Chanakya Karra admitted to PhD at Purdue University, USA
 Once you are a part of SRM University-AP, we ensure that your future is secured! With the guidance of Dr Sujith Kalluri, Assistant Professor, Electronics and Communication Engineering, Mr Chanakya wends his way to Purdue University, USA, a world-renowned research university, for doing his PhD. He secured admission with a full tuition fee waiver and teaching assistantship. Chanakya Karra spent his two years DST-SERB JRF position at SRM AP and has made remarkable contributions to SRM-Amararaja Centre for Energy Storage Devices.
Once you are a part of SRM University-AP, we ensure that your future is secured! With the guidance of Dr Sujith Kalluri, Assistant Professor, Electronics and Communication Engineering, Mr Chanakya wends his way to Purdue University, USA, a world-renowned research university, for doing his PhD. He secured admission with a full tuition fee waiver and teaching assistantship. Chanakya Karra spent his two years DST-SERB JRF position at SRM AP and has made remarkable contributions to SRM-Amararaja Centre for Energy Storage Devices.
DST-SERB JRF position helped Chanakya resume his research career, which had a pause for over a year. “It fills me with immense joy to see the SRM-Amararaja Centre for Energy Storage Devices shape up with every possible equipment to conduct research on batteries. Kudos to the management and the efforts of the faculty associated with the centre,” says Mr Chanakya. He further mentioned that the research work conducted at SRM-Amara Raja Centre enabled him to write over three papers that catapulted his chances of admission.
“I would urge the students to make the best use of the opportunities available at SRM-AP and discuss their plans with the faculty. I am sure new avenues will open with the mentoring of world-class faculty at SRM”, says Mr Chanakya to the junior batches of students aspiring for a research career.
Mr Chanakya expressed his gratitude to the faculty members associated with Amararaja Centre for Energy Storage Devices- Dr Pardha Saradhi Maram, Associate Professor, Chemistry, Dr Surfarazhussain S Halkarni, Assistant Professor, Mechanical Engineering, Dr Laxmi Narayana Patro, Assistant Professor, Physics, and others.
- Published in Chemistry-news, Departmental News, ECE NEWS, Mechanical Engineering NEWS, News, Physics News
Accelerating research in the Quantum-dot Cellular Automata domain
The Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering is glad to announce that our PhD scholar, Mr Vasudeva Bevara and BTech students, Mr Shakamuri Narendra Chowdary and Mr Bolem Venkata Surendra Babu, published a paper titled ‘High performance 2n: 1: 2n Reversible MUX/DEMUX Architecture for Quantum-dot Cellular Automata’ in the international journal ‘Numerical Modelling: Electronic Networks, Devices and Fields (SCI Index)’ under the supervision of Dr Pradyut Kumar Sanki.
Abstract of the Research
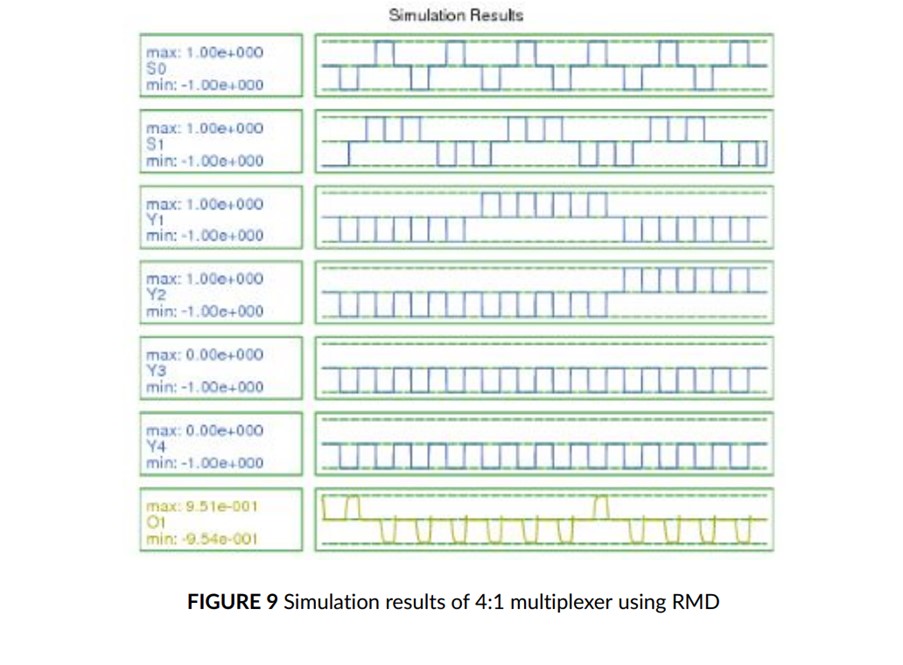
Quantum-dot Cellular Automata (QCA) lead to fundamental changes in nanoscale technology. It promises small area, low power & high-speed structures for digital circuit design. This paper presents efficient low power structures of Reversible Multiplexer & Demultiplexer (RMD) modules based on the QCA technology. The simulation result shows that the proposed RMD modules have utilised less area & low power consumption. The simulation, layout & energy dissipation analysis of the proposed RMD module has been carried out using the QCA Designer-E simulation tool.
