophy and Poetic Aesthetics
 Dr Sayantan Thakur, Assistant Professor in the Department of Literature & Languages have published his research paper, ‘Vaishnava Philosophy and the Poetic Aesthetics: An Analysis of Jayadeva’s Gita Govindam‘ in Tattva: Journal of Philosophy, an esteemed EBSCO-indexed and UGC-CARE Listed Journal. Dr Thakur’s work embodies the spirit of academic rigor and philosophical inquiry. Join us in traversing the landscapes of wisdom, where intellect meets aesthetics, and knowledge transcends boundaries. Explore the rich tapestry of ideas that define SRM University-AP‘s commitment to intellectual excellence.
Dr Sayantan Thakur, Assistant Professor in the Department of Literature & Languages have published his research paper, ‘Vaishnava Philosophy and the Poetic Aesthetics: An Analysis of Jayadeva’s Gita Govindam‘ in Tattva: Journal of Philosophy, an esteemed EBSCO-indexed and UGC-CARE Listed Journal. Dr Thakur’s work embodies the spirit of academic rigor and philosophical inquiry. Join us in traversing the landscapes of wisdom, where intellect meets aesthetics, and knowledge transcends boundaries. Explore the rich tapestry of ideas that define SRM University-AP‘s commitment to intellectual excellence.
Abstract
Literature finds the best expression when literary aesthetics and philosophy run side by side. The former offers the external charm, while the latter inculcates the more profound implication with the aim of providing it with a superior stature and permanence. Jayadeva’s Gitagovindam, being a colossal work in the field of Vaishnava literature, does contain the brilliant juxtaposition of both. This article attempts to show how Jayadeva’s Gitagovindam, a colossal work in the field of Vaishnava literature, does contain the brilliant juxtaposition of both. On the one hand, like a typical lyrical poem, its melodic nature does have a soothing effect and on the other, the use of philosophy instils in it a greater depth and seriousness to uplift itself as a book of devotion and religious inspiration. Moreover, the importance of this Holy Scripture lies in the fact that it not only played a significant role in paving the way to form a new sect in the Vaishnava religion, known as ‘Gaudiya Vaishnavism’, but also showed the later Vaishnava lyricists the art of portraying in words the amorous love of Lord Krishna and Radha with compassion and tears.
Practical implementation and social implications of the research
Cultural Preservation: Understanding and analysing ancient texts like the Gitagovindam helps in preserving cultural and religious heritage. This research can contribute to the preservation and understanding of Vaishnava philosophy and its cultural significance.
Literary Understanding: Analysis of the text can provide insights into the interplay between philosophy and aesthetics in literature. It can be used as a tool for students, scholars, and enthusiasts to comprehend how profound thoughts are conveyed through art and literature.
Religious Studies: It will be valuable for religious scholars and practitioners, shedding light on the philosophical underpinnings of Vaishnavism. It can deepen the understanding of the religious sentiments associated with the worship of Lord Krishna.
Artistic Inspiration: By examining the poetic aesthetics the research might inspire contemporary artists, poets, and musicians in exploring similar thematic elements in their creations. It could lead to the creation of new artistic works that incorporate similar philosophical depth.
Community Understanding: Studies like mine can also bridge gaps in understanding between different communities by shedding light on the beliefs and values encapsulated in ancient texts. This understanding might foster better cultural appreciation and harmony.
Interdisciplinary Insights: The analysis might encourage interdisciplinary studies by merging literary analysis with philosophy, offering new avenues for exploration and collaboration between these fields.
Collaborations
Dr. Uday Kumar Mishra, Professor, Department of English, TMBU
Future Research Plans
- Regional Literature in Translation
- Tantric Tradition and Eastern Indian Literature,
- Folk Music of Bengal,
- Indian Philosophy, Aesthetics & Literature
Link to the Article
https://journals.christuniversity.in/index.php/tattva/article/view/3640/2480
- Published in Departmental News, English Current Happenings, News, Research News
A Novel IRS-relay Network for ITS with Nakagami-m Fading Channels

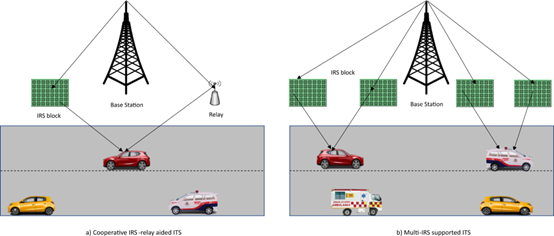
The Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering is proud to announce the publication of a research paper by Dr Sunil Chinnadurai, Assistant Professor and Research scholar Shaik Rajak titled “Novel Energy Efficient IRS-relay Network for ITS with Nakagami-m Fading Channels” in the Q1 journal ICT Express, having an Impact Factor of 5.4. The paper focused on developing an energy-efficient network for ITS that utilises Nakagami-m fading channels to improve communication reliability and efficiency.
In this work, the research duo introduced a cooperative system involving relay technology and an IRS (Intelligent Reflective Surface) with passive elements. Evaluating energy efficiency and achievable rates, they found that the cooperative relay-IRS system outperformed individual relay and IRS setups. The study also compared multi-IRS setups, highlighting their effectiveness in reducing power consumption and deployment costs for improved ITS development.
Abstract
The research paper investigates the performance of energy efficiency (EE) for Intelligent Transportation Systems (ITS) using a cooperative IRS-relay network. The proposed cooperative IRS-relay-aided ITS network integrates an IRS block with a number of passive reflective elements to improve EE. The research analyses the ITS in terms of EE and achievable rate under Nakagami-m fading channel conditions. The research aims to reduce power consumption over long distances and operate the system faster and safer.
Practical implementation/ social implications of the research
The proposed cooperative IRS-relay network for Intelligent Transportation Systems (ITS) has practical implications for improving energy efficiency and achieving higher data rates in ITS networks. Integrating an IRS block with passive reflective elements in the relay model enhances the coverage area and reduces power consumption in ITS. The research highlights the significance of cooperative IRS-relay and multi-IRS-aided networks in the development of ITS, which can contribute to safer and faster transportation.
Dr Chinnadurai and Mr Rajak Future will continue to work on their research focusing on optimizing the design of the cooperative IRS-relay network for ITS to improve energy efficiency and achievable data rates further in real-world scenarios.
- Published in Departmental News, ECE NEWS, News, Research News