Essentially, CMOS is used as a well-known traditional technology in the design of the Very Large-Scale Integration (VLSI) circuits, which leads to the introduction of QCA as new nanotechnology to overcome the limitations of CMOS technology, such as material, physical, power, heat & economic challenges.
In reversible computation, the power dissipation occurs only when the computation is started or when the output is permanently stored. The reversible logic circuits are being investigated to prevent data loss in irreversible logic circuits. The reversible logic circuits provide zero loss of energy/information making the logic circuits the most suitable for QCA nanotechnologies. This has resulted in widespread interest in the design of reversible logic circuits based on QCA over the last few years.
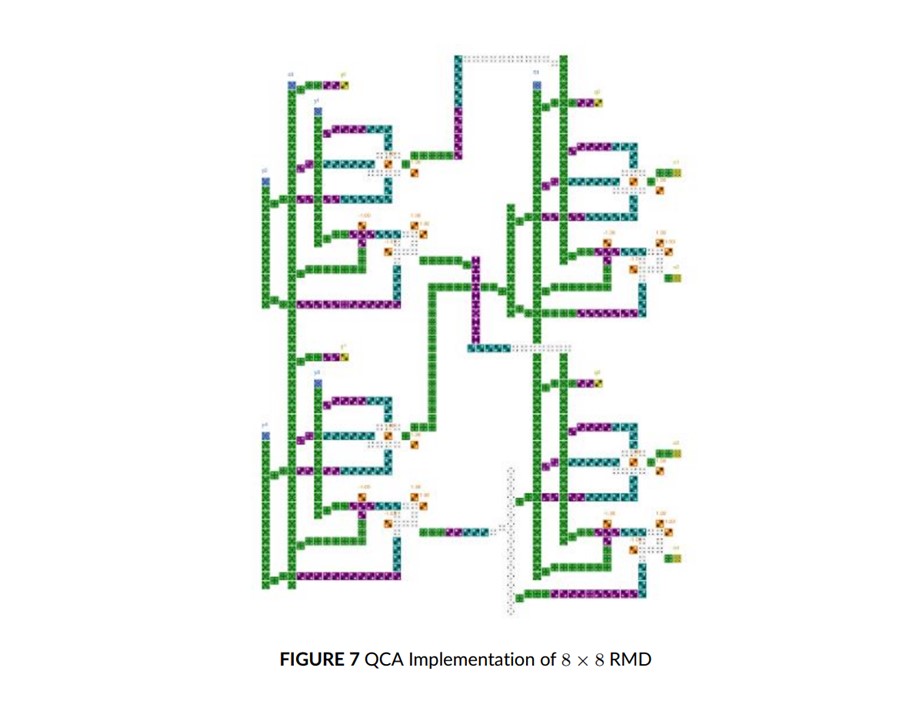
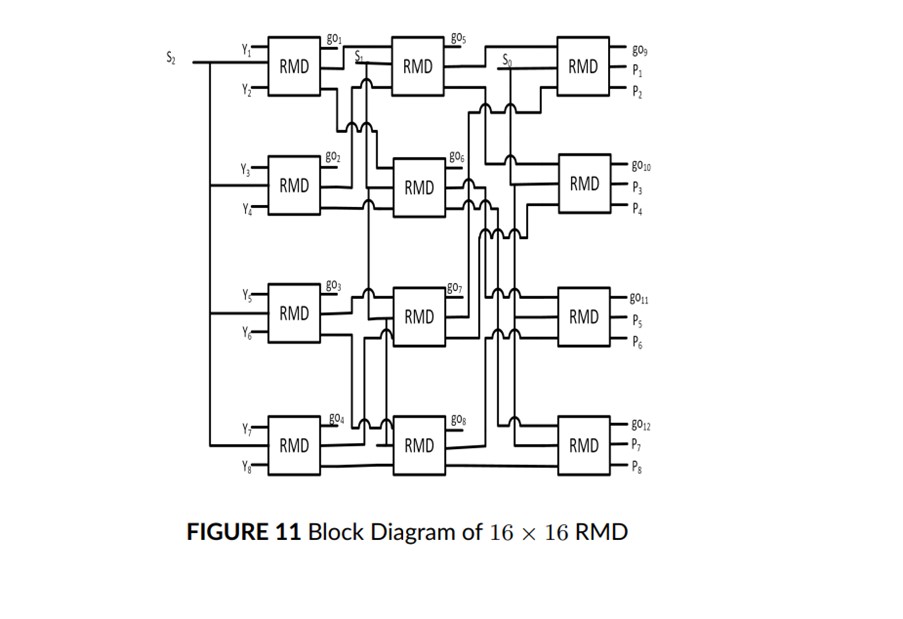
In this paper, a modular 2n: 1 reversible multiplexer & 1: 2n reversible demultiplexer design in a single circuit is proposed. The 2:1 multiplexer & 1: 2 demultiplexer is realised in a single module i.e., 3 × 3 RMD. The 3 × 3 RMD is formed fundamental building block of the modular 2n: 1 reversible multiplexer & 1: 2n reversible demultiplexer design is extended to large RMD design.
Practical Implementations of the Research
This work can push forward research in the QCA domain and overcome the limitations of Complementary Metal Oxide Semiconductor (CMOS) technology. Soon the era of Beyond CMOS will start as the scaling of the current CMOS technology will reach the fundamental limit. QCA (Quantum-dot Cellular Automata) is the transistor less computation paradigm and viable candidate for Beyond CMOS device technology.
So, they have implemented the High Performance 2n: 1: 2n Reversible MUX/DEMUX Architecture for Quantum-dot Cellular Automata compared to other researcher works. In future, the research team would like to explore deeper into QCA technology and design efficient circuits which are small sized, with less cell count and less power consumption.
- Published in Departmental News, ECE NEWS, News, Research News
Launching antenna-multiplexer for seamless IoMT connectivity
Dr Divya Chaturvedi, Assistant Professor, Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering, has come up with an exciting proposal for enhanced connectivity and high-speed data transmission across the Internet of Medical Things (IoMT) devices. Her research paper titled “Design of Antenna-Multiplexer for Seamless On-Body Internet of Medical Things (IoMT) Connectivity” has been published in the journal ‘IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems II: Express Briefs’, having an impact factor of 3.71. It was published in collaboration with Dr Arvind Kumar from Vellore Institute of Technology and Dr Imaculate Rosaline from Ramaiah Institute of Technology, Bangalore.
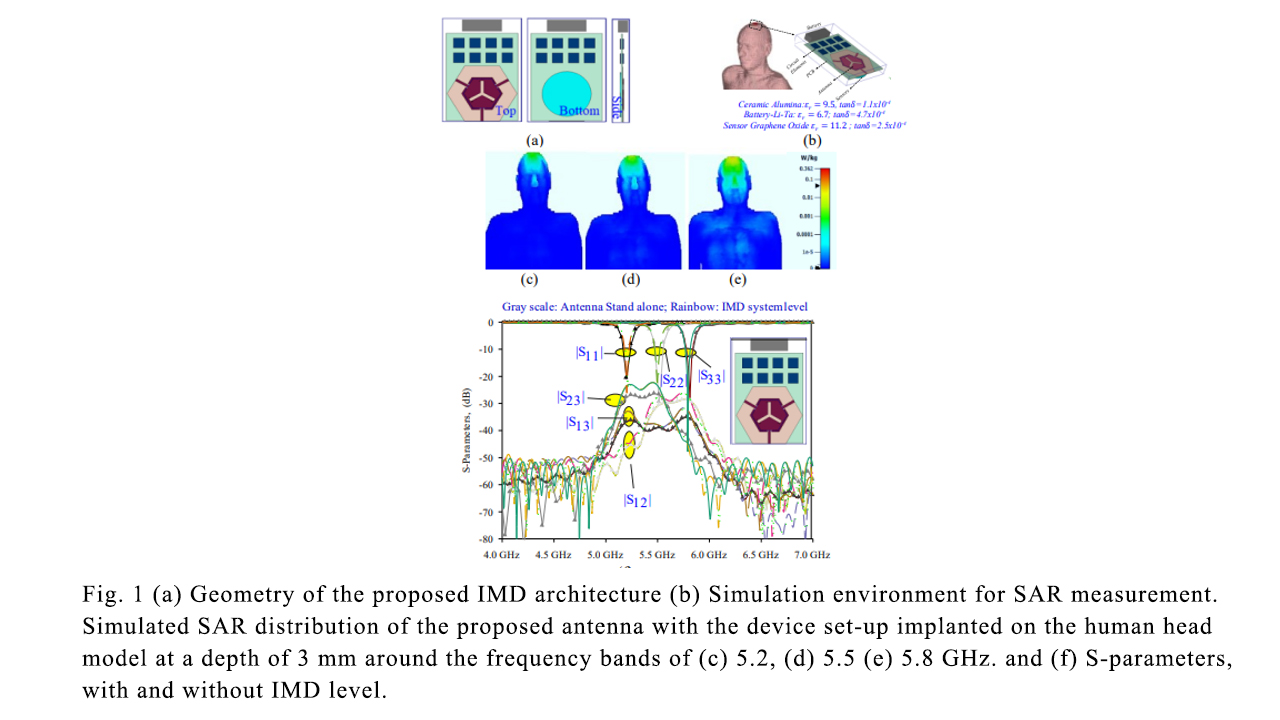
The research looks into the design and development of a multi-band self-triplexing antenna for Medical Things (IoMT) applications. The antenna is designed to operate at 5.2, 5.5 and 5.8 GHz and self-isolation is achieved below -23.9 dB. It also offers seamless communication links to other devices operating at the same frequencies. The designed antenna is cost-effective and compact in size, that can easily fit into any implantable medical device. To avoid the harmful effect of radiation, the SAR value should be <1.6 W/kg. The SAR for this antenna is achieved at 0.362 W/kg in a very simple profile. Due to its compact size, the antenna can be easily mounted in a wireless portable device. The self- triplexing property of the device also enables full-duplex communication between different devices in a single antenna. This design suggestively simplifies the density of the RF front-end subsystem and leads to a simple and efficient communication system.
Abstract of the Research
Here, a compact design of antenna-multiplexer is engineered specifically to meet the stringent requirement imposed by intricate subsystems operating at 5.2, 5.5, and 5.8 GHz frequency bands for Internet of Medical Things (IoMT) applications. The proposed design includes a hexagonal-shaped substrate integrated waveguide (HSIW) cavity, tripole-shaped radiating slot, tuning vias, and three inset microstrip feedlines. A tripole-shaped slot is imprinted on the top of the SIW. This slot subdivides the cavity into trio-radiating segments and each segment offers a single frequency band. Further, the frequency bands are tuned at 5.2/5.5/5.8 GHz. The design maintains mutual port isolation better than 23.9 dB. Compared with the conventional tri-frequency antennas, the proposed design is highly compact and doesn’t need any additional circuitry to improve the port isolations. The measured results confirm the expected performance of the design. Furthermore, the proposed antenna is optimized within an implantable medical device (IMD) and simulated inside a realistic Human Head model at a depth of 3 mm and the Specific Absorption Rate (SAR) value is estimated. The SAR values are well below 0.362 W/Kg at the functioning bands due to the unidirectional radiation pattern from the antenna.
Her future research plan includes designing and developing a cost-effective bra-like prototype of Antenna-Array Sensors for breast cancer detection.
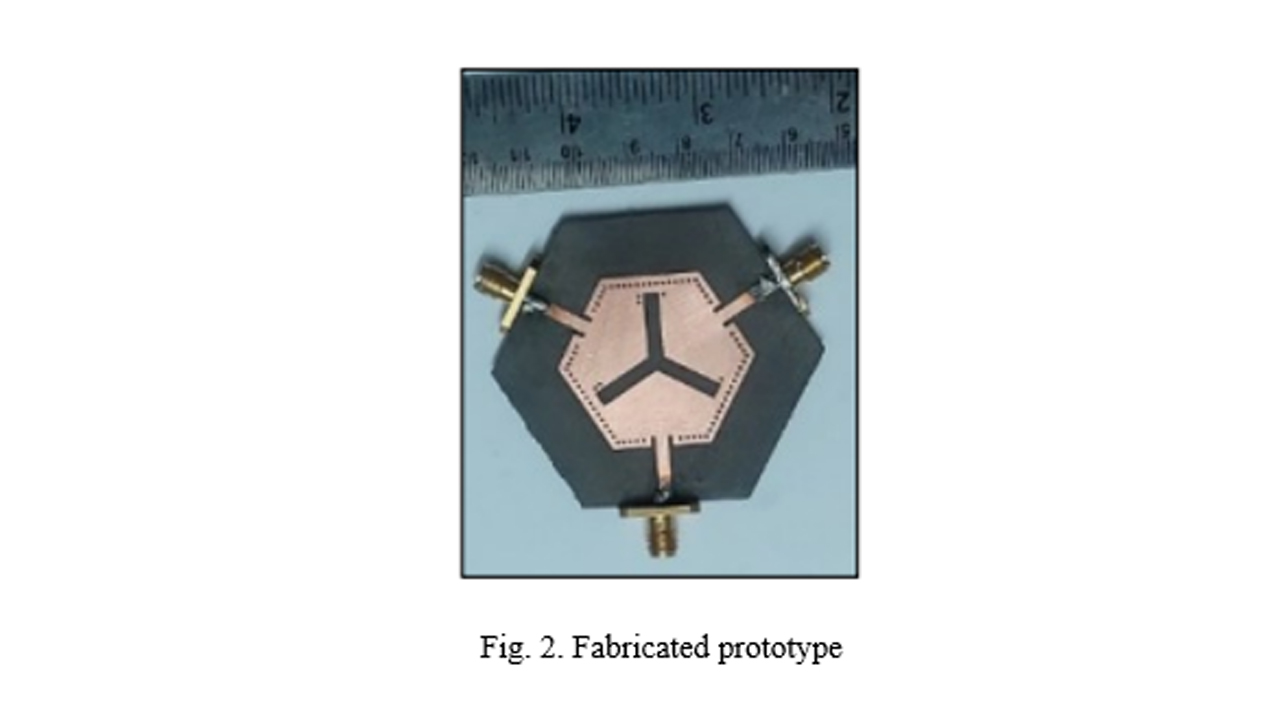
- Published in Departmental News, ECE NEWS, News, Research News
Dr Divya Chaturvedi steps up her research with SERB-POWER grant

Dr Divya Chaturvedi from the Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering has been awarded the SERB-POWER research grant that amounts to a total of 29 lakhs for a period of three years. The grant was sanctioned for her research titled “Development of Breast Cancer Detecting System Based on Microwave Antenna-Array-Sensors and its Implementation to Internet of Medical Things (IoMT)”.
SERB- POWER (Promoting Opportunities for Women in Exploratory Research) research grants is a scheme initiated by the Government of India with an aim to encourage emerging and eminent women researchers for individual-centric and competitive mode of research funding to undertake R&D activities in frontier areas of science and engineering.
Her study on developing a breast cancer detection system has gained immense attention due to the global increase of the malady in recent decades. It has become the most common cancer diagnosed in women across all age groups. Despite the different tests such as Mammograms, ultrasound, and MRI available to diagnose the disease, there has been little considerable improvement in bringing down the caseload.
Dr Divya’s research intends to develop an advanced detection technique based on Antenna-Array-Sensors and she is attempting to put it into implementation through the Internet of Medical Things (IoMT). Connecting the medical devices to healthcare IT systems through online computer networks will allow the easier and quicker detection of the defect. This may go down as a milestone achievement in the medical domain.
The research grant will help in building better- equipped research lab with the most modern amenities and hiring more manpower to fulfil the project objectives. In the words of Dr Divya, “Better research facilities will aid the faculty in performing various experiments. They will save their travelling time to other universities for accessing research infrastructure. The students can also avail the advantage to intensify their research initiatives”. Through the project she envisions to establish a collaborative dedicated research group that will help in fulfilling the various objectives of the project.
- Published in Departmental News, ECE NEWS, Faculty Achievements, News, Research News
Department of ECE publish paper on Fourier holography

A paper titled “Sparse reconstruction for integral Fourier holography using Dictionary Learning method” has been published by Dr Inbarasan Muniraj, Dr Karthikeyan Elumalai and Dr Sunil Chinnadurai – Assistant Professors of Electronics and Communications Engineering at SRM University-AP, along with PhD students Lakshmi Kuruguntla and Vineela Chandra Dodda.
The paper proposes reconstructing holograms from fewer data, thereby reducing the need for processing the complete hologram data, which is otherwise computationally expensive.
Abstract: A simplified method was demonstrated to generate a hologram from multiple two-dimensional (2D) images. Sparse reconstruction was shown using the Sequential Generalised K-means (SGK) algorithm. It is shown that the proposed sparse reconstruction method provides a good hologram quality, in terms of peak signal-to-noise ratio, even under ~90% sparsity.
The paper is written in collaboration with Professor John T Sheridan, Vice-Principal for Research & Innovation – College of Engineering & Architecture, Head of School of Electrical and Electronic Engineering, University College Dublin, Ireland.
Holography has been shown useful for biomedical imaging, cryptography, data storage, and entertainment. The future plans of the research group include extending this approach to other holographic systems such as digital holography and holographic microscopy.
- Published in Departmental News, ECE NEWS, News, Research News
Network resource allocation for emergency management
The focus of the network keeps changing with every generation of communication technology. The 5G era is waiting for the next generation to bring a remarkable revolution in communication technologies. Applying various changes and modifying the drawbacks of 5G technology can help us to improve the features of the upcoming 6G. The Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering is delighted to inform you that the paper, “Network Resource Allocation for Emergency Management based on Closed Loop Analysis” has been published by Dr Udaya Sankar, Assistant Professor, and BTech students; Sai Jnaneswar J and VMVS Aditya, in “ ITU Journal on Future and Evolving Technologies – 2nd special issue on AI and machine learning solutions in 5G and future networks”.
Abstract of the research
 Telecommunication systems being a critical pillar of emergency management, intelligent deployment, and management of slices in an affected area, will help emergency responders. Techniques such as automated management of ML (machine learning) pipelines across the edge and emergency responder devices, usage of hierarchical closed-loops, and offloading inference tasks closer to the edge, can reduce latencies for first responders in case of emergencies. This paper describes the major findings of building a Proof of Concept (PoC) for network resource allocation for emergency management using a hierarchical autonomous artificial intelligence (AI)/ML-based closed-loops in the mobile network, which was organized by the Internal Telecommunication Union Focus Group on Autonomous Network (ITU FGAN). The background scenario for this PoC included the interaction between a higher closed-loop in the Operations Support System (OSS) and a lower closed-loop in RAN (Radio Access Network) to intelligently share RAN resources between the public and emergency responder slice. Representation of closed-loop “controllers” in a declarative fashion (Intent), triggering “imperative actions” in the “underlay” based on the intent, setup of a data pipeline between various components, and methods of “influencing” lower layer loops using specific logic/models, were some of the important aspects investigated by various teams. The main conclusions are summarised in this work, along with the significant observations and limitations from the PoC as well as future directions.
Telecommunication systems being a critical pillar of emergency management, intelligent deployment, and management of slices in an affected area, will help emergency responders. Techniques such as automated management of ML (machine learning) pipelines across the edge and emergency responder devices, usage of hierarchical closed-loops, and offloading inference tasks closer to the edge, can reduce latencies for first responders in case of emergencies. This paper describes the major findings of building a Proof of Concept (PoC) for network resource allocation for emergency management using a hierarchical autonomous artificial intelligence (AI)/ML-based closed-loops in the mobile network, which was organized by the Internal Telecommunication Union Focus Group on Autonomous Network (ITU FGAN). The background scenario for this PoC included the interaction between a higher closed-loop in the Operations Support System (OSS) and a lower closed-loop in RAN (Radio Access Network) to intelligently share RAN resources between the public and emergency responder slice. Representation of closed-loop “controllers” in a declarative fashion (Intent), triggering “imperative actions” in the “underlay” based on the intent, setup of a data pipeline between various components, and methods of “influencing” lower layer loops using specific logic/models, were some of the important aspects investigated by various teams. The main conclusions are summarised in this work, along with the significant observations and limitations from the PoC as well as future directions.
Explanation of the research
 This is a collaborative study where the researchers have developed and implemented a hierarchical closed-loop that autonomously handles an emergency case. This project contains several groups working on separate functions such as monitoring, computing, ML selection, and resource allocation. Some presented how the AI agents and the network can be adapted to assist mobile network users in Search, Diagnostic, and Rescue (SDAR) missions. Some integrated the implementation of the closed loops in O-RAN based software. The researcher’s role in this project is to generate the data which will be used for analysis and this gets integrated with another team. Rather than putting dummy data and analysing or creating and training a machine learning model, we use the Simu5g simulator which is library-based on OMNET++ framework to generate data, mainly resource allocation data. In Simu5g they configure the required network, set all the input parameters such as and simulate it for a specific duration of time. After simulation, the various results are obtained like SINR, throughput, resource block allocation, and many more. This data of the selected parameter results is converted into CSV files and handed over to the required for ML. This project blends all the chunks of work like monitoring, computing, ML selection, and resource combination, to facilitate network resource allocation for emergency management.
This is a collaborative study where the researchers have developed and implemented a hierarchical closed-loop that autonomously handles an emergency case. This project contains several groups working on separate functions such as monitoring, computing, ML selection, and resource allocation. Some presented how the AI agents and the network can be adapted to assist mobile network users in Search, Diagnostic, and Rescue (SDAR) missions. Some integrated the implementation of the closed loops in O-RAN based software. The researcher’s role in this project is to generate the data which will be used for analysis and this gets integrated with another team. Rather than putting dummy data and analysing or creating and training a machine learning model, we use the Simu5g simulator which is library-based on OMNET++ framework to generate data, mainly resource allocation data. In Simu5g they configure the required network, set all the input parameters such as and simulate it for a specific duration of time. After simulation, the various results are obtained like SINR, throughput, resource block allocation, and many more. This data of the selected parameter results is converted into CSV files and handed over to the required for ML. This project blends all the chunks of work like monitoring, computing, ML selection, and resource combination, to facilitate network resource allocation for emergency management.
Practical implementations of the research
In this project, the researchers have gathered the simulated data and want to analyse it and apply machine learning algorithms to improve the condition of existing 5G networks. AI/ML model will help to analyse the data which helps in optimizing resource allocation. Optimization algorithms for resource allocation like Interference minimization, Throughput maximization, and many more. Optimising such parameters would be really helpful for the development of new generation networks.
Collaborations
The paper was developed as part of a build-a-thon track, “ITU AI/ML in 5G Challenge: applying machine learning in communication networks” challenge. The researchers worked under the problem statement “ITU-ML5G-PS-014: Build-a-thon (PoC) Network resource allocation for emergency management based on closed-loop analysis”. This project is guided by Dr. V Udaya Sankar under AI-Designed Wireless (AIDW) Project Simulated network scenarios using simu5g for measuring resource allocation. This build-a-thon challenge was started on June 7, 2021 and ended on November 5, 2021. The research team was placed fifth among 12 teams who participated across the world in the “build a thon” track of the global challenge. While the overall challenge saw over 600 participants across more than 80 countries, the “build a thon” track was a unique coding challenge from ITU FG AN. The team worked on the simulation of the 5G system and corresponding analysis using Simu5G from ITU global partners. After the build-a-thon, the teams that have participated in the build-a-thon under the problem statement “ITU-ML5G-PS-014: Build-a-thon (PoC) Network resource allocation for emergency management based on closed-loop analysis” were collaboratively developed the journal from the observations and results that were made during this build-a-thon.
The current research work focuses on the Implementation of a simulation environment to generate data for model training and testing purposes, and serve as a simulation underlay for testing. The simulations allow us to study various configurations and analyse them to optimize the allocations. For the later stages, various machine learning techniques can be applied for the data that was generated through simulation, and further, the comparison can be done for various machine learning techniques.
- Published in Departmental News, ECE NEWS, News, Research News
Research article accepted for IEEE conference IEMTRONICS 2022

SRM University-AP preserves a research-empowered ecosystem stimulating its faculty and students to roll out original and discerning studies capable of making instrumental contributions aiming the scientific and societal progress. Making strides with impactful research publications and groundbreaking achievements, the institution has carved a niche for itself in the academic milieu. We are glad to present yet another success story of our research community that keeps bringing laurels to the institutions from far and wide.
Dr Pradyut Kumar Sanki and his PhD scholar Bevara Vasudeva, from the Department of Electronics and Communications Engineering, along with a group of Computer Science and Engineering students: Medarametla Depthi Supriya, Devireddy Vignesh, Peram Bhanu Sai Harshath, and Sravya Kuchina have got their paper titled ‘’VLSI Implementation of a Real-Time Modified Decision-Based Algorithm for Impulse Noise Removal’’ accepted in the IEEE conference IEMTRONICS 2022. This publication is a part of the Capstone project contributed by the students.
IEMTRONICS 2022 (International IOT, Electronics and Mechatronics Conference) is an international conclave that aims to bring together scholars from different backgrounds to disseminate inventive ideas in the fields of IOT, Electronics and Mechatronics. The conference will also promote an intense dialogue between academia and industry to bridge the gap between academic research, industry initiatives, and governmental policies. This is fostered by panel discussions, invited talks, and industry exhibits where academia and industry will mutually benefit from each other.
Through the research paper, the team proposes a real-time impulse noise removal (RTINR) algorithm and its hardware architecture for denoising images corrupted with fixed valued impulse noise.
Abstract of the Research
A decision-based algorithm is modified in the proposed RTINR algorithm where the corrupted pixel is first detected and is restored with median or previous pixel value depending on the number of corrupted pixels in the image. The proposed RTINR architecture has been designed to reduce the hardware complexity as it requires 21 comparators, 4 adders, and 2 line buffers which in turn improve the execution time. The proposed architecture results better in qualitative and quantitative performance in comparison to different denoising schemes while evaluated based on the following parameters: PSNR, IEF, MSE, EKI, SSIM, FOM, and visual quality. The proposed architecture has been simulated using the XC7VX330T-FFG1761 VIRTEX7 FPGA device and the reported maximum post place and route frequency is 360.88 MHz. The proposed RTINR architecture is capable of denoising images of size 512 × 512 at 686 frames per second. The architecture has also been synthesized using UMC 90 nm technology where 103 mW power is consumed at a clock frequency of 100 MHz with a gate count of 2.3K (NAND2) including two memory buffers.
- Published in CSE NEWS, Departmental News, ECE NEWS, News, Research News
Matrix enabled road distress classification system

The Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering is glad to announce that Dr V Udaya Sankar, Assistant Professor has published the patent (App no. 202141056542), ‘A system and method with Matrix enabled Road distress classification with reduced computational complexity and reduced memory requirements’, in collaboration with Dr Siva Sankar Yellampalli and Ms Gayathri Lakshmi Chinthakrindi.
This work has applications related to visual inspection systems. While this research considers road crack detection application, the same can be extended to various applications such as leaf disease prediction, covid prediction etc. This invention provides an alternative approach instead of using traditional machine learning algorithms that has less computational complexity as opposed to deep neural networks that take more complex operations. This method will also lead to further research in matrix-based machine learning applications related to image processing and image classification.
The research team is planning to collaborate with Efftronics Systems Pvt ltd. for PCB defect detection and discussions are initiated with some start-ups for visual inspection applications. Their future research plan is to look deeper into these algorithms in combination with some of the deep neural networks to reduce computational complexity. In addition, Dr Udaya Sankar is also looking forward to establishing his own start-up in the incubation centre soon.
Abstract of the Research
A method for image classification is provided, wherein, the pre-processed gray scale image is first sent to the feature extraction block, and the said feature extraction block considers every image as a matrix and computes the metrics for features, viz., 1) EMD distance which is popularly known as Wassertain distance/Earth movers distance and is computed with respect to block image and 2) Frobenius Norm which is the square root of the sum of the absolute squares of its elements and finally, 3) Condition Number, which measures the ratio of the maximum relative stretching to the maximum relative shrinking that matrix does to any non-zero vectors. This method is preferred over the existing methods due to the drastic reduction in computational complexities and, utilizing lesser memory. Also, with this method and system, the communicational complexities too are significantly reduced and also, and the results yielded are far more significantly accurate.
- Published in Departmental News, ECE NEWS, News, Research News
Restoring the highly corrupted digital image
The Electrochemical Society Transactions (ECST) is the official conference proceedings publication of The Electrochemical Society. Recently, a research paper was published in ECST by Mr Vasudeva Bevara, a PhD scholar of the Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering, under the supervision of Assistant professor Dr Pradyut Kumar Sanki. The paper is titled VLSI Architecture of Decision Based Adaptive Denoising Filter for Removing Salt & Pepper Noise and proposes an innovative concept to restore a highly corrupted digital image.
Abstract
 A new Decision Based Adaptive Denoising Filter (DBADF) algorithm and hardware architecture are proposed for restoring the digital image that is highly corrupted with impulse noise. The proposed DBADF detects only the corrupted pixels, and that pixel is restored by the noise-free median value or previous value based upon the noise density in the image. The proposed DBADF uses a 3×3 window initially and adaptively goes up to a 7×7 window based on the noise corruption of more than 50% by impulse noise in the current processing window. The proposed architecture was found to exhibit better visual qualitative and quantitative evaluation based on PSNR, IEF, EKI, SSIM, FOM, and error rate. The DBAMF architecture also preserves the original information of digital image with a high density of salt and pepper noise compared to many standard conventional algorithms. The proposed architecture has been simulated using the VIRTEX7 FPGA device, and the reported maximum post place and route frequency are 149.995MHz, and the dynamic power consumption is 179mW.
A new Decision Based Adaptive Denoising Filter (DBADF) algorithm and hardware architecture are proposed for restoring the digital image that is highly corrupted with impulse noise. The proposed DBADF detects only the corrupted pixels, and that pixel is restored by the noise-free median value or previous value based upon the noise density in the image. The proposed DBADF uses a 3×3 window initially and adaptively goes up to a 7×7 window based on the noise corruption of more than 50% by impulse noise in the current processing window. The proposed architecture was found to exhibit better visual qualitative and quantitative evaluation based on PSNR, IEF, EKI, SSIM, FOM, and error rate. The DBAMF architecture also preserves the original information of digital image with a high density of salt and pepper noise compared to many standard conventional algorithms. The proposed architecture has been simulated using the VIRTEX7 FPGA device, and the reported maximum post place and route frequency are 149.995MHz, and the dynamic power consumption is 179mW.
- Published in Departmental News, ECE NEWS, News, Research News
Deep learning enabled IRS for 6G intelligent transportation systems

Intelligent Transportation System (ITS) is on its way to becoming the biggest player in the coming-of-age transportation system. However, the sheer demand for the enormous amount of data to secure seamless connectivity and functioning with maximum speed and safety tends to increase the power consumption of the ITS. Dr Sunil Chinnadurai and his PhD scholar Mr Shaik Rajak from the Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering present Intelligent Reflecting Surfaces (IRS) as the key enabling technology to provide the data required by the ITS with less power consumption.
Their article “Deep Learning Enabled IRS for 6G Intelligent Transportation Systems: A Comprehensive Study” which makes a comprehensive study on the DL-enabled IRS-aided ITS was published in the esteemed journal ‘IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems’ having an Impact factor of 6.5. The article elucidates the ways and means to overcome the channel estimation, secrecy rate, and energy efficiency optimisation problems.
The research suggests that connecting ITS to wireless networks via IRS will help in reaching the destination within the stipulated time duration with enhanced safety and comfort. Besides highlighting the reduced power consumption and hardware cost of the DL-enabled IRS-aided ITS, the article also projects that IRS usage in 6G-ITS massively helps the traffic control system to precisely send and receive the information of school buses as well as healthcare vehicles like ambulances, fire safety vehicles, etc. Their future research plans also include the experimental analysis of energy efficiency for wireless networks and Intelligent Transportation Systems with IRS.
Abstract of the Research
Intelligent Transportation Systems (ITS) play an increasingly significant role in our life, where safe and effective vehicular networks supported by sixth generation (6G) communication technologies are the essence of ITS. Vehicle-to-vehicle (V2V) and vehicle-to-infrastructure (V2I) communications need to be studied to implement ITS in a secure, robust, and efficient manner, allowing massive connectivity in vehicular communications networks. Besides, with the rapid growth of different types of autonomous vehicles, it becomes challenging to facilitate the heterogeneous requirements of ITS. To meet the above needs, intelligent reflecting surfaces (IRS) are introduced to vehicular communications and ITS, containing the reflecting elements that can intelligently configure incident signals from and to vehicles. As a novel vehicular communication paradigm at its infancy, it is key to understand the latest research efforts on applying IRS to 6G ITS as well as the fundamental differences with other existing alternatives and the new challenges brought by implementing IRS in 6G ITS. In this paper, we provide a big picture of deep learning enabled IRS for 6G ITS and appraise most of the important literature in this field. By appraising and summarizing the existing literature, we also point out the challenges and worthwhile research directions related to IRS aided 6G ITS.
- Published in Departmental News, ECE NEWS, News, Research